[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-6sb0: cryo-EM structure of mTORC1 bound to PRAS40-fused active RagA/C G... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6sb0 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | cryo-EM structure of mTORC1 bound to PRAS40-fused active RagA/C GTPases | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | SIGNALING PROTEIN / small GTPases / mTORC1 activator / roadblock domain / GTPase domain | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationGtr1-Gtr2 GTPase complex / FNIP-folliculin RagC/D GAP / RNA polymerase III type 2 promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / RNA polymerase III type 1 promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / positive regulation of cytoplasmic translational initiation / regulation of locomotor rhythm / T-helper 1 cell lineage commitment / positive regulation of pentose-phosphate shunt / positive regulation of wound healing, spreading of epidermal cells / TORC2 complex ...Gtr1-Gtr2 GTPase complex / FNIP-folliculin RagC/D GAP / RNA polymerase III type 2 promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / RNA polymerase III type 1 promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / positive regulation of cytoplasmic translational initiation / regulation of locomotor rhythm / T-helper 1 cell lineage commitment / positive regulation of pentose-phosphate shunt / positive regulation of wound healing, spreading of epidermal cells / TORC2 complex / regulation of membrane permeability / TORC2 signaling / regulation of TORC1 signaling / cellular response to leucine starvation / TFIIIC-class transcription factor complex binding / heart valve morphogenesis / negative regulation of lysosome organization / TORC1 complex / voluntary musculoskeletal movement / positive regulation of transcription of nucleolar large rRNA by RNA polymerase I / positive regulation of odontoblast differentiation / calcineurin-NFAT signaling cascade / protein localization to lysosome / RNA polymerase III type 3 promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / positive regulation of keratinocyte migration / regulation of osteoclast differentiation / MTOR signalling / regulation of lysosome organization / cellular response to L-leucine / energy reserve metabolic process / regulation of autophagosome assembly / regulation of TOR signaling / Energy dependent regulation of mTOR by LKB1-AMPK / cellular response to nutrient / Amino acids regulate mTORC1 / cellular response to methionine / serine/threonine protein kinase complex / ruffle organization / negative regulation of cell size / positive regulation of ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / positive regulation of osteoclast differentiation / cellular response to osmotic stress / negative regulation of TOR signaling / anoikis / inositol hexakisphosphate binding / negative regulation of protein localization to nucleus / protein localization to membrane / cardiac muscle cell development / AKT phosphorylates targets in the cytosol / negative regulation of calcineurin-NFAT signaling cascade / regulation of myelination / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase III / small GTPase-mediated signal transduction / negative regulation of macroautophagy / TORC1 signaling / positive regulation of myotube differentiation / Macroautophagy / neurotrophin TRK receptor signaling pathway / regulation of cell size / Constitutive Signaling by AKT1 E17K in Cancer / protein kinase inhibitor activity / positive regulation of actin filament polymerization / germ cell development / behavioral response to pain / oligodendrocyte differentiation / positive regulation of oligodendrocyte differentiation / TOR signaling / positive regulation of translational initiation / mTORC1-mediated signalling / CD28 dependent PI3K/Akt signaling / HSF1-dependent transactivation / regulation of macroautophagy / social behavior / positive regulation of TOR signaling / enzyme-substrate adaptor activity / positive regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / protein serine/threonine kinase inhibitor activity / protein kinase activator activity / 'de novo' pyrimidine nucleobase biosynthetic process / response to amino acid / positive regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition / positive regulation of lipid biosynthetic process / vascular endothelial cell response to laminar fluid shear stress / heart morphogenesis / negative regulation of protein kinase activity / neuronal action potential / regulation of cellular response to heat / positive regulation of lamellipodium assembly / cardiac muscle contraction / positive regulation of stress fiber assembly / T cell costimulation / phagocytic vesicle / 14-3-3 protein binding / protein-membrane adaptor activity / positive regulation of endothelial cell proliferation / negative regulation of TORC1 signaling / cellular response to nutrient levels / cytoskeleton organization / endomembrane system / positive regulation of TORC1 signaling Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 5.5 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Anandapadamanaban, M. / Berndt, A. / Masson, G.R. / Perisic, O. / Williams, R.L. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 3items United Kingdom, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2019 Journal: Science / Year: 2019Title: Architecture of human Rag GTPase heterodimers and their complex with mTORC1. Authors: Madhanagopal Anandapadamanaban / Glenn R Masson / Olga Perisic / Alex Berndt / Jonathan Kaufman / Chris M Johnson / Balaji Santhanam / Kacper B Rogala / David M Sabatini / Roger L Williams /   Abstract: The Rag guanosine triphosphatases (GTPases) recruit the master kinase mTORC1 to lysosomes to regulate cell growth and proliferation in response to amino acid availability. The nucleotide state of Rag ...The Rag guanosine triphosphatases (GTPases) recruit the master kinase mTORC1 to lysosomes to regulate cell growth and proliferation in response to amino acid availability. The nucleotide state of Rag heterodimers is critical for their association with mTORC1. Our cryo-electron microscopy structure of RagA/RagC in complex with mTORC1 shows the details of RagA/RagC binding to the RAPTOR subunit of mTORC1 and explains why only the RagA/RagC nucleotide state binds mTORC1. Previous kinetic studies suggested that GTP binding to one Rag locks the heterodimer to prevent GTP binding to the other. Our crystal structures and dynamics of RagA/RagC show the mechanism for this locking and explain how oncogenic hotspot mutations disrupt this process. In contrast to allosteric activation by RHEB, Rag heterodimer binding does not change mTORC1 conformation and activates mTORC1 by targeting it to lysosomes. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6sb0.cif.gz 6sb0.cif.gz | 1.2 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6sb0.ent.gz pdb6sb0.ent.gz | 867.7 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6sb0.json.gz 6sb0.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sb/6sb0 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sb/6sb0 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sb/6sb0 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sb/6sb0 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  10132MC  6s6aC  6s6dC  6sb2C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 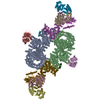
