[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
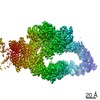
Yorodumi- EMDB-13392: GAP-SecPH region of human neurofibromin isoform 2 in closed confo... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
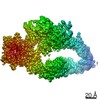
| Title | GAP-SecPH region of human neurofibromin isoform 2 in closed conformation. | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | |||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Neurofibromin / Cancer / GAP / Ras / Neurofibromatosis type 1 / SIGNALING PROTEIN | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of mast cell apoptotic process / negative regulation of Rac protein signal transduction / regulation of glial cell differentiation / observational learning / negative regulation of Schwann cell migration / Schwann cell migration / vascular associated smooth muscle cell migration / amygdala development / Schwann cell proliferation / negative regulation of mast cell proliferation ...positive regulation of mast cell apoptotic process / negative regulation of Rac protein signal transduction / regulation of glial cell differentiation / observational learning / negative regulation of Schwann cell migration / Schwann cell migration / vascular associated smooth muscle cell migration / amygdala development / Schwann cell proliferation / negative regulation of mast cell proliferation / mast cell apoptotic process / gamma-aminobutyric acid secretion, neurotransmission / regulation of intracellular signal transduction / vascular associated smooth muscle cell proliferation / glutamate secretion, neurotransmission / negative regulation of Schwann cell proliferation / mast cell proliferation / negative regulation of leukocyte migration / forebrain morphogenesis / regulation of cell-matrix adhesion / regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration / hair follicle maturation / cell communication / camera-type eye morphogenesis / smooth muscle tissue development / negative regulation of oligodendrocyte differentiation / sympathetic nervous system development / myeloid leukocyte migration / peripheral nervous system development / negative regulation of neurotransmitter secretion / phosphatidylcholine binding / myelination in peripheral nervous system / negative regulation of Ras protein signal transduction / metanephros development / phosphatidylethanolamine binding / positive regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand / endothelial cell proliferation / regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation / collagen fibril organization / regulation of postsynapse organization / regulation of bone resorption / artery morphogenesis / neural tube development / adrenal gland development / negative regulation of neuroblast proliferation / forebrain astrocyte development / negative regulation of protein import into nucleus / regulation of synaptic transmission, GABAergic / negative regulation of astrocyte differentiation / negative regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell migration / spinal cord development / negative regulation of endothelial cell proliferation / negative regulation of osteoclast differentiation / pigmentation / Rac protein signal transduction / oligodendrocyte differentiation / RAS signaling downstream of NF1 loss-of-function variants / extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors / negative regulation of cell-matrix adhesion / positive regulation of GTPase activity / neuroblast proliferation / regulation of angiogenesis / Schwann cell development / regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / negative regulation of stem cell proliferation / skeletal muscle tissue development / negative regulation of fibroblast proliferation / negative regulation of MAPK cascade / positive regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell proliferation / positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation / extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in absence of ligand / extracellular matrix organization / osteoclast differentiation / GTPase activator activity / negative regulation of cell migration / negative regulation of angiogenesis / stem cell proliferation / phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signal transduction / wound healing / liver development / cerebral cortex development / regulation of long-term neuronal synaptic plasticity / brain development / visual learning / cognition / protein import into nucleus / Regulation of RAS by GAPs / osteoblast differentiation / long-term synaptic potentiation / positive regulation of neuron apoptotic process / MAPK cascade / cellular response to heat / presynapse / heart development / regulation of gene expression / actin cytoskeleton organization / neuron apoptotic process / angiogenesis / fibroblast proliferation / Ras protein signal transduction Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
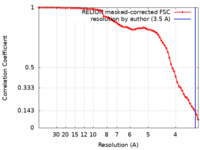
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.5 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Naschberger A / Baradaran R / Carroni M / Rupp B | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Austria, 3 items Austria, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2021 Journal: Nature / Year: 2021Title: The structure of neurofibromin isoform 2 reveals different functional states. Authors: Andreas Naschberger / Rozbeh Baradaran / Bernhard Rupp / Marta Carroni /    Abstract: The autosomal dominant monogenetic disease neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) affects approximately one in 3,000 individuals and is caused by mutations in the NF1 tumour suppressor gene, leading to ...The autosomal dominant monogenetic disease neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) affects approximately one in 3,000 individuals and is caused by mutations in the NF1 tumour suppressor gene, leading to dysfunction in the protein neurofibromin (Nf1). As a GTPase-activating protein, a key function of Nf1 is repression of the Ras oncogene signalling cascade. We determined the human Nf1 dimer structure at an overall resolution of 3.3 Å. The cryo-electron microscopy structure reveals domain organization and structural details of the Nf1 exon 23a splicing isoform 2 in a closed, self-inhibited, Zn-stabilized state and an open state. In the closed conformation, HEAT/ARM core domains shield the GTPase-activating protein-related domain (GRD) so that Ras binding is sterically inhibited. In a distinctly different, open conformation of one protomer, a large-scale movement of the GRD occurs, which is necessary to access Ras, whereas Sec14-PH reorients to allow interaction with the cellular membrane. Zn incubation of Nf1 leads to reduced Ras-GAP activity with both protomers in the self-inhibited, closed conformation stabilized by a Zn binding site between the N-HEAT/ARM domain and the GRD-Sec14-PH linker. The transition between closed, self-inhibited states of Nf1 and open states provides guidance for targeted studies deciphering the complex molecular mechanism behind the widespread neurofibromatosis syndrome and Nf1 dysfunction in carcinogenesis. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_13392.map.gz emd_13392.map.gz | 28.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-13392-v30.xml emd-13392-v30.xml emd-13392.xml emd-13392.xml | 17.1 KB 17.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
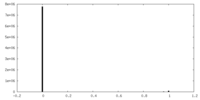
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_13392_fsc.xml emd_13392_fsc.xml | 7.1 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_13392.png emd_13392.png | 68.8 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_13392_msk_1.map emd_13392_msk_1.map | 30.5 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-13392.cif.gz emd-13392.cif.gz | 7.4 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_13392_half_map_1.map.gz emd_13392_half_map_1.map.gz emd_13392_half_map_2.map.gz emd_13392_half_map_2.map.gz | 23.5 MB 23.5 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13392 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13392 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13392 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-13392 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7pgqMC  7pgpC  7pgrC  7pgsC  7pgtC  7pguC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_13392.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 30.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_13392.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 30.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
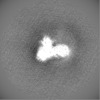
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.72 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_13392_msk_1.map emd_13392_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
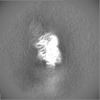
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
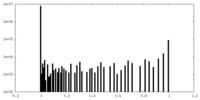
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_13392_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_13392_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Homo-dimer of human Neurofibromin Isoform 2
