[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
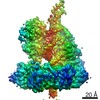
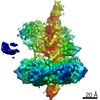
Yorodumi- PDB-7rpx: Archaeal DNA ligase and heterotrimeric PCNA in complex with end-j... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7rpx | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
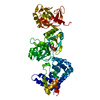
| Title | Archaeal DNA ligase and heterotrimeric PCNA in complex with end-joined DNA | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | LIGASE/DNA / DNA ligase / PCNA / cryo-EM / LIGASE-DNA complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationDNA ligase (ATP) / DNA ligase (ATP) activity / lagging strand elongation / DNA biosynthetic process / DNA polymerase processivity factor activity / leading strand elongation / regulation of DNA replication / DNA recombination / cell division / DNA repair ...DNA ligase (ATP) / DNA ligase (ATP) activity / lagging strand elongation / DNA biosynthetic process / DNA polymerase processivity factor activity / leading strand elongation / regulation of DNA replication / DNA recombination / cell division / DNA repair / DNA binding / ATP binding / metal ion binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Saccharolobus solfataricus (archaea) Saccharolobus solfataricus (archaea) Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.2 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Sverzhinsky, A. / Pascal, J.M. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2items United States, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Structure / Year: 2022 Journal: Structure / Year: 2022Title: Cryo-EM structures and biochemical insights into heterotrimeric PCNA regulation of DNA ligase. Authors: Aleksandr Sverzhinsky / Alan E Tomkinson / John M Pascal /   Abstract: DNA ligases act in the final step of many DNA repair pathways and are commonly regulated by the DNA sliding clamp proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), but there are limited insights into the ...DNA ligases act in the final step of many DNA repair pathways and are commonly regulated by the DNA sliding clamp proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), but there are limited insights into the physical basis for this regulation. Here, we use single-particle cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) to analyze an archaeal DNA ligase and heterotrimeric PCNA in complex with a single-strand DNA break. The cryo-EM structures highlight a continuous DNA-binding surface formed between DNA ligase and PCNA that supports the distorted conformation of the DNA break undergoing repair and contributes to PCNA stimulation of DNA ligation. DNA ligase is conformationally flexible within the complex, with its domains fully ordered only when encircling the repaired DNA to form a stacked ring structure with PCNA. The structures highlight DNA ligase structural transitions while docked on PCNA, changes in DNA conformation during ligation, and the potential for DNA ligase domains to regulate PCNA accessibility to other repair factors. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7rpx.cif.gz 7rpx.cif.gz | 278.1 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7rpx.ent.gz pdb7rpx.ent.gz | 214.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7rpx.json.gz 7rpx.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/rp/7rpx https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/rp/7rpx ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/rp/7rpx ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/rp/7rpx | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 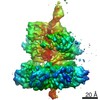 24625MC 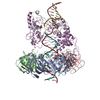 7rpoC 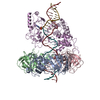 7rpwC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-DNA polymerase sliding clamp ... , 3 types, 3 molecules ABC
| #1: Protein | Mass: 28711.961 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Saccharolobus solfataricus (archaea) / Strain: ATCC 35092 / DSM 1617 / JCM 11322 / P2 / Gene: pcn1, pcnA-like, SSO0397, C41_008 / Production host: Saccharolobus solfataricus (archaea) / Strain: ATCC 35092 / DSM 1617 / JCM 11322 / P2 / Gene: pcn1, pcnA-like, SSO0397, C41_008 / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 27461.084 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Saccharolobus solfataricus (archaea) / Strain: ATCC 35092 / DSM 1617 / JCM 11322 / P2 / Gene: pcn2, pcnA-2, SSO1047 / Production host: Saccharolobus solfataricus (archaea) / Strain: ATCC 35092 / DSM 1617 / JCM 11322 / P2 / Gene: pcn2, pcnA-2, SSO1047 / Production host:  |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 28560.268 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Saccharolobus solfataricus (archaea) / Strain: ATCC 35092 / DSM 1617 / JCM 11322 / P2 / Gene: pcn3, pcnA-1, SSO0405, C41_016 / Production host: Saccharolobus solfataricus (archaea) / Strain: ATCC 35092 / DSM 1617 / JCM 11322 / P2 / Gene: pcn3, pcnA-1, SSO0405, C41_016 / Production host:  |
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules XZ
| #4: DNA chain | Mass: 14549.299 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
|---|---|
| #5: DNA chain | Mass: 14403.264 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Protein / Non-polymers , 2 types, 4 molecules E

| #6: Protein | Mass: 69998.375 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Saccharolobus solfataricus (archaea) / Strain: ATCC 35092 / DSM 1617 / JCM 11322 / P2 / Gene: lig, SSO0189 / Production host: Saccharolobus solfataricus (archaea) / Strain: ATCC 35092 / DSM 1617 / JCM 11322 / P2 / Gene: lig, SSO0189 / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #7: Chemical |
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Ternary complex of DNA Ligase with PCNA1-2-3 and end-joined DNA Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#6 / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.175 MDa / Experimental value: YES |
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Saccharolobus solfataricus (archaea) Saccharolobus solfataricus (archaea) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.35 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: UltrAuFoil R1.2/1.3 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K Details: wait time 0, blot force 1, blot time 1, drain time 0 |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 100 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 2 / Num. of real images: 8060 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.19.2_4158: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 192490 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | 3D fitting-ID: 1 / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 120.74 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj