[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-7mqs: The insulin receptor ectodomain in complex with three venom hybri... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7mqs | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
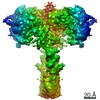
| Title | The insulin receptor ectodomain in complex with three venom hybrid insulin molecules - asymmetric conformation | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | HORMONE / TOXIN / insulin / receptor / venom / cone snail | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of glycogen catabolic process / positive regulation of nitric oxide mediated signal transduction / negative regulation of fatty acid metabolic process / negative regulation of feeding behavior / Signaling by Insulin receptor / IRS activation / regulation of protein secretion / Insulin processing / positive regulation of peptide hormone secretion / positive regulation of respiratory burst ...negative regulation of glycogen catabolic process / positive regulation of nitric oxide mediated signal transduction / negative regulation of fatty acid metabolic process / negative regulation of feeding behavior / Signaling by Insulin receptor / IRS activation / regulation of protein secretion / Insulin processing / positive regulation of peptide hormone secretion / positive regulation of respiratory burst / negative regulation of acute inflammatory response / Regulation of gene expression in beta cells / alpha-beta T cell activation / positive regulation of dendritic spine maintenance / Synthesis, secretion, and deacylation of Ghrelin / activation of protein kinase B activity / negative regulation of protein secretion / negative regulation of gluconeogenesis / positive regulation of glycogen biosynthetic process / fatty acid homeostasis / Signal attenuation / positive regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway / negative regulation of respiratory burst involved in inflammatory response / FOXO-mediated transcription of oxidative stress, metabolic and neuronal genes / negative regulation of lipid catabolic process / positive regulation of lipid biosynthetic process / negative regulation of oxidative stress-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / nitric oxide-cGMP-mediated signaling / transport vesicle / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / positive regulation of nitric-oxide synthase activity / Insulin receptor recycling / negative regulation of reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process / positive regulation of brown fat cell differentiation / insulin-like growth factor receptor binding / NPAS4 regulates expression of target genes / neuron projection maintenance / endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / positive regulation of mitotic nuclear division / Insulin receptor signalling cascade / positive regulation of glycolytic process / positive regulation of cytokine production / endosome lumen / positive regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation / acute-phase response / positive regulation of protein secretion / positive regulation of D-glucose import across plasma membrane / insulin receptor binding / positive regulation of cell differentiation / Regulation of insulin secretion / wound healing / positive regulation of neuron projection development / receptor protein-tyrosine kinase / hormone activity / regulation of synaptic plasticity / negative regulation of protein catabolic process / positive regulation of protein localization to nucleus / Golgi lumen / vasodilation / cognition / glucose metabolic process / insulin receptor signaling pathway / cell-cell signaling / glucose homeostasis / regulation of protein localization / PI5P, PP2A and IER3 Regulate PI3K/AKT Signaling / positive regulation of cell growth / protease binding / secretory granule lumen / positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signal transduction / positive regulation of canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / positive regulation of MAPK cascade / positive regulation of cell migration / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / endoplasmic reticulum lumen / Amyloid fiber formation / Golgi membrane / negative regulation of gene expression / positive regulation of cell population proliferation / positive regulation of gene expression / regulation of DNA-templated transcription / extracellular space / extracellular region / identical protein binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.4 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Blakely, A.D. / Xiong, X. / Kim, J.H. / Menting, J. / Schafer, I.B. / Schubert, H.L. / Agrawal, R. / Gutmann, T. / Delaine, C. / Zhang, Y. ...Blakely, A.D. / Xiong, X. / Kim, J.H. / Menting, J. / Schafer, I.B. / Schubert, H.L. / Agrawal, R. / Gutmann, T. / Delaine, C. / Zhang, Y. / Artik, G.O. / Merriman, A. / Eckert, D. / Lawrence, M.C. / Coskun, U. / Fisher, S.J. / Forbes, B.E. / Safavi-Hemami, H. / Hill, C.P. / Chou, D.H.C. | ||||||
| Funding support | 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Chem Biol / Year: 2022 Journal: Nat Chem Biol / Year: 2022Title: Symmetric and asymmetric receptor conformation continuum induced by a new insulin. Authors: Xiaochun Xiong / Alan Blakely / Jin Hwan Kim / John G Menting / Ingmar B Schäfer / Heidi L Schubert / Rahul Agrawal / Theresia Gutmann / Carlie Delaine / Yi Wolf Zhang / Gizem Olay Artik / ...Authors: Xiaochun Xiong / Alan Blakely / Jin Hwan Kim / John G Menting / Ingmar B Schäfer / Heidi L Schubert / Rahul Agrawal / Theresia Gutmann / Carlie Delaine / Yi Wolf Zhang / Gizem Olay Artik / Allanah Merriman / Debbie Eckert / Michael C Lawrence / Ünal Coskun / Simon J Fisher / Briony E Forbes / Helena Safavi-Hemami / Christopher P Hill / Danny Hung-Chieh Chou /     Abstract: Cone snail venoms contain a wide variety of bioactive peptides, including insulin-like molecules with distinct structural features, binding modes and biochemical properties. Here, we report an active ...Cone snail venoms contain a wide variety of bioactive peptides, including insulin-like molecules with distinct structural features, binding modes and biochemical properties. Here, we report an active humanized cone snail venom insulin with an elongated A chain and a truncated B chain, and use cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) and protein engineering to elucidate its interactions with the human insulin receptor (IR) ectodomain. We reveal how an extended A chain can compensate for deletion of B-chain residues, which are essential for activity of human insulin but also compromise therapeutic utility by delaying dissolution from the site of subcutaneous injection. This finding suggests approaches to developing improved therapeutic insulins. Curiously, the receptor displays a continuum of conformations from the symmetric state to a highly asymmetric low-abundance structure that displays coordination of a single humanized venom insulin using elements from both of the previously characterized site 1 and site 2 interactions. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7mqs.cif.gz 7mqs.cif.gz | 320.2 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7mqs.ent.gz pdb7mqs.ent.gz | 257.9 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7mqs.json.gz 7mqs.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mq/7mqs https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mq/7mqs ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mq/7mqs ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mq/7mqs | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 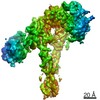 23951MC  7mqoC  7mqrC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-10736 (Title: Cryo-EM of the human insulin receptor ectodomain in complex with an insulin analog with truncated B chain and enlongated A chain EMPIAR-10736 (Title: Cryo-EM of the human insulin receptor ectodomain in complex with an insulin analog with truncated B chain and enlongated A chainData size: 11.7 TB Data #1: Unaligned multi-frame micrographs (40 e-/A2 dose) [micrographs - multiframe] Data #2: unaligned micrographs (60 e-/A2 dose) [micrographs - multiframe]) |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 104632.695 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Fragment: Ectodomain, UNP residues 28-943 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: INSR / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: INSR / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)References: UniProt: P06213-2, receptor protein-tyrosine kinase #2: Protein/peptide | Mass: 2736.106 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Mutation: N21H / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P01308 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P01308#3: Protein/peptide | Mass: 2537.951 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Mutation: H10E, G20L / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P01308 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P01308Has protein modification | Y | Sequence details | Elongated Insulin chain A was modified to contain three additional C-terminal residues (SQL) | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Insulin receptor ectodomain in complex with insulin analog Vh-Ins-HSLQ - asymmetric conformation. Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.209 MDa / Experimental value: NO | |||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 Details: Equal parts HBS(50 mM HEPES pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl ) and TBS (25 mM Tris pH 8.5, 150 mM NaCl) | |||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | |||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 | |||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK II / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 80 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 40 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.19.1_4122: / Classification: refinement | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.4 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 43457 / Symmetry type: POINT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 200.72 Å2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 PDBj
PDBj

















