+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7d99 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
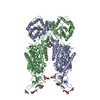
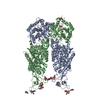
| Title | human potassium-chloride co-transporter KCC4 | ||||||
 Components Components | potassium-chloride co-transporter KCC4 | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSPORT PROTEIN / potassium-chloride / co-transporter | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpotassium:chloride symporter activity / Cation-coupled Chloride cotransporters / chloride ion homeostasis / potassium ion homeostasis / cell volume homeostasis / potassium ion import across plasma membrane / monoatomic ion transport / potassium ion transmembrane transport / chloride transmembrane transport / cellular response to glucose stimulus ...potassium:chloride symporter activity / Cation-coupled Chloride cotransporters / chloride ion homeostasis / potassium ion homeostasis / cell volume homeostasis / potassium ion import across plasma membrane / monoatomic ion transport / potassium ion transmembrane transport / chloride transmembrane transport / cellular response to glucose stimulus / chemical synaptic transmission / synapse / protein kinase binding / protein-containing complex / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
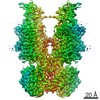
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.9 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Xie, Y. / Chang, S. / Zhao, C. / Ye, S. / Guo, J. | ||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1items China, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2020 Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2020Title: Structures and an activation mechanism of human potassium-chloride cotransporters. Authors: Yuan Xie / Shenghai Chang / Cheng Zhao / Feng Wang / Si Liu / Jin Wang / Eric Delpire / Sheng Ye / Jiangtao Guo /   Abstract: Potassium-chloride cotransporters KCC1 to KCC4 mediate the coupled export of potassium and chloride across the plasma membrane and play important roles in cell volume regulation, auditory system ...Potassium-chloride cotransporters KCC1 to KCC4 mediate the coupled export of potassium and chloride across the plasma membrane and play important roles in cell volume regulation, auditory system function, and γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and glycine-mediated inhibitory neurotransmission. Here, we present 2.9- to 3.6-Å resolution structures of full-length human KCC2, KCC3, and KCC4. All three KCCs adopt a similar overall architecture, a domain-swap dimeric assembly, and an inward-facing conformation. The structural and functional studies reveal that one unexpected N-terminal peptide binds at the cytosolic facing cavity and locks KCC2 and KCC4 at an autoinhibition state. The C-terminal domain (CTD) directly interacts with the N-terminal inhibitory peptide, and the relative motions between the CTD and the transmembrane domain (TMD) suggest that CTD regulates KCCs' activities by adjusting the autoinhibitory effect. These structures provide the first glimpse of full-length structures of KCCs and an autoinhibition mechanism among the amino acid-polyamine-organocation transporter superfamily. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7d99.cif.gz 7d99.cif.gz | 323.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7d99.ent.gz pdb7d99.ent.gz | 252.5 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7d99.json.gz 7d99.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/d9/7d99 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/d9/7d99 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/d9/7d99 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/d9/7d99 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 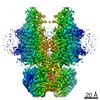 30617MC  7d8zC  7d90C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 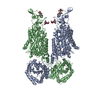
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 123069.492 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: SLC12A7, KCC4 / Cell line (production host): HEK293T / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: SLC12A7, KCC4 / Cell line (production host): HEK293T / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9Y666 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9Y666#2: Polysaccharide | 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source #3: Chemical | #4: Chemical | ChemComp-CL / Has ligand of interest | Y | Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: potassium-chloride cotransporter 4 / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / Cell: HEK293T Homo sapiens (human) / Cell: HEK293T |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 62 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.13_2998: / Classification: refinement |
|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.9 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 95572 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj



