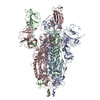
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7jwb | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
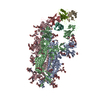
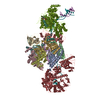
| Title | SARS CoV2 Spike ectodomain with engineered trimerized VH binder | |||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | VIRAL PROTEIN/IMMUNE SYSTEM / Spike / VH / SARS / CoV2 / VIRAL PROTEIN-IMMUNE SYSTEM complex | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationsymbiont-mediated disruption of host tissue / Maturation of spike protein / Translation of Structural Proteins / Virion Assembly and Release / host cell surface / host extracellular space / symbiont-mediated-mediated suppression of host tetherin activity / Induction of Cell-Cell Fusion / structural constituent of virion / membrane fusion ...symbiont-mediated disruption of host tissue / Maturation of spike protein / Translation of Structural Proteins / Virion Assembly and Release / host cell surface / host extracellular space / symbiont-mediated-mediated suppression of host tetherin activity / Induction of Cell-Cell Fusion / structural constituent of virion / membrane fusion / Attachment and Entry / entry receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell / host cell endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / positive regulation of viral entry into host cell / receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell / host cell surface receptor binding / symbiont-mediated suppression of host innate immune response / endocytosis involved in viral entry into host cell / receptor ligand activity / fusion of virus membrane with host plasma membrane / fusion of virus membrane with host endosome membrane / viral envelope / symbiont entry into host cell / virion attachment to host cell / host cell plasma membrane / SARS-CoV-2 activates/modulates innate and adaptive immune responses / virion membrane / membrane / identical protein binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 6 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | QCRG Structural Biology Consortium | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 4items United States, 4items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Chem Biol / Year: 2021 Journal: Nat Chem Biol / Year: 2021Title: Bi-paratopic and multivalent VH domains block ACE2 binding and neutralize SARS-CoV-2. Authors: Colton J Bracken / Shion A Lim / Paige Solomon / Nicholas J Rettko / Duy P Nguyen / Beth Shoshana Zha / Kaitlin Schaefer / James R Byrnes / Jie Zhou / Irene Lui / Jia Liu / Katarina Pance / ...Authors: Colton J Bracken / Shion A Lim / Paige Solomon / Nicholas J Rettko / Duy P Nguyen / Beth Shoshana Zha / Kaitlin Schaefer / James R Byrnes / Jie Zhou / Irene Lui / Jia Liu / Katarina Pance / / Xin X Zhou / Kevin K Leung / James A Wells /  Abstract: Neutralizing agents against SARS-CoV-2 are urgently needed for the treatment and prophylaxis of COVID-19. Here, we present a strategy to rapidly identify and assemble synthetic human variable heavy ...Neutralizing agents against SARS-CoV-2 are urgently needed for the treatment and prophylaxis of COVID-19. Here, we present a strategy to rapidly identify and assemble synthetic human variable heavy (VH) domains toward neutralizing epitopes. We constructed a VH-phage library and targeted the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) binding interface of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike receptor-binding domain (Spike-RBD). Using a masked selection approach, we identified VH binders to two non-overlapping epitopes and further assembled these into multivalent and bi-paratopic formats. These VH constructs showed increased affinity to Spike (up to 600-fold) and neutralization potency (up to 1,400-fold) on pseudotyped SARS-CoV-2 virus when compared to standalone VH domains. The most potent binder, a trivalent VH, neutralized authentic SARS-CoV-2 with a half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC) of 4.0 nM (180 ng ml). A cryo-EM structure of the trivalent VH bound to Spike shows each VH domain engaging an RBD at the ACE2 binding site, confirming our original design strategy. #1: Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2020 Title: Bi-paratopic and multivalent human VH domains neutralize SARS-CoV-2 by targeting distinct epitopes within the ACE2 binding interface of Spike. Authors: Colton J Bracken / Shion A Lim / Paige Solomon / Nicholas J Rettko / Duy P Nguyen / Beth Shoshana Zha / Kaitlin Schaefer / James R Byrnes / Jie Zhou / Irene Lui / Jia Liu / Katarina Pance / ...Authors: Colton J Bracken / Shion A Lim / Paige Solomon / Nicholas J Rettko / Duy P Nguyen / Beth Shoshana Zha / Kaitlin Schaefer / James R Byrnes / Jie Zhou / Irene Lui / Jia Liu / Katarina Pance / / Xin X Zhou / Kevin K Leung / James A Wells /  Abstract: Neutralizing agents against SARS-CoV-2 are urgently needed for treatment and prophylaxis of COVID-19. Here, we present a strategy to rapidly identify and assemble synthetic human variable heavy (VH) ...Neutralizing agents against SARS-CoV-2 are urgently needed for treatment and prophylaxis of COVID-19. Here, we present a strategy to rapidly identify and assemble synthetic human variable heavy (VH) domain binders with high affinity toward neutralizing epitopes without the need for high-resolution structural information. We constructed a VH-phage library and targeted a known neutralizing site, the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) binding interface of the trimeric SARS-CoV-2 Spike receptor-binding domain (Spike-RBD). Using a masked selection approach, we identified 85 unique VH binders to two non-overlapping epitopes within the ACE2 binding site on Spike-RBD. This enabled us to systematically link these VH domains into multivalent and bi-paratopic formats. These multivalent and bi-paratopic VH constructs showed a marked increase in affinity to Spike (up to 600-fold) and neutralization potency (up to 1400-fold) on pseudotyped SARS-CoV-2 virus when compared to the standalone VH domains. The most potent binder, a trivalent VH, neutralized authentic SARS-CoV-2 with half-minimal inhibitory concentration (IC ) of 4.0 nM (180 ng/mL). A cryo-EM structure of the trivalent VH bound to Spike shows each VH domain bound an RBD at the ACE2 binding site, explaining its increased neutralization potency and confirming our original design strategy. Our results demonstrate that targeted selection and engineering campaigns using a VH-phage library can enable rapid assembly of highly avid and potent molecules towards therapeutically important protein interfaces. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7jwb.cif.gz 7jwb.cif.gz | 587 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7jwb.ent.gz pdb7jwb.ent.gz | 472.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7jwb.json.gz 7jwb.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jw/7jwb https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jw/7jwb ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jw/7jwb ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jw/7jwb | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 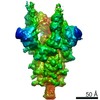 22514MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Antibody | Mass: 44264.402 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Production host:  | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 133753.250 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Mutation: R682G,R683S,R685S,R986P,V987P Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: S, 2 / Production host:  Has protein modification | Y | |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.445 MDa / Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 / Details: 20 mM HEPES, pH 8, 200 mM NaCl | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.9 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 200 divisions/in. / Grid type: UltrAuFoil R1.2/1.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 78 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name:  UCSF Chimera / Category: model fitting UCSF Chimera / Category: model fitting | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Image processing |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Entry-ID: 7JWB / Num. of particles: 21000 / Symmetry type: POINT
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Target criteria: cross correlation | ||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | 3D fitting-ID: 1 / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj