+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-13016 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
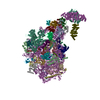
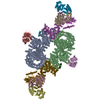
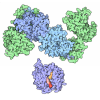
| Title | Pol II-CSB-CRL4CSA-UVSSA-SPT6-PAF (Structure 5) | |||||||||
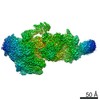
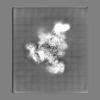
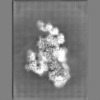
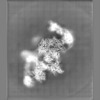
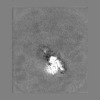
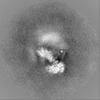
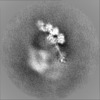
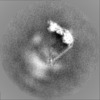
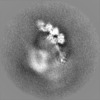
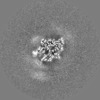
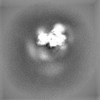
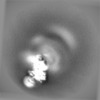
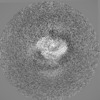
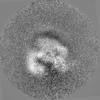
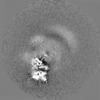
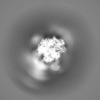
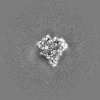
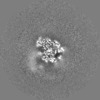
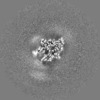
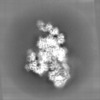
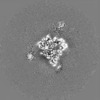
 Map data Map data | The main map. | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | transcription / DNA repair / ubiquitin | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationProlactin receptor signaling / RNA polymerase inhibitor activity / Recognition of DNA damage by PCNA-containing replication complex / Regulation of BACH1 activity / Formation of TC-NER Pre-Incision Complex / DNA Damage Recognition in GG-NER / Dual Incision in GG-NER / Dual incision in TC-NER / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER / Formation of Incision Complex in GG-NER ...Prolactin receptor signaling / RNA polymerase inhibitor activity / Recognition of DNA damage by PCNA-containing replication complex / Regulation of BACH1 activity / Formation of TC-NER Pre-Incision Complex / DNA Damage Recognition in GG-NER / Dual Incision in GG-NER / Dual incision in TC-NER / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER / Formation of Incision Complex in GG-NER / regulation of transcription-coupled nucleotide-excision repair / negative regulation of double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining / Regulation of RAS by GAPs / Regulation of RUNX2 expression and activity / Degradation of GLI1 by the proteasome / Degradation of DVL / FBXL7 down-regulates AURKA during mitotic entry and in early mitosis / blastocyst growth / Orc1 removal from chromatin / GSK3B and BTRC:CUL1-mediated-degradation of NFE2L2 / Hedgehog 'on' state / Ski complex / Oxygen-dependent proline hydroxylation of Hypoxia-inducible Factor Alpha / Degradation of beta-catenin by the destruction complex / nucleotide-excision repair complex / mRNA decay by 3' to 5' exoribonuclease / RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain phosphoserine binding / negative regulation of granulocyte differentiation / inner cell mass cell differentiation / positive regulation of mRNA 3'-end processing / regulation of isotype switching / eukaryotic initiation factor 4E binding / Cdc73/Paf1 complex / nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process, 3'-5' exonucleolytic nonsense-mediated decay / : / Interleukin-1 signaling / endodermal cell fate commitment / regulation of muscle cell differentiation / negative regulation of myeloid cell differentiation / anaphase-promoting complex / GLI3 is processed to GLI3R by the proteasome / positive regulation of cell cycle G1/S phase transition / trophectodermal cell differentiation / response to auditory stimulus / Neddylation / regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / DNA protection / B-WICH complex / blastocyst hatching / single strand break repair / cullin-RING-type E3 NEDD8 transferase / KEAP1-NFE2L2 pathway / cullin-RING ubiquitin ligase complex / Formation of RNA Pol II elongation complex / Formation of the Early Elongation Complex / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / RNA Polymerase II Pre-transcription Events / TP53 Regulates Transcription of DNA Repair Genes / FGFR2 alternative splicing / RNA polymerase II transcribes snRNA genes / mRNA Capping / mRNA Splicing - Minor Pathway / Processing of Capped Intron-Containing Pre-mRNA / RNA Polymerase II Promoter Escape / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Pre-Initiation And Promoter Opening / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Elongation / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation And Promoter Clearance / RNA Pol II CTD phosphorylation and interaction with CE / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / response to superoxide / Formation of TC-NER Pre-Incision Complex / Dual incision in TC-NER / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER / mRNA Splicing - Major Pathway / Cul7-RING ubiquitin ligase complex / nucleosome organization / regulation of DNA damage checkpoint / photoreceptor cell maintenance / double-strand break repair via classical nonhomologous end joining / blastocyst formation / Antigen processing: Ubiquitination & Proteasome degradation / ATP-dependent chromatin remodeler activity / positive regulation by virus of viral protein levels in host cell / positive regulation of protein autoubiquitination / regulation of nucleotide-excision repair / mRNA 3'-end processing / RNA polymerase II transcription initiation surveillance / protein neddylation / RNA polymerase binding / chromatin-protein adaptor activity / positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription, elongation / spindle assembly involved in female meiosis / response to UV-B / epigenetic programming in the zygotic pronuclei / NEDD8 ligase activity / UV-damage excision repair / negative regulation of response to oxidative stress / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase III / Cul5-RING ubiquitin ligase complex Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /  | |||||||||
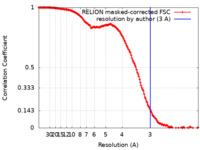
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Kokic G / Cramer P | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, 2 items Germany, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2021 Journal: Nature / Year: 2021Title: Structural basis of human transcription-DNA repair coupling. Authors: Goran Kokic / Felix R Wagner / Aleksandar Chernev / Henning Urlaub / Patrick Cramer /  Abstract: Transcription-coupled DNA repair removes bulky DNA lesions from the genome and protects cells against ultraviolet (UV) irradiation. Transcription-coupled DNA repair begins when RNA polymerase II ...Transcription-coupled DNA repair removes bulky DNA lesions from the genome and protects cells against ultraviolet (UV) irradiation. Transcription-coupled DNA repair begins when RNA polymerase II (Pol II) stalls at a DNA lesion and recruits the Cockayne syndrome protein CSB, the E3 ubiquitin ligase, CRL4 and UV-stimulated scaffold protein A (UVSSA). Here we provide five high-resolution structures of Pol II transcription complexes containing human transcription-coupled DNA repair factors and the elongation factors PAF1 complex (PAF) and SPT6. Together with biochemical and published data, the structures provide a model for transcription-repair coupling. Stalling of Pol II at a DNA lesion triggers replacement of the elongation factor DSIF by CSB, which binds to PAF and moves upstream DNA to SPT6. The resulting elongation complex, EC, uses the CSA-stimulated translocase activity of CSB to pull on upstream DNA and push Pol II forward. If the lesion cannot be bypassed, CRL4 spans over the Pol II clamp and ubiquitylates the RPB1 residue K1268, enabling recruitment of TFIIH to UVSSA and DNA repair. Conformational changes in CRL4 lead to ubiquitylation of CSB and to release of transcription-coupled DNA repair factors before transcription may continue over repaired DNA. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7opdMC  7oo3C  7oobC  7oopC  7opcC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_13016.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 282.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_13016.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 282.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | The main map. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
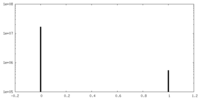
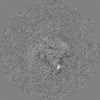
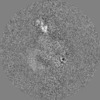
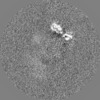
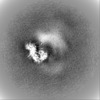
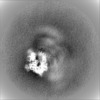
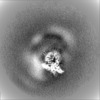
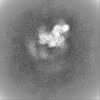
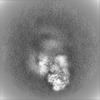
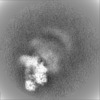
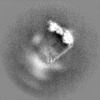
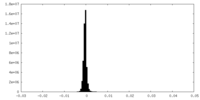
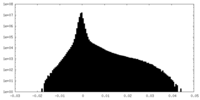
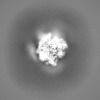
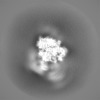
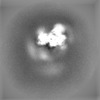
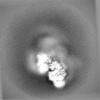
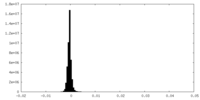
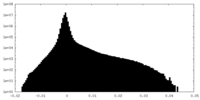
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
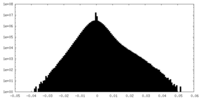
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.05 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
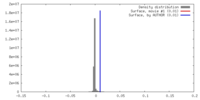
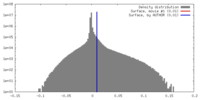
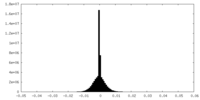
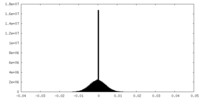
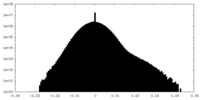
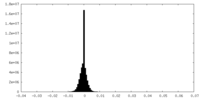
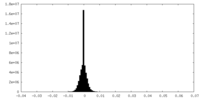
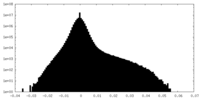
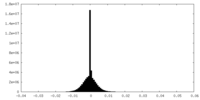
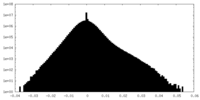
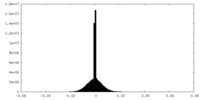
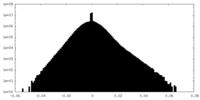
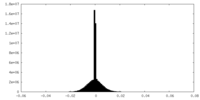
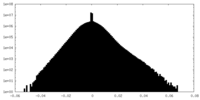
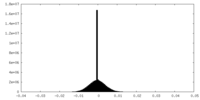
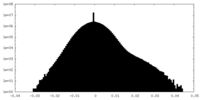
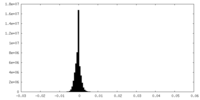
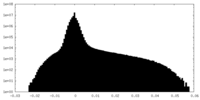
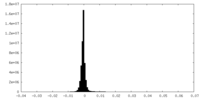
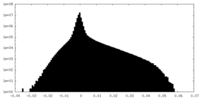
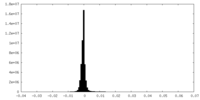
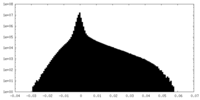
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
+Mask #1
+Mask #2
+Mask #3
+Mask #4
+Mask #5
+Mask #6
+Additional map: Half map corresponding to the map focused refined...
+Additional map: Half map corresponding to the map focused refined on PAF.
+Additional map: Half map corresponding to the map focused refined on SPT6.
+Additional map: Half map corresponding to the map focused refined on SPT6.
+Additional map: Half map corresponding to the map focused refined...
+Additional map: Half map corresponding to the map focused refined...
+Additional map: Half map corresponding to the map focused refined...
+Additional map: Half map corresponding to the map focused refined on PAF.
+Additional map: Half map corresponding to the map focused refined on Pol II.
+Additional map: Half map corresponding to the map focused refined on CSA-DDB1-CSB.
+Additional map: Half map corresponding to the map focused refined on Pol II.
+Additional map: Half map corresponding to the map focused refined on CSA-DDB1-CSB.
+Half map: Half map corresponding to the main map.
+Half map: Half map corresponding to the main map.
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : Transcribing Pol II bound to TRC factors, SPT6 and PAF.
+Supramolecule #1: Transcribing Pol II bound to TRC factors, SPT6 and PAF.
+Supramolecule #2: DNA-directed RNA polymerase with RNA_pol_L_2 and RNA polymerase
+Supramolecule #3: Supplementary proteins
+Supramolecule #4: NTS, RNA, TS
+Supramolecule #5: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RBX1
+Macromolecule #1: DNA-directed RNA polymerase II subunit RPB1
+Macromolecule #2: DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit beta
+Macromolecule #3: DNA-directed RNA polymerase II subunit RPB3
+Macromolecule #4: RPOL4c domain-containing protein
+Macromolecule #5: DNA-directed RNA polymerase II subunit E
+Macromolecule #6: DNA-directed RNA polymerase II subunit F
+Macromolecule #7: DNA-directed RNA polymerase II subunit RPB7
+Macromolecule #8: DNA-directed RNA polymerases I, II, and III subunit RPABC3
+Macromolecule #9: DNA-directed RNA polymerase II subunit RPB9
+Macromolecule #10: DNA-directed RNA polymerases I, II, and III subunit RPABC5
+Macromolecule #11: RNA_pol_L_2 domain-containing protein
+Macromolecule #12: RNA polymerase II subunit K
+Macromolecule #13: Transcription elongation factor SPT6
+Macromolecule #16: LEO1 helix
+Macromolecule #17: RNA polymerase-associated protein CTR9 homolog
+Macromolecule #19: RNA polymerase-associated protein LEO1
+Macromolecule #20: RNA polymerase II-associated factor 1 homolog
+Macromolecule #21: WD repeat-containing protein 61
+Macromolecule #22: Parafibromin
+Macromolecule #23: DNA excision repair protein ERCC-8
+Macromolecule #24: DNA excision repair protein ERCC-6
+Macromolecule #25: UV-stimulated scaffold protein A
+Macromolecule #26: DNA damage-binding protein 1
+Macromolecule #27: Cullin-4A
+Macromolecule #28: E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RBX1
+Macromolecule #14: NTS
+Macromolecule #18: TS
+Macromolecule #15: RNA
+Macromolecule #29: ZINC ION
+Macromolecule #30: MAGNESIUM ION
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.3 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R2/1 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 40.4 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 81000 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)
















































 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper)
Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper)