+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7pgs | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
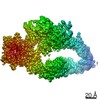
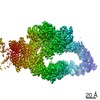
| Title | Consensus structure of human Neurofibromin isoform 2 | ||||||||||||
 Components Components | Neurofibromin | ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | SIGNALING PROTEIN / Neurofibromin / Cancer / GAP / Ras / Neurofibromatosis type 1 | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of mast cell apoptotic process / negative regulation of Rac protein signal transduction / regulation of glial cell differentiation / observational learning / negative regulation of Schwann cell migration / Schwann cell migration / amygdala development / vascular associated smooth muscle cell migration / Schwann cell proliferation / negative regulation of mast cell proliferation ...positive regulation of mast cell apoptotic process / negative regulation of Rac protein signal transduction / regulation of glial cell differentiation / observational learning / negative regulation of Schwann cell migration / Schwann cell migration / amygdala development / vascular associated smooth muscle cell migration / Schwann cell proliferation / negative regulation of mast cell proliferation / mast cell apoptotic process / gamma-aminobutyric acid secretion, neurotransmission / regulation of intracellular signal transduction / vascular associated smooth muscle cell proliferation / negative regulation of Schwann cell proliferation / glutamate secretion, neurotransmission / mast cell proliferation / negative regulation of leukocyte migration / forebrain morphogenesis / regulation of cell-matrix adhesion / regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration / hair follicle maturation / cell communication / camera-type eye morphogenesis / smooth muscle tissue development / negative regulation of oligodendrocyte differentiation / sympathetic nervous system development / negative regulation of neurotransmitter secretion / myeloid leukocyte migration / peripheral nervous system development / phosphatidylcholine binding / myelination in peripheral nervous system / negative regulation of Ras protein signal transduction / metanephros development / phosphatidylethanolamine binding / positive regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand / regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation / endothelial cell proliferation / collagen fibril organization / regulation of postsynapse organization / regulation of bone resorption / artery morphogenesis / neural tube development / negative regulation of neuroblast proliferation / adrenal gland development / forebrain astrocyte development / negative regulation of protein import into nucleus / regulation of synaptic transmission, GABAergic / negative regulation of astrocyte differentiation / negative regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell migration / spinal cord development / negative regulation of endothelial cell proliferation / negative regulation of osteoclast differentiation / pigmentation / Rac protein signal transduction / oligodendrocyte differentiation / RAS signaling downstream of NF1 loss-of-function variants / negative regulation of cell-matrix adhesion / extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors / neuroblast proliferation / positive regulation of GTPase activity / regulation of angiogenesis / Schwann cell development / regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / negative regulation of stem cell proliferation / skeletal muscle tissue development / negative regulation of fibroblast proliferation / negative regulation of MAPK cascade / positive regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell proliferation / positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation / extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand / extracellular matrix organization / osteoclast differentiation / GTPase activator activity / negative regulation of cell migration / negative regulation of angiogenesis / stem cell proliferation / phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signal transduction / wound healing / liver development / regulation of long-term neuronal synaptic plasticity / cerebral cortex development / brain development / visual learning / cognition / protein import into nucleus / Regulation of RAS by GAPs / osteoblast differentiation / long-term synaptic potentiation / MAPK cascade / positive regulation of neuron apoptotic process / cellular response to heat / presynapse / heart development / regulation of gene expression / actin cytoskeleton organization / neuron apoptotic process / angiogenesis / fibroblast proliferation / Ras protein signal transduction Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.4 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Naschberger, A. / Baradaran, R. / Carroni, M. / Rupp, B. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Austria, 3items Austria, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2021 Journal: Nature / Year: 2021Title: The structure of neurofibromin isoform 2 reveals different functional states. Authors: Andreas Naschberger / Rozbeh Baradaran / Bernhard Rupp / Marta Carroni /    Abstract: The autosomal dominant monogenetic disease neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) affects approximately one in 3,000 individuals and is caused by mutations in the NF1 tumour suppressor gene, leading to ...The autosomal dominant monogenetic disease neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) affects approximately one in 3,000 individuals and is caused by mutations in the NF1 tumour suppressor gene, leading to dysfunction in the protein neurofibromin (Nf1). As a GTPase-activating protein, a key function of Nf1 is repression of the Ras oncogene signalling cascade. We determined the human Nf1 dimer structure at an overall resolution of 3.3 Å. The cryo-electron microscopy structure reveals domain organization and structural details of the Nf1 exon 23a splicing isoform 2 in a closed, self-inhibited, Zn-stabilized state and an open state. In the closed conformation, HEAT/ARM core domains shield the GTPase-activating protein-related domain (GRD) so that Ras binding is sterically inhibited. In a distinctly different, open conformation of one protomer, a large-scale movement of the GRD occurs, which is necessary to access Ras, whereas Sec14-PH reorients to allow interaction with the cellular membrane. Zn incubation of Nf1 leads to reduced Ras-GAP activity with both protomers in the self-inhibited, closed conformation stabilized by a Zn binding site between the N-HEAT/ARM domain and the GRD-Sec14-PH linker. The transition between closed, self-inhibited states of Nf1 and open states provides guidance for targeted studies deciphering the complex molecular mechanism behind the widespread neurofibromatosis syndrome and Nf1 dysfunction in carcinogenesis. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7pgs.cif.gz 7pgs.cif.gz | 1.4 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7pgs.ent.gz pdb7pgs.ent.gz | 1.1 MB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7pgs.json.gz 7pgs.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pg/7pgs https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pg/7pgs ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pg/7pgs ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pg/7pgs | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  13394MC 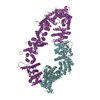 7pgpC 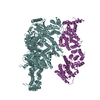 7pgqC  7pgrC  7pgtC  7pguC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 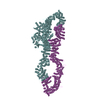
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 319757.656 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NF1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NF1 / Production host:  #2: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / | Has ligand of interest | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Homo-dimer of human Neurofibromin Isoform 2 / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.64 MDa / Experimental value: YES |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 1 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.4 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 582742 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller












 PDBj
PDBj




