[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
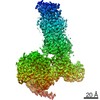
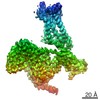
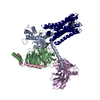
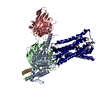
Yorodumi- PDB-7l1u: Orexin Receptor 2 (OX2R) in Complex with G Protein and Natural Pe... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7l1u | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Orexin Receptor 2 (OX2R) in Complex with G Protein and Natural Peptide-Agonist Orexin B (OxB) | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / Class A GPCR / Orexin receptor 2 / OX2R / Peptide agonist | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationtype 1 orexin receptor binding / type 2 orexin receptor binding / regulation of circadian sleep/wake cycle, wakefulness / circadian sleep/wake cycle process / orexin receptor activity / negative regulation of transmission of nerve impulse / positive regulation of transmission of nerve impulse / Orexin and neuropeptides FF and QRFP bind to their respective receptors / neuronal dense core vesicle lumen / neuropeptide receptor activity ...type 1 orexin receptor binding / type 2 orexin receptor binding / regulation of circadian sleep/wake cycle, wakefulness / circadian sleep/wake cycle process / orexin receptor activity / negative regulation of transmission of nerve impulse / positive regulation of transmission of nerve impulse / Orexin and neuropeptides FF and QRFP bind to their respective receptors / neuronal dense core vesicle lumen / neuropeptide receptor activity / regulation of neurotransmitter secretion / neuropeptide hormone activity / positive regulation of calcium ion transport / sleep / feeding behavior / locomotion / response to alcohol / eating behavior / response to starvation / temperature homeostasis / negative regulation of DNA replication / peptide hormone binding / negative regulation of potassium ion transport / regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration / neuropeptide signaling pathway / cellular response to hormone stimulus / rough endoplasmic reticulum / excitatory postsynaptic potential / Olfactory Signaling Pathway / Activation of the phototransduction cascade / G beta:gamma signalling through PLC beta / Presynaptic function of Kainate receptors / Thromboxane signalling through TP receptor / G protein-coupled acetylcholine receptor signaling pathway / Activation of G protein gated Potassium channels / Inhibition of voltage gated Ca2+ channels via Gbeta/gamma subunits / G-protein activation / G beta:gamma signalling through CDC42 / Prostacyclin signalling through prostacyclin receptor / Glucagon signaling in metabolic regulation / synaptic vesicle / G beta:gamma signalling through BTK / Synthesis, secretion, and inactivation of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) / ADP signalling through P2Y purinoceptor 12 / photoreceptor disc membrane / Sensory perception of sweet, bitter, and umami (glutamate) taste / Glucagon-type ligand receptors / Adrenaline,noradrenaline inhibits insulin secretion / Vasopressin regulates renal water homeostasis via Aquaporins / Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP1) regulates insulin secretion / G alpha (z) signalling events / ADP signalling through P2Y purinoceptor 1 / cellular response to catecholamine stimulus / ADORA2B mediated anti-inflammatory cytokines production / G beta:gamma signalling through PI3Kgamma / adenylate cyclase-activating dopamine receptor signaling pathway / Cooperation of PDCL (PhLP1) and TRiC/CCT in G-protein beta folding / GPER1 signaling / G-protein beta-subunit binding / cellular response to prostaglandin E stimulus / heterotrimeric G-protein complex / Inactivation, recovery and regulation of the phototransduction cascade / G alpha (12/13) signalling events / extracellular vesicle / sensory perception of taste / positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis / Thrombin signalling through proteinase activated receptors (PARs) / signaling receptor complex adaptor activity / positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration / retina development in camera-type eye / GTPase binding / Ca2+ pathway / fibroblast proliferation / High laminar flow shear stress activates signaling by PIEZO1 and PECAM1:CDH5:KDR in endothelial cells / G alpha (i) signalling events / G alpha (s) signalling events / phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / G alpha (q) signalling events / chemical synaptic transmission / Ras protein signal transduction / Extra-nuclear estrogen signaling / cell population proliferation / postsynapse / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / lysosomal membrane / GTPase activity / synapse / protein-containing complex binding / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / signal transduction / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / nucleoplasm / membrane / plasma membrane / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Hong, C. / Byrne, N.J. / Zamlynny, B. / Tummala, S. / Xiao, L. / Shipman, J.M. / Partridge, A.T. / Minnick, C. / Breslin, M.J. / Rudd, M.T. ...Hong, C. / Byrne, N.J. / Zamlynny, B. / Tummala, S. / Xiao, L. / Shipman, J.M. / Partridge, A.T. / Minnick, C. / Breslin, M.J. / Rudd, M.T. / Stachel, S.J. / Rada, V.L. / Kern, J.C. / Armacost, K.A. / Hollingsworth, S.A. / O'Brien, J.A. / Hall, D.L. / McDonald, T.P. / Strickland, C. / Brooun, A. / Soisson, S.M. / Hollenstein, K. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2021 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2021Title: Structures of active-state orexin receptor 2 rationalize peptide and small-molecule agonist recognition and receptor activation. Authors: Chuan Hong / Noel J Byrne / Beata Zamlynny / Srivanya Tummala / Li Xiao / Jennifer M Shipman / Andrea T Partridge / Christina Minnick / Michael J Breslin / Michael T Rudd / Shawn J Stachel / ...Authors: Chuan Hong / Noel J Byrne / Beata Zamlynny / Srivanya Tummala / Li Xiao / Jennifer M Shipman / Andrea T Partridge / Christina Minnick / Michael J Breslin / Michael T Rudd / Shawn J Stachel / Vanessa L Rada / Jeffrey C Kern / Kira A Armacost / Scott A Hollingsworth / Julie A O'Brien / Dawn L Hall / Terrence P McDonald / Corey Strickland / Alexei Brooun / Stephen M Soisson / Kaspar Hollenstein /  Abstract: Narcolepsy type 1 (NT1) is a chronic neurological disorder that impairs the brain's ability to control sleep-wake cycles. Current therapies are limited to the management of symptoms with modest ...Narcolepsy type 1 (NT1) is a chronic neurological disorder that impairs the brain's ability to control sleep-wake cycles. Current therapies are limited to the management of symptoms with modest effectiveness and substantial adverse effects. Agonists of the orexin receptor 2 (OXR) have shown promise as novel therapeutics that directly target the pathophysiology of the disease. However, identification of drug-like OXR agonists has proven difficult. Here we report cryo-electron microscopy structures of active-state OXR bound to an endogenous peptide agonist and a small-molecule agonist. The extended carboxy-terminal segment of the peptide reaches into the core of OXR to stabilize an active conformation, while the small-molecule agonist binds deep inside the orthosteric pocket, making similar key interactions. Comparison with antagonist-bound OXR suggests a molecular mechanism that rationalizes both receptor activation and inhibition. Our results enable structure-based discovery of therapeutic orexin agonists for the treatment of NT1 and other hypersomnia disorders. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7l1u.cif.gz 7l1u.cif.gz | 216.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7l1u.ent.gz pdb7l1u.ent.gz | 162.9 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7l1u.json.gz 7l1u.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/l1/7l1u https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/l1/7l1u ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/l1/7l1u ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/l1/7l1u | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 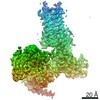 23118MC  7l1vC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 2 types, 2 molecules AR
| #1: Protein | Mass: 28040.881 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #5: Protein | Mass: 43470.875 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HCRTR2 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HCRTR2 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q548Y0, UniProt: O43614*PLUS Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q548Y0, UniProt: O43614*PLUS |
-Guanine nucleotide-binding protein ... , 2 types, 2 molecules BC
| #2: Protein | Mass: 38579.148 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GNB1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GNB1 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P62873 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P62873 |
|---|---|
| #3: Protein | Mass: 7845.078 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GNG2 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GNG2 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P59768 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P59768 |
-Antibody / Protein/peptide , 2 types, 2 molecules HL
| #4: Antibody | Mass: 26610.615 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|---|
| #6: Protein/peptide | Mass: 2902.364 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O43612 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O43612 |
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Orexin Receptor 2 (OX2R) in Complex with G Protein and Natural Peptide-Agonist Orexin B (OxB) Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#5 / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 5 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Details: Carbon side facing up / Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: C-flat | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 105000 X / Calibrated magnification: 59524 X / Nominal defocus max: 1800 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm / Calibrated defocus min: 600 nm / Calibrated defocus max: 2200 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm / Alignment procedure: BASIC |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Temperature (max): 93 K / Temperature (min): 83 K |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 0.05 sec. / Electron dose: 1.0625 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 3 / Num. of real images: 38810 / Details: 40 frames with total 2second exposure |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: GIF Bioquantum / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV |
| Image scans | Sampling size: 5 µm / Width: 5700 / Height: 4100 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 14000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 800000 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Details: Gold standard and masking effect correction / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | B value: 131 / Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL / Space: REAL / Target criteria: Correlation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | 3D fitting-ID: 1 / Accession code: 7L1V / Initial refinement model-ID: 1 / PDB-ID: 7L1V / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj






















