[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-7ly5: Proteolyzed crystal structure of the bacillamide NRPS, BmdB, in c... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7ly5 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
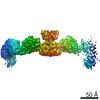
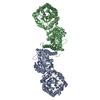
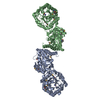
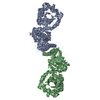
| Title | Proteolyzed crystal structure of the bacillamide NRPS, BmdB, in complex with the oxidase BmdC | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | BIOSYNTHETIC PROTEIN/OXIDOREDUCTASE / Nonribosomal peptide synthetases / Bacillamide / FLAVOPROTEIN / BIOSYNTHETIC PROTEIN / BIOSYNTHETIC PROTEIN-OXIDOREDUCTASE complex | ||||||
| Function / homology | NADH Oxidase / NADH Oxidase / 3-Layer(aba) Sandwich / Alpha Beta / FLAVIN MONONUCLEOTIDE Function and homology information Function and homology information | ||||||
| Biological species |  Thermoactinomyces vulgaris (bacteria) Thermoactinomyces vulgaris (bacteria) | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.5 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.5 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Fortinez, C.M. / Schmeing, T.M. | ||||||
| Funding support |  Canada, 1items Canada, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022Title: Structures and function of a tailoring oxidase in complex with a nonribosomal peptide synthetase module. Authors: Camille Marie Fortinez / Kristjan Bloudoff / Connor Harrigan / Itai Sharon / Mike Strauss / T Martin Schmeing /  Abstract: Nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs) are large modular enzymes that synthesize secondary metabolites and natural product therapeutics. Most NRPS biosynthetic pathways include an NRPS and ...Nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs) are large modular enzymes that synthesize secondary metabolites and natural product therapeutics. Most NRPS biosynthetic pathways include an NRPS and additional proteins that introduce chemical modifications before, during or after assembly-line synthesis. The bacillamide biosynthetic pathway is a common, three-protein system, with a decarboxylase that prepares an NRPS substrate, an NRPS, and an oxidase. Here, the pathway is reconstituted in vitro. The oxidase is shown to perform dehydrogenation of the thiazoline in the peptide intermediate while it is covalently attached to the NRPS, as the penultimate step in bacillamide D synthesis. Structural analysis of the oxidase reveals a dimeric, two-lobed architecture with a remnant RiPP recognition element and a dramatic wrapping loop. The oxidase forms a stable complex with the NRPS and dimerizes it. We visualized co-complexes of the oxidase bound to the elongation module of the NRPS using X-ray crystallography and cryo-EM. The three active sites (for adenylation, condensation/cyclization, and oxidation) form an elegant arc to facilitate substrate delivery. The structures enabled a proof-of-principle bioengineering experiment in which the BmdC oxidase domain is embedded into the NRPS. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7ly5.cif.gz 7ly5.cif.gz | 186.5 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7ly5.ent.gz pdb7ly5.ent.gz | 143.5 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7ly5.json.gz 7ly5.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ly/7ly5 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ly/7ly5 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ly/7ly5 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ly/7ly5 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 
| ||||||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 23143.449 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Thermoactinomyces vulgaris (bacteria) / Production host: Thermoactinomyces vulgaris (bacteria) / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 32135.408 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Thermoactinomyces vulgaris (bacteria) / Production host: Thermoactinomyces vulgaris (bacteria) / Production host:  |
| #3: Chemical | ChemComp-FMN / |
| #4: Water | ChemComp-HOH / |
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.64 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 53.46 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 295.15 K / Method: vapor diffusion, sitting drop Details: 50mM Tris-HCl pH7.5, 160mM KCl and 21% PEG3350 (wt/vol) |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K / Serial crystal experiment: N |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  APS APS  / Beamline: 24-ID-E / Wavelength: 0.979 Å / Beamline: 24-ID-E / Wavelength: 0.979 Å |
| Detector | Type: DECTRIS EIGER X 16M / Detector: PIXEL / Date: Feb 9, 2019 |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 0.979 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 2.5→46.3 Å / Num. obs: 20730 / % possible obs: 99.7 % / Redundancy: 11.7 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 53.54 Å2 / Rpim(I) all: 0.033 / Rrim(I) all: 0.111 / Net I/σ(I): 29.5 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 2.5→2.54 Å / Mean I/σ(I) obs: 2.6 / Num. unique obs: 20730 / CC1/2: 0.933 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: BmdC, oxidase Resolution: 2.5→46.3 Å / SU ML: 0.3077 / Cross valid method: FREE R-VALUE / σ(F): 1.39 / Phase error: 26.4027 Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.11 Å / Solvent model: FLAT BULK SOLVENT MODEL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 65.77 Å2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 2.5→46.3 Å
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller













 PDBj
PDBj