| Entire | Name: Homo-dimer of human Neurofibromin Isoform 2 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Homo-dimer of human Neurofibromin Isoform 2
| Supramolecule | Name: Homo-dimer of human Neurofibromin Isoform 2 / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 640 kDa/nm |
-Macromolecule #1: Neurofibromin
| Macromolecule | Name: Neurofibromin / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 319.757656 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MAAHRPVEWV QAVVSRFDEQ LPIKTGQQNT HTKVSTEHNK ECLINISKYK FSLVISGLTT ILKNVNNMRI FGEAAEKNLY LSQLIILDT LEKCLAGQPK DTMRLDETML VKQLLPEICH FLHTCREGNQ HAAELRNSAS GVLFSLSCNN FNAVFSRIST R LQELTVCS ...String: MAAHRPVEWV QAVVSRFDEQ LPIKTGQQNT HTKVSTEHNK ECLINISKYK FSLVISGLTT ILKNVNNMRI FGEAAEKNLY LSQLIILDT LEKCLAGQPK DTMRLDETML VKQLLPEICH FLHTCREGNQ HAAELRNSAS GVLFSLSCNN FNAVFSRIST R LQELTVCS EDNVDVHDIE LLQYINVDCA KLKRLLKETA FKFKALKKVA QLAVINSLEK AFWNWVENYP DEFTKLYQIP QT DMAECAE KLFDLVDGFA ESTKRKAAVW PLQIILLILC PEIIQDISKD VVDENNMNKK LFLDSLRKAL AGHGGSRQLT ESA AIACVK LCKASTYINW EDNSVIFLLV QSMVVDLKNL LFNPSKPFSR GSQPADVDLM IDCLVSCFRI SPHNNQHFKI CLAQ NSPST FHYVLVNSLH RIITNSALDW WPKIDAVYCH SVELRNMFGE TLHKAVQGCG AHPAIRMAPS LTFKEKVTSL KFKEK PTDL ETRSYKYLLL SMVKLIHADP KLLLCNPRKQ GPETQGSTAE LITGLVQLVP QSHMPEIAQE AMEALLVLHQ LDSIDL WNP DAPVETFWEI SSQMLFYICK KLTSHQMLSS TEILKWLREI LICRNKFLLK NKQADRSSCH FLLFYGVGCD IPSSGNT SQ MSMDHEELLR TPGASLRKGK GNSSMDSAAG CSGTPPICRQ AQTKLEVALY MFLWNPDTEA VLVAMSCFRH LCEEADIR C GVDEVSVHNL LPNYNTFMEF ASVSNMMSTG RAALQKRVMA LLRRIEHPTA GNTEAWEDTH AKWEQATKLI LNYPKAKME DGQAAESLHK TIVKRRMSHV SGGGSIDLSD TDSLQEWINM TGFLCALGGV CLQQRSNSGL ATYSPPMGPV SERKGSMISV MSSEGNADT PVSKFMDRLL SLMVCNHEKV GLQIRTNVKD LVGLELSPAL YPMLFNKLKN TISKFFDSQG QVLLTDTNTQ F VEQTIAIM KNLLDNHTEG SSEHLGQASI ETMMLNLVRY VRVLGNMVHA IQIKTKLCQL VEVMMARRDD LSFCQEMKFR NK MVEYLTD WVMGTSNQAA DDDVKCLTRD LDQASMEAVV SLLAGLPLQP EEGDGVELME AKSQLFLKYF TLFMNLLNDC SEV EDESAQ TGGRKRGMSR RLASLRHCTV LAMSNLLNAN VDSGLMHSIG LGYHKDLQTR ATFMEVLTKI LQQGTEFDTL AETV LADRF ERLVELVTMM GDQGELPIAM ALANVVPCSQ WDELARVLVT LFDSRHLLYQ LLWNMFSKEV ELADSMQTLF RGNSL ASKI MTFCFKVYGA TYLQKLLDPL LRIVITSSDW QHVSFEVDPT RLEPSESLEE NQRNLLQMTE KFFHAIISSS SEFPPQ LRS VCHCLYQATC HSLLNKATVK EKKENKKSVV SQRFPQNSIG AVGSAMFLRF INPAIVSPYE AGILDKKPPP RIERGLK LM SKILQSIANH VLFTKEEHMR PFNDFVKSNF DAARRFFLDI ASDCPTSDAV NHSLSFISDG NVLALHRLLW NNQEKIGQ Y LSSNRDHKAV GRRPFDKMAT LLAYLGPPEH KPVADTHWSS LNLTSSKFEE FMTRHQVHEK EEFKALKTLS IFYQAGTSK AGNPIFYYVA RRFKTGQING DLLIYHVLLT LKPYYAKPYE IVVDLTHTGP SNRFKTDFLS KWFVVFPGFA YDNVSAVYIY NCNSWVREY TKYHERLLTG LKGSKRLVFI DCPGKLAEHI EHEQQKLPAA TLALEEDLKV FHNALKLAHK DTKVSIKVGS T AVQVTSAE RTKVLGQSVF LNDIYYASEI EEICLVDENQ FTLTIANQGT PLTFMHQECE AIVQSIIHIR TRWELSQPDS IP QHTKIRP KDVPGTLLNI ALLNLGSSDP SLRSAAYNLL CALTCTFNLK IEGQLLETSG LCIPANNTLF IVSISKTLAA NEP HLTLEF LEECISGFSK SSIELKHLCL EYMTPWLSNL VRFCKHNDDA KRQRVTAILD KLITMTINEK QMYPSIQAKI WGSL GQITD LLDVVLDSFI KTSATGGLGS IKAEVMADTA VALASGNVKL VSSKVIGRMC KIIDKTCLSP TPTLEQHLMW DDIAI LARY MLMLSFNNSL DVAAHLPYLF HVVTFLVATG PLSLRASTHG LVINIIHSLC TCSQLHFSEE TKQVLRLSLT EFSLPK FYL LFGISKVKSA AVIAFRSSYR DRSFSPGSYE RETFALTSLE TVTEALLEIM EACMRDIPTC KWLDQWTELA QRFAFQY NP SLQPRALVVF GCISKRVSHG QIKQIIRILS KALESCLKGP DTYNSQVLIE ATVIALTKLQ PLLNKDSPLH KALFWVAV A VLQLDEVNLY SAGTALLEQN LHTLDSLRIF NDKSPEEVFM AIRNPLEWHC KQMDHFVGLN FNSNFNFALV GHLLKGYRH PSPAIVARTV RILHTLLTLV NKHRNCDKFE VNTQSVAYLA ALLTVSEEVR SRCSLKHRKS LLLTDISMEN VPMDTYPIHH GDPSYRTLK ETQPWSSPKG SEGYLAATYP TVGQTSPRAR KSMSLDMGQP SQANTKKLLG TRKSFDHLIS DTKAPKRQEM E SGITTPPK MRRVAETDYE METQRISSSQ QHPHLRKVSV SESNVLLDEE VLTDPKIQAL LLTVLATLVK YTTDEFDQRI LY EYLAEAS VVFPKVFPVV HNLLDSKINT LLSLCQDPNL LNPIHGIVQS VVYHEESPPQ YQTSYLQSFG FNGLWRFAGP FSK QTQIPD YAELIVKFLD ALIDTYLPGI DEETSEESLL TPTSPYPPAL QSQLSITANL NLSNSMTSLA TSQHSPGIDK ENVE LSPTT GHCNSGRTRH GSASQVQKQR SAGSFKRNSI KKIV UniProtKB: Neurofibromin |
-Macromolecule #2: (1S)-2-{[(2-AMINOETHOXY)(HYDROXY)PHOSPHORYL]OXY}-1-[(PALMITOYLOXY...
| Macromolecule | Name: (1S)-2-{[(2-AMINOETHOXY)(HYDROXY)PHOSPHORYL]OXY}-1-[(PALMITOYLOXY)METHYL]ETHYL STEARATE type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: PEV |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 720.012 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-PEV: |
-Macromolecule #3: ZINC ION
| Macromolecule | Name: ZINC ION / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: ZN |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 65.409 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 1.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: OTHER / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.1 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)