+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7dlr | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Mycobacterium tuberculosis enolase mutant - E163A | ||||||
 Components Components | Enolase | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | LYASE / Mycobacterium tuberculosis / enolase / mutant / complex / PEP | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationphosphopyruvate hydratase / phosphopyruvate hydratase complex / phosphopyruvate hydratase activity / glycolytic process / magnesium ion binding / cell surface / extracellular region Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.25 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.25 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Ahmad, M. / Biswal, B.K. | ||||||
| Funding support |  India, 1items India, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: IUCrJ / Year: 2023 Journal: IUCrJ / Year: 2023Title: Structural snapshots of Mycobacterium tuberculosis enolase reveal dual mode of 2PG binding and its implication in enzyme catalysis. Authors: Mohammed Ahmad / Bhavya Jha / Sucharita Bose / Satish Tiwari / Abhisek Dwivedy / Deepshikha Kar / Ravikant Pal / Richard Mariadasse / Tanya Parish / Jeyaraman Jeyakanthan / Kutti R ...Authors: Mohammed Ahmad / Bhavya Jha / Sucharita Bose / Satish Tiwari / Abhisek Dwivedy / Deepshikha Kar / Ravikant Pal / Richard Mariadasse / Tanya Parish / Jeyaraman Jeyakanthan / Kutti R Vinothkumar / Bichitra Kumar Biswal /   Abstract: Enolase, a ubiquitous enzyme, catalyzes the reversible conversion of 2-phosphoglycerate (2PG) to phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) in the glycolytic pathway of organisms of all three domains of life. The ...Enolase, a ubiquitous enzyme, catalyzes the reversible conversion of 2-phosphoglycerate (2PG) to phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) in the glycolytic pathway of organisms of all three domains of life. The underlying mechanism of the 2PG to PEP conversion has been studied in great detail in previous work, however that of the reverse reaction remains to be explored. Here we present structural snapshots of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) enolase in apo, PEP-bound and two 2PG-bound forms as it catalyzes the conversion of PEP to 2PG. The two 2PG-bound complex structures differed in the conformation of the bound product (2PG) viz the widely reported canonical conformation and a novel binding pose, which we refer to here as the alternate conformation. Notably, we observed two major differences compared with the forward reaction: the presence of Mg is non-obligatory for the reaction and 2PG assumes an alternate conformation that is likely to facilitate its dissociation from the active site. Molecular dynamics studies and binding free energy calculations further substantiate that the alternate conformation of 2PG causes distortions in both metal ion coordination and hydrogen-bonding interactions, resulting in an increased flexibility of the active-site loops and aiding product release. Taken together, this study presents a probable mechanism involved in PEP to 2PG catalysis that is likely to be mediated by the conformational change of 2PG at the active site. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7dlr.cif.gz 7dlr.cif.gz | 175.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7dlr.ent.gz pdb7dlr.ent.gz | 136.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7dlr.json.gz 7dlr.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  7dlr_validation.pdf.gz 7dlr_validation.pdf.gz | 793.3 KB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  7dlr_full_validation.pdf.gz 7dlr_full_validation.pdf.gz | 794.3 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  7dlr_validation.xml.gz 7dlr_validation.xml.gz | 18.6 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  7dlr_validation.cif.gz 7dlr_validation.cif.gz | 26.6 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dl/7dlr https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dl/7dlr ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dl/7dlr ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dl/7dlr | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6l7dC  7ckpC  7clkC  7cllSC  7e4fC  7e4xC  7e51C S: Starting model for refinement C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | x 8
| |||||||||
| Unit cell |
| |||||||||
| Components on special symmetry positions |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 1 types, 1 molecules A
| #1: Protein | Mass: 45904.320 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Mutation: E163A Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: eno, DSI38_18100, ERS007663_02163, ERS013471_01432, ERS024276_01771, ERS027659_01730, ERS075361_03197, ERS094182_03347, F6W99_03724, SAMEA2683035_03102 Production host:  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) / References: UniProt: A0A0E8NV14, phosphopyruvate hydratase Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) / References: UniProt: A0A0E8NV14, phosphopyruvate hydratase |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 7 types, 148 molecules 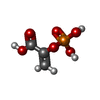










| #2: Chemical | ChemComp-PEP / | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
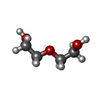
| #3: Chemical | ChemComp-PEG / | ||||||||
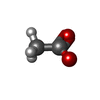
| #4: Chemical | | #5: Chemical | #6: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / | #7: Chemical | #8: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | |
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.5 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 50.88 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 289 K / Method: vapor diffusion, hanging drop Details: 20% PEG 3350, 0.2 M Ammonium acetate, Bis Tris pH 6.5 |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K / Serial crystal experiment: N |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  ROTATING ANODE / Type: RIGAKU FR-E+ SUPERBRIGHT / Wavelength: 1.54178 Å ROTATING ANODE / Type: RIGAKU FR-E+ SUPERBRIGHT / Wavelength: 1.54178 Å |
| Detector | Type: RIGAKU RAXIS IV++ / Detector: IMAGE PLATE / Date: Aug 9, 2020 |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 1.54178 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 2.25→35 Å / Num. obs: 21190 / % possible obs: 98.3 % / Redundancy: 5 % / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.071 / Net I/σ(I): 20.37 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 2.25→2.29 Å / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.563 / Mean I/σ(I) obs: 2.16 / Num. unique obs: 991 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: 7CLL Resolution: 2.25→27.71 Å / Cor.coef. Fo:Fc: 0.962 / Cor.coef. Fo:Fc free: 0.929 / SU B: 13.252 / SU ML: 0.144 / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / σ(F): 0 / ESU R: 0.279 / ESU R Free: 0.213 / Stereochemistry target values: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD Details: HYDROGENS HAVE BEEN ADDED IN THE RIDING POSITIONS U VALUES : WITH TLS ADDED
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Ion probe radii: 0.8 Å / Shrinkage radii: 0.8 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.2 Å / Solvent model: MASK | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso max: 87.85 Å2 / Biso mean: 31.716 Å2 / Biso min: 18.83 Å2
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: final / Resolution: 2.25→27.71 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell | Resolution: 2.254→2.312 Å / Rfactor Rfree error: 0 / Total num. of bins used: 20
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement TLS params. | Method: refined / Origin x: 15.5649 Å / Origin y: -41.2583 Å / Origin z: 3.5431 Å
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 PDBj
PDBj






