+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7pfo | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
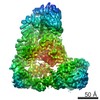
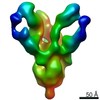
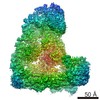
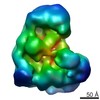
| Title | Core human replisome | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | REPLICATION / DNA replication / helicase / CMG / TIMELESS / TIPIN / CLASPIN / AND-1 / EPSILON / POLYMERASE / REPLISOME | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcellular response to bleomycin / DNA secondary structure binding / detection of abiotic stimulus / regulation of nuclear cell cycle DNA replication / replication fork arrest / Switching of origins to a post-replicative state / Unwinding of DNA / cell cycle phase transition / DNA replication initiation / epsilon DNA polymerase complex ...cellular response to bleomycin / DNA secondary structure binding / detection of abiotic stimulus / regulation of nuclear cell cycle DNA replication / replication fork arrest / Switching of origins to a post-replicative state / Unwinding of DNA / cell cycle phase transition / DNA replication initiation / epsilon DNA polymerase complex / DNA strand elongation involved in mitotic DNA replication / GINS complex / mitotic DNA replication preinitiation complex assembly / activation of protein kinase activity / replication fork protection complex / cellular response to cisplatin / nuclear origin of replication recognition complex / cellular response to hydroxyurea / alpha DNA polymerase:primase complex / anaphase-promoting complex binding / nucleotide-excision repair, DNA gap filling / Regulation of MITF-M-dependent genes involved in DNA replication, damage repair and senescence / mitotic DNA replication / CMG complex / DNA replication checkpoint signaling / regulation of phosphorylation / DNA replication proofreading / DNA replication preinitiation complex / single-stranded DNA 3'-5' DNA exonuclease activity / MCM complex / mitotic DNA replication checkpoint signaling / double-strand break repair via break-induced replication / mitotic DNA replication initiation / mitotic intra-S DNA damage checkpoint signaling / regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication initiation / Hydrolases; Acting on ester bonds; Exodeoxyribonucleases producing 5'-phosphomonoesters / inner cell mass cell proliferation / DNA strand elongation involved in DNA replication / Apoptotic cleavage of cellular proteins / branching morphogenesis of an epithelial tube / positive regulation of double-strand break repair / DNA synthesis involved in DNA repair / G1/S-Specific Transcription / leading strand elongation / mitotic G2 DNA damage checkpoint signaling / nuclear replication fork / replication fork processing / DNA replication origin binding / cochlea development / PCNA-Dependent Long Patch Base Excision Repair / DNA replication initiation / Activation of the pre-replicative complex / embryonic organ development / error-prone translesion synthesis / Activation of ATR in response to replication stress / response to UV / positive regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / base-excision repair, gap-filling / cellular response to interleukin-4 / DNA helicase activity / lung development / cellular response to epidermal growth factor stimulus / DNA damage checkpoint signaling / morphogenesis of an epithelium / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in GG-NER / Assembly of the pre-replicative complex / Termination of translesion DNA synthesis / enzyme activator activity / G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / Recognition of DNA damage by PCNA-containing replication complex / helicase activity / circadian rhythm / regulation of circadian rhythm / peptidyl-serine phosphorylation / DNA-templated DNA replication / HDR through Homologous Recombination (HRR) / Dual Incision in GG-NER / cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus / multicellular organism growth / Orc1 removal from chromatin / Dual incision in TC-NER / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER / cellular senescence / mitotic cell cycle / nucleosome assembly / single-stranded DNA binding / site of double-strand break / 4 iron, 4 sulfur cluster binding / Processing of DNA double-strand break ends / histone binding / DNA-directed DNA polymerase / DNA helicase / DNA-directed DNA polymerase activity / DNA replication / chromosome, telomeric region / cell population proliferation / Ub-specific processing proteases / nuclear body / cilium / ciliary basal body Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Jones, M.J. / Yeeles, J.T.P. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 1items United Kingdom, 1items
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: EMBO J / Year: 2021 Journal: EMBO J / Year: 2021Title: Structure of a human replisome shows the organisation and interactions of a DNA replication machine. Authors: Morgan L Jones / Yasemin Baris / Martin R G Taylor / Joseph T P Yeeles /  Abstract: The human replisome is an elaborate arrangement of molecular machines responsible for accurate chromosome replication. At its heart is the CDC45-MCM-GINS (CMG) helicase, which, in addition to ...The human replisome is an elaborate arrangement of molecular machines responsible for accurate chromosome replication. At its heart is the CDC45-MCM-GINS (CMG) helicase, which, in addition to unwinding the parental DNA duplex, arranges many proteins including the leading-strand polymerase Pol ε, together with TIMELESS-TIPIN, CLASPIN and AND-1 that have key and varied roles in maintaining smooth replisome progression. How these proteins are coordinated in the human replisome is poorly understood. We have determined a 3.2 Å cryo-EM structure of a human replisome comprising CMG, Pol ε, TIMELESS-TIPIN, CLASPIN and AND-1 bound to replication fork DNA. The structure permits a detailed understanding of how AND-1, TIMELESS-TIPIN and Pol ε engage CMG, reveals how CLASPIN binds to multiple replisome components and identifies the position of the Pol ε catalytic domain. Furthermore, the intricate network of contacts contributed by MCM subunits and TIMELESS-TIPIN with replication fork DNA suggests a mechanism for strand separation. #1:  Journal: Nature / Year: 2021 Journal: Nature / Year: 2021Title: A conserved mechanism for regulating replisome disassembly in eukaryotes. Authors: Michael Jenkyn-Bedford / Morgan L Jones / Yasemin Baris / Karim P M Labib / Giuseppe Cannone / Joseph T P Yeeles / Tom D Deegan /  Abstract: Replisome disassembly is the final step of eukaryotic DNA replication and is triggered by ubiquitylation of the CDC45-MCM-GINS (CMG) replicative helicase. Despite being driven by evolutionarily ...Replisome disassembly is the final step of eukaryotic DNA replication and is triggered by ubiquitylation of the CDC45-MCM-GINS (CMG) replicative helicase. Despite being driven by evolutionarily diverse E3 ubiquitin ligases in different eukaryotes (SCF in budding yeast, CUL2 in metazoa), replisome disassembly is governed by a common regulatory principle, in which ubiquitylation of CMG is suppressed before replication termination, to prevent replication fork collapse. Recent evidence suggests that this suppression is mediated by replication fork DNA. However, it is unknown how SCF and CUL2 discriminate terminated from elongating replisomes, to selectively ubiquitylate CMG only after termination. Here we used cryo-electron microscopy to solve high-resolution structures of budding yeast and human replisome-E3 ligase assemblies. Our structures show that the leucine-rich repeat domains of Dia2 and LRR1 are structurally distinct, but bind to a common site on CMG, including the MCM3 and MCM5 zinc-finger domains. The LRR-MCM interaction is essential for replisome disassembly and, crucially, is occluded by the excluded DNA strand at replication forks, establishing the structural basis for the suppression of CMG ubiquitylation before termination. Our results elucidate a conserved mechanism for the regulation of replisome disassembly in eukaryotes, and reveal a previously unanticipated role for DNA in preserving replisome integrity. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7pfo.cif.gz 7pfo.cif.gz | 2.9 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7pfo.ent.gz pdb7pfo.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7pfo.json.gz 7pfo.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pf/7pfo https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pf/7pfo ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pf/7pfo ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pf/7pfo | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  13375MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 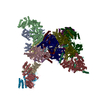
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-DNA replication licensing factor ... , 6 types, 6 molecules 234567
| #1: Protein | Mass: 102034.102 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MCM2, BM28, CCNL1, CDCL1, KIAA0030 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MCM2, BM28, CCNL1, CDCL1, KIAA0030 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P49736, DNA helicase Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P49736, DNA helicase |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 91110.852 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MCM3 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MCM3 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P25205, DNA helicase Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P25205, DNA helicase |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 96684.852 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MCM4, CDC21 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MCM4, CDC21 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P33991, DNA helicase Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P33991, DNA helicase |
| #4: Protein | Mass: 82406.633 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MCM5, CDC46 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MCM5, CDC46 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P33992, DNA helicase Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P33992, DNA helicase |
| #5: Protein | Mass: 93010.273 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MCM6 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MCM6 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q14566, DNA helicase Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q14566, DNA helicase |
| #6: Protein | Mass: 81411.875 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MCM7, CDC47, MCM2 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MCM7, CDC47, MCM2 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P33993, DNA helicase Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P33993, DNA helicase |
-DNA polymerase epsilon ... , 2 types, 2 molecules AB
| #7: Protein | Mass: 59600.887 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLE2, DPE2 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLE2, DPE2 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P56282 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P56282 |
|---|---|
| #8: Protein | Mass: 261855.266 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLE, POLE1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLE, POLE1 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper)References: UniProt: Q07864, DNA-directed DNA polymerase, Hydrolases; Acting on ester bonds; Exodeoxyribonucleases producing 5'-phosphomonoesters |
-Protein , 5 types, 7 molecules CHIJKLQ
| #9: Protein | Mass: 66016.891 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CDC45, CDC45L, CDC45L2, UNQ374/PRO710 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CDC45, CDC45L, CDC45L2, UNQ374/PRO710 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: O75419 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: O75419 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #14: Protein | Mass: 130098.148 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: WDHD1, AND1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: WDHD1, AND1 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: O75717 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: O75717#15: Protein | | Mass: 138903.031 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: TIMELESS, TIM, TIM1, TIMELESS1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: TIMELESS, TIM, TIM1, TIMELESS1 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UNS1 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UNS1#16: Protein | | Mass: 34600.223 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: TIPIN / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: TIPIN / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9BVW5 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9BVW5#19: Protein | | Mass: 155184.703 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CLSPN / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CLSPN / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9HAW4 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9HAW4 |
-DNA replication complex GINS protein ... , 4 types, 4 molecules DEFG
| #10: Protein | Mass: 23022.469 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GINS1, KIAA0186, PSF1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GINS1, KIAA0186, PSF1 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q14691 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q14691 |
|---|---|
| #11: Protein | Mass: 21453.713 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GINS2, PSF2, CGI-122, DC5, HSPC037 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GINS2, PSF2, CGI-122, DC5, HSPC037 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9Y248 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9Y248 |
| #12: Protein | Mass: 24562.611 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GINS3, PSF3 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GINS3, PSF3 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9BRX5 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9BRX5 |
| #13: Protein | Mass: 30114.236 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GINS4, SLD5 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GINS4, SLD5 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9BRT9 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9BRT9 |
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules MN
| #17: DNA chain | Mass: 26396.836 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
|---|---|
| #18: DNA chain | Mass: 16407.533 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) |
-Non-polymers , 4 types, 12 molecules 






| #20: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / #21: Chemical | #22: Chemical | #23: Chemical | ChemComp-SO4 / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | N |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Core human replisome / Type: COMPLEX Entity ID: #8, #7, #3, #5-#6, #2, #1, #4, #10-#13, #9, #15-#17, #14, #18-#19 Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.8 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 400 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/2 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1500 nm / Cs: 0.1 mm |
| Specimen holder | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 39.8 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
| Image scans | Movie frames/image: 40 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 490000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 110000 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








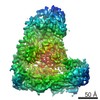
 PDBj
PDBj