+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7oob | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
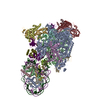
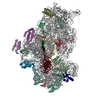
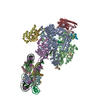
| Title | Pol II-CSB-CSA-DDB1-UVSSA-ADPBeF3 (Structure2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSCRIPTION / DNA repair | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of transcription-coupled nucleotide-excision repair / negative regulation of double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining / nucleotide-excision repair complex / : / response to auditory stimulus / regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / DNA protection / B-WICH complex / single strand break repair / Formation of RNA Pol II elongation complex ...regulation of transcription-coupled nucleotide-excision repair / negative regulation of double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining / nucleotide-excision repair complex / : / response to auditory stimulus / regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / DNA protection / B-WICH complex / single strand break repair / Formation of RNA Pol II elongation complex / Formation of the Early Elongation Complex / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / RNA Polymerase II Pre-transcription Events / TP53 Regulates Transcription of DNA Repair Genes / FGFR2 alternative splicing / RNA polymerase II transcribes snRNA genes / mRNA Capping / mRNA Splicing - Minor Pathway / Processing of Capped Intron-Containing Pre-mRNA / RNA Polymerase II Promoter Escape / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Pre-Initiation And Promoter Opening / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Elongation / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation And Promoter Clearance / RNA Pol II CTD phosphorylation and interaction with CE / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / response to superoxide / Formation of TC-NER Pre-Incision Complex / Dual incision in TC-NER / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER / mRNA Splicing - Major Pathway / photoreceptor cell maintenance / double-strand break repair via classical nonhomologous end joining / ATP-dependent chromatin remodeler activity / positive regulation by virus of viral protein levels in host cell / RNA polymerase binding / chromatin-protein adaptor activity / positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription, elongation / spindle assembly involved in female meiosis / response to UV-B / epigenetic programming in the zygotic pronuclei / UV-damage excision repair / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase III / biological process involved in interaction with symbiont / ATP-dependent DNA damage sensor activity / WD40-repeat domain binding / regulation of mitotic cell cycle phase transition / positive regulation of nuclear-transcribed mRNA poly(A) tail shortening / Cul4A-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase complex / Cul4-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase complex / organelle membrane / Cul4B-RING E3 ubiquitin ligase complex / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase I / ubiquitin ligase complex scaffold activity / negative regulation of reproductive process / negative regulation of developmental process / maintenance of transcriptional fidelity during transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / RNA Polymerase I Transcription Initiation / protein tyrosine kinase activator activity / positive regulation of translational initiation / pyrimidine dimer repair / viral release from host cell / cullin family protein binding / response to X-ray / positive regulation of transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II / ATP-dependent activity, acting on DNA / ectopic germ cell programmed cell death / RNA polymerase I complex / site of DNA damage / RNA polymerase III complex / transcription elongation by RNA polymerase I / positive regulation of viral genome replication / RNA polymerase II, core complex / tRNA transcription by RNA polymerase III / response to UV / protein autoubiquitination / ubiquitin-like ligase-substrate adaptor activity / positive regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / transcription by RNA polymerase I / proteasomal protein catabolic process / sperm end piece / JNK cascade / transcription-coupled nucleotide-excision repair / translation initiation factor binding / neurogenesis / positive regulation of gluconeogenesis / sperm principal piece / DNA damage checkpoint signaling / positive regulation of RNA splicing / positive regulation of DNA repair / regulation of DNA-templated transcription elongation / transcription elongation factor complex / response to gamma radiation / ERCC6 (CSB) and EHMT2 (G9a) positively regulate rRNA expression / nucleotide-excision repair / transcription initiation at RNA polymerase II promoter / promoter-specific chromatin binding / P-body / helicase activity / Recognition of DNA damage by PCNA-containing replication complex Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.7 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Kokic, G. / Cramer, P. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, 2items Germany, 2items
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2021 Journal: Nature / Year: 2021Title: Structural basis of human transcription-DNA repair coupling. Authors: Goran Kokic / Felix R Wagner / Aleksandar Chernev / Henning Urlaub / Patrick Cramer /  Abstract: Transcription-coupled DNA repair removes bulky DNA lesions from the genome and protects cells against ultraviolet (UV) irradiation. Transcription-coupled DNA repair begins when RNA polymerase II ...Transcription-coupled DNA repair removes bulky DNA lesions from the genome and protects cells against ultraviolet (UV) irradiation. Transcription-coupled DNA repair begins when RNA polymerase II (Pol II) stalls at a DNA lesion and recruits the Cockayne syndrome protein CSB, the E3 ubiquitin ligase, CRL4 and UV-stimulated scaffold protein A (UVSSA). Here we provide five high-resolution structures of Pol II transcription complexes containing human transcription-coupled DNA repair factors and the elongation factors PAF1 complex (PAF) and SPT6. Together with biochemical and published data, the structures provide a model for transcription-repair coupling. Stalling of Pol II at a DNA lesion triggers replacement of the elongation factor DSIF by CSB, which binds to PAF and moves upstream DNA to SPT6. The resulting elongation complex, EC, uses the CSA-stimulated translocase activity of CSB to pull on upstream DNA and push Pol II forward. If the lesion cannot be bypassed, CRL4 spans over the Pol II clamp and ubiquitylates the RPB1 residue K1268, enabling recruitment of TFIIH to UVSSA and DNA repair. Conformational changes in CRL4 lead to ubiquitylation of CSB and to release of transcription-coupled DNA repair factors before transcription may continue over repaired DNA. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7oob.cif.gz 7oob.cif.gz | 1.9 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7oob.ent.gz pdb7oob.ent.gz | 1.5 MB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7oob.json.gz 7oob.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/oo/7oob https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/oo/7oob ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/oo/7oob ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/oo/7oob | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  13009MC  7oo3C  7oopC  7opcC  7opdC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-DNA-directed RNA polymerase II subunit ... , 6 types, 6 molecules ACEFGI
| #1: Protein | Mass: 217450.078 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|---|
| #3: Protein | Mass: 31439.074 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #5: Protein | Mass: 24644.318 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #6: Protein | Mass: 14477.001 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #7: Protein | Mass: 19314.283 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #9: Protein | Mass: 14541.221 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
-Protein , 5 types, 5 molecules BDKLd
| #2: Protein | Mass: 134041.422 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|---|
| #4: Protein | Mass: 16331.255 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #11: Protein | Mass: 13310.284 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #12: Protein | Mass: 7018.244 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #14: Protein | Mass: 127369.719 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: DDB1, XAP1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: DDB1, XAP1 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q16531 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q16531 |
-DNA-directed RNA polymerases I, II, and III subunit ... , 2 types, 2 molecules HJ
| #8: Protein | Mass: 17162.273 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|---|
| #10: Protein | Mass: 7655.123 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
-DNA excision repair protein ERCC- ... , 2 types, 2 molecules ba
| #13: Protein | Mass: 168945.797 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ERCC6, CSB / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ERCC6, CSB / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper)References: UniProt: Q03468, Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement |
|---|---|
| #18: Protein | Mass: 44107.160 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ERCC8, CKN1, CSA / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ERCC8, CKN1, CSA / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q13216 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q13216 |
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules NT
| #15: DNA chain | Mass: 14494.314 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
|---|---|
| #16: DNA chain | Mass: 14269.129 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-RNA chain , 1 types, 1 molecules P
| #17: RNA chain | Mass: 3264.036 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 4 types, 12 molecules 






| #19: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / #20: Chemical | #21: Chemical | ChemComp-ADP / | #22: Chemical | ChemComp-BEF / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | N |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.3 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid type: Quantifoil R2/1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 41.2 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 10940 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.18.2_3874: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 1855061 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
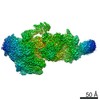
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.7 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 100000 Details: Different final number of particles was used for different focused refined maps. Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj













