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Noncrystallographic symmetry (NCS) | NCS domain:
NCS domain segments:
NCS ensembles :
NCS oper:
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 4 types, 8 molecules ABEHYNTO
| #1: Protein | Mass: 287012.031 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MTOR, FRAP, FRAP1, FRAP2, RAFT1, RAPT1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MTOR, FRAP, FRAP1, FRAP2, RAFT1, RAPT1 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)References: UniProt: P42345, non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase #2: Protein | Mass: 35910.090 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MLST8, GBL, LST8 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MLST8, GBL, LST8 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9BVC4 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9BVC4#5: Protein | Mass: 149200.016 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RPTOR, KIAA1303, RAPTOR / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RPTOR, KIAA1303, RAPTOR / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q8N122 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q8N122#6: Protein | Mass: 27412.293 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: AKT1S1, PRAS40 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: AKT1S1, PRAS40 / Production host:  |
|---|
-Ras-related GTP-binding protein ... , 2 types, 4 molecules CIDJ
| #3: Protein | Mass: 36600.195 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Mutation: Q66L Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RRAGA / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RRAGA / Production host:  #4: Protein | Mass: 44284.832 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Mutation: T90N Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RRAGC / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RRAGC / Production host:  |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 2 types, 4 molecules 


| #7: Chemical | | #8: Chemical | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 1.09 MDa / Experimental value: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7 / Details: 50mM HEPES pH 7.0, 100mM NaCl, 2mM MgCl2, 1mM TCEP | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.05 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES Details: mTORC1 (mTOR complex 1) is a dimer consists of three proteins: mTOR, mLST8 and RAPTOR. The interacting partner, PRAS40-fused-RagA/C (referred as RagA/C here) forms complex with mTORC1 for ...Details: mTORC1 (mTOR complex 1) is a dimer consists of three proteins: mTOR, mLST8 and RAPTOR. The interacting partner, PRAS40-fused-RagA/C (referred as RagA/C here) forms complex with mTORC1 for its activation. We solved the cryo-EM structure of mTORC1 bound to RagA/C. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 200 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 95 % |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 1.8 sec. / Electron dose: 40 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
| Image scans | Width: 3838 / Height: 3710 / Movie frames/image: 22 / Used frames/image: 1-22 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: REFMAC / Version: 5.8.0238 / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Image processing | Details: The selected images were processed using MotionCor2 within the RELION-3.0.6 package. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 580707 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 5.5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 90809 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE Details: For the final reconstruction of mTORC1-RagA/C structure we used a strategy taking advantage of the relion particle symmetry expand program, and duplicated the C2-refined particles and ...Details: For the final reconstruction of mTORC1-RagA/C structure we used a strategy taking advantage of the relion particle symmetry expand program, and duplicated the C2-refined particles and applied the appropriate rotation and translation to generate a set of monomers. We performed mTORC1-RagA/C 'pseudo-monomer' focussed classification with signal subtraction and obtained a reconstruction of 5.5 A resolution map. This cryo-EM density corresponded to the mTORC1-RagA/C pseudomonomer, where the previously published structure for apo-mTORC1 (PDB ID 6BCX) and our high-resolution crystal structure of RagA/C (6S6A) were fitted with great confidence from our experimental analysis including Pulldown assays, mutational at per-residue level in the binding interface and HDX-Mass Spectrometry. Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | B value: 283 / Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Space: REAL Details: Cryo-EM model of mTORC1-RagA/C was refined using REFMAC5 program in CCPEM package, with a composite map of the 3D reconstruction of mTORC1-RagA/C pseudo-monomer (as mentioned in ...Details: Cryo-EM model of mTORC1-RagA/C was refined using REFMAC5 program in CCPEM package, with a composite map of the 3D reconstruction of mTORC1-RagA/C pseudo-monomer (as mentioned in Reconstruction section) of one protomer together with the generated map for the other second protomer of mTORC1-RagA/C. This second protomer of mTORC1-RagA/C map was generated by simply aligning the first 3D reconstructed pseudomonomer map onto the mTORC1 dimer consensus C2 map and then obtained the rotation-translation matrix with CHIMERA and then used Maputils program in CCP4i. From the resulting mTORC1-RagA/C dimer map, the model of mTORC1-RagA/C was built by using previously published structure of apo-mTORC1 (PDB ID 6BCX) and our crystal structure of RagA/C was fitted (PDB ID 6S6A, unreleased). The entire mTORC1-RagA/C final model was refined using REFMAC5 program using the restraints from the crystal structure of RagA/C and previously published mTORC1 structure. Side chains were removed before refinement, since these were not evident in the cryo-EM densities. Separate model refinements were performed against single half-maps, and the resulting models were compared with the other half-maps to confirm the absence of overfitting. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Resolution: 5.5→321.75 Å / Cor.coef. Fo:Fc: 0.895 / SU B: 104.924 / SU ML: 1.049 Stereochemistry target values: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD WITH PHASES
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Solvent model: PARAMETERS FOR MASK CACLULATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 288.4 Å2
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: 1 / Total: 66022 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj