+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7otv | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
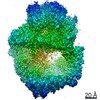
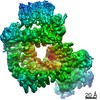
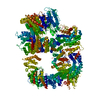
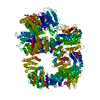
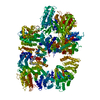
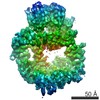
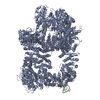
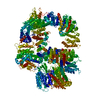
| Title | DNA-PKcs in complex with wortmannin | ||||||
 Components Components | DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit,DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit,DNA-PKcs | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | DNA BINDING PROTEIN / complex / inhibitor / DNA repair | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of platelet formation / T cell receptor V(D)J recombination / pro-B cell differentiation / DNA-dependent protein kinase activity / small-subunit processome assembly / positive regulation of lymphocyte differentiation / histone H2AXS139 kinase activity / DNA-dependent protein kinase complex / DNA-dependent protein kinase-DNA ligase 4 complex / immunoglobulin V(D)J recombination ...positive regulation of platelet formation / T cell receptor V(D)J recombination / pro-B cell differentiation / DNA-dependent protein kinase activity / small-subunit processome assembly / positive regulation of lymphocyte differentiation / histone H2AXS139 kinase activity / DNA-dependent protein kinase complex / DNA-dependent protein kinase-DNA ligase 4 complex / immunoglobulin V(D)J recombination / nonhomologous end joining complex / immature B cell differentiation / regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation / regulation of epithelial cell proliferation / double-strand break repair via alternative nonhomologous end joining / Cytosolic sensors of pathogen-associated DNA / telomere capping / IRF3-mediated induction of type I IFN / regulation of hematopoietic stem cell differentiation / U3 snoRNA binding / maturation of 5.8S rRNA / T cell lineage commitment / negative regulation of cGAS/STING signaling pathway / positive regulation of double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining / B cell lineage commitment / negative regulation of protein phosphorylation / peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation / somitogenesis / ectopic germ cell programmed cell death / mitotic G1 DNA damage checkpoint signaling / activation of innate immune response / telomere maintenance / positive regulation of erythrocyte differentiation / positive regulation of translation / response to gamma radiation / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / small-subunit processome / protein-DNA complex / regulation of circadian rhythm / peptidyl-serine phosphorylation / brain development / protein destabilization / protein modification process / double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining / cellular response to insulin stimulus / intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage / T cell differentiation in thymus / rhythmic process / double-strand break repair / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / heart development / double-stranded DNA binding / transcription regulator complex / RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding / chromosome, telomeric region / protein phosphorylation / protein kinase activity / non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase / positive regulation of apoptotic process / protein domain specific binding / innate immune response / protein serine kinase activity / protein serine/threonine kinase activity / DNA damage response / negative regulation of apoptotic process / chromatin / nucleolus / enzyme binding / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / protein-containing complex / RNA binding / nucleoplasm / ATP binding / nucleus / membrane / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.24 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Liang, S. / Thomas, S.E. / Blundell, T.L. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 1items United Kingdom, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2022 Journal: Nature / Year: 2022Title: Structural insights into inhibitor regulation of the DNA repair protein DNA-PKcs. Authors: Shikang Liang / Sherine E Thomas / Amanda K Chaplin / Steven W Hardwick / Dimitri Y Chirgadze / Tom L Blundell /  Abstract: The DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit (DNA-PKcs) has a central role in non-homologous end joining, one of the two main pathways that detect and repair DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) in ...The DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit (DNA-PKcs) has a central role in non-homologous end joining, one of the two main pathways that detect and repair DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) in humans. DNA-PKcs is of great importance in repairing pathological DSBs, making DNA-PKcs inhibitors attractive therapeutic agents for cancer in combination with DSB-inducing radiotherapy and chemotherapy. Many of the selective inhibitors of DNA-PKcs that have been developed exhibit potential as treatment for various cancers. Here we report cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of human DNA-PKcs natively purified from HeLa cell nuclear extracts, in complex with adenosine-5'-(γ-thio)-triphosphate (ATPγS) and four inhibitors (wortmannin, NU7441, AZD7648 and M3814), including drug candidates undergoing clinical trials. The structures reveal molecular details of ATP binding at the active site before catalysis and provide insights into the modes of action and specificities of the competitive inhibitors. Of note, binding of the ligands causes movement of the PIKK regulatory domain (PRD), revealing a connection between the p-loop and PRD conformations. Electrophoretic mobility shift assay and cryo-EM studies on the DNA-dependent protein kinase holoenzyme further show that ligand binding does not have a negative allosteric or inhibitory effect on assembly of the holoenzyme complex and that inhibitors function through direct competition with ATP. Overall, the structures described in this study should greatly assist future efforts in rational drug design targeting DNA-PKcs, demonstrating the potential of cryo-EM in structure-guided drug development for large and challenging targets. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7otv.cif.gz 7otv.cif.gz | 647.8 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7otv.ent.gz pdb7otv.ent.gz | 522 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7otv.json.gz 7otv.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ot/7otv https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ot/7otv ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ot/7otv ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ot/7otv | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  13067MC  7otmC 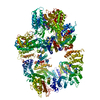 7otpC 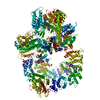 7otwC 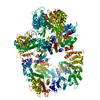 7otyC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
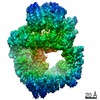
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 471375.406 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)References: UniProt: P78527, non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase |
|---|---|
| #2: Chemical | ChemComp-KWT / ( |
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: DNA-PKcs in complex with wortmannin / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.6 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 47.9 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.24 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 64179 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj