[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
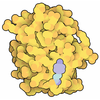
Yorodumi- PDB-7bpy: X-ray structure of human PPARalpha ligand binding domain-clofibri... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7bpy | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | X-ray structure of human PPARalpha ligand binding domain-clofibric acid-SRC1 coactivator peptide co-crystals obtained by delipidation and co-crystallization | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSCRIPTION / Nuclear receptor / Protein-ligand complex / PPAR | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of transformation of host cell by virus / regulation of fatty acid transport / enamel mineralization / positive regulation of fatty acid beta-oxidation / regulation of ketone metabolic process / cellular response to fructose stimulus / negative regulation of cell growth involved in cardiac muscle cell development / regulation of fatty acid metabolic process / negative regulation of appetite / negative regulation of hepatocyte apoptotic process ...positive regulation of transformation of host cell by virus / regulation of fatty acid transport / enamel mineralization / positive regulation of fatty acid beta-oxidation / regulation of ketone metabolic process / cellular response to fructose stimulus / negative regulation of cell growth involved in cardiac muscle cell development / regulation of fatty acid metabolic process / negative regulation of appetite / negative regulation of hepatocyte apoptotic process / positive regulation of fatty acid oxidation / behavioral response to nicotine / lipoprotein metabolic process / negative regulation of leukocyte cell-cell adhesion / : / labyrinthine layer morphogenesis / positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter by galactose / regulation of thyroid hormone receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of female receptivity / negative regulation of glycolytic process / mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase binding / ubiquitin conjugating enzyme binding / NR1H2 & NR1H3 regulate gene expression to control bile acid homeostasis / positive regulation of fatty acid metabolic process / DNA-binding transcription activator activity / NFAT protein binding / male mating behavior / hypothalamus development / negative regulation of cholesterol storage / positive regulation of ATP biosynthetic process / nuclear steroid receptor activity / cellular response to Thyroglobulin triiodothyronine / Synthesis of bile acids and bile salts / negative regulation of macrophage derived foam cell differentiation / progesterone receptor signaling pathway / protein-lysine-acetyltransferase activity / epidermis development / Synthesis of bile acids and bile salts via 27-hydroxycholesterol / Endogenous sterols / Synthesis of bile acids and bile salts via 7alpha-hydroxycholesterol / response to retinoic acid / estrous cycle / positive regulation of lipid biosynthetic process / nuclear retinoid X receptor binding / phosphatase binding / RORA,B,C and NR1D1 (REV-ERBA) regulate gene expression / Transcriptional regulation of brown and beige adipocyte differentiation by EBF2 / Expression of BMAL (ARNTL), CLOCK, and NPAS2 / Recycling of bile acids and salts / histone acetyltransferase / cellular response to hormone stimulus / NR1H3 & NR1H2 regulate gene expression linked to cholesterol transport and efflux / : / negative regulation of blood pressure / estrogen receptor signaling pathway / intracellular receptor signaling pathway / negative regulation of reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process / nitric oxide metabolic process / lactation / positive regulation of adipose tissue development / Regulation of lipid metabolism by PPARalpha / hormone-mediated signaling pathway / peroxisome proliferator activated receptor signaling pathway / negative regulation of cytokine production involved in inflammatory response / positive regulation of neuron differentiation / regulation of cellular response to insulin stimulus / response to nutrient / MDM2/MDM4 family protein binding / BMAL1:CLOCK,NPAS2 activates circadian expression / positive regulation of gluconeogenesis / SUMOylation of transcription cofactors / Activation of gene expression by SREBF (SREBP) / response to progesterone / negative regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signal transduction / negative regulation of miRNA transcription / cerebellum development / cellular response to starvation / nuclear estrogen receptor binding / nuclear receptor binding / gluconeogenesis / RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding / hippocampus development / SUMOylation of intracellular receptors / circadian regulation of gene expression / negative regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway / wound healing / Heme signaling / PPARA activates gene expression / Transcriptional activation of mitochondrial biogenesis / Cytoprotection by HMOX1 / fatty acid metabolic process / regulation of circadian rhythm / cerebral cortex development / Nuclear Receptor transcription pathway / Transcriptional regulation of white adipocyte differentiation / mRNA transcription by RNA polymerase II / response to insulin / negative regulation of inflammatory response / DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific / RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT /  molecular replacement / Resolution: 2.09 Å molecular replacement / Resolution: 2.09 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Kamata, S. / Ishikawa, R. / Akahane, M. / Oyama, T. / Ishii, I. | ||||||
| Funding support |  Japan, 1items Japan, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Iscience / Year: 2020 Journal: Iscience / Year: 2020Title: PPAR alpha Ligand-Binding Domain Structures with Endogenous Fatty Acids and Fibrates. Authors: Kamata, S. / Oyama, T. / Saito, K. / Honda, A. / Yamamoto, Y. / Suda, K. / Ishikawa, R. / Itoh, T. / Watanabe, Y. / Shibata, T. / Uchida, K. / Suematsu, M. / Ishii, I. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7bpy.cif.gz 7bpy.cif.gz | 128.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7bpy.ent.gz pdb7bpy.ent.gz | 99 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7bpy.json.gz 7bpy.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bp/7bpy https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bp/7bpy ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bp/7bpy ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bp/7bpy | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6kaxC  6kayC  6kazC  6kb0C  6kb1C  6kb2C  6kb3C  6kb4C  6kb5C  6kb6C  6kb7C  6kb8C  6kb9C  6kbaC  6kypC  6l36C  6l37C  6l38C  6lx4C  6lx5C  6lx6C  6lx7C  6lx8C  6lx9C  6lxaC  6lxbC  6lxcC  7bpzC  7bq0C  7bq1C  7bq2C  7bq3C  7bq4C  3sp6S S: Starting model for refinement C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 
| ||||||||
| 2 | 
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
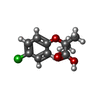
| #1: Protein | Mass: 30856.053 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Plasmid: pET28a / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Plasmid: pET28a / Production host:  #2: Protein/peptide | Mass: 1848.177 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q15788, histone acetyltransferase Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q15788, histone acetyltransferase#3: Chemical | ChemComp-E0O / #4: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | Has ligand of interest | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.83 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 56.51 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 277 K / Method: vapor diffusion / Details: 0.1 M Tris (pH 8.5), 30 %(w/v) PEG3350 |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K / Serial crystal experiment: N | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  Photon Factory Photon Factory  / Beamline: BL-17A / Wavelength: 1 Å / Beamline: BL-17A / Wavelength: 1 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Detector | Type: DECTRIS EIGER X 16M / Detector: PIXEL / Date: Mar 7, 2020 / Details: Mirrors | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Radiation | Monochromator: Si(111) / Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 1 Å / Relative weight: 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reflection | Resolution: 2.09→47.32 Å / Num. obs: 42307 / % possible obs: 98.3 % / Redundancy: 3.5 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 30.46 Å2 / CC1/2: 0.999 / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.042 / Rpim(I) all: 0.026 / Rrim(I) all: 0.049 / Net I/σ(I): 19.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reflection shell | Diffraction-ID: 1
|
-Phasing
| Phasing | Method:  molecular replacement molecular replacement | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phasing MR |
|
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: 3SP6 Resolution: 2.09→38.576 Å / SU ML: 0.25 / Cross valid method: FREE R-VALUE / σ(F): 1.94 / Phase error: 23.02 Details: SF FILE CONTAINS FRIEDEL PAIRS UNDER I/F_MINUS AND I/F_PLUS COLUMNS.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.11 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso max: 95.12 Å2 / Biso mean: 36.8841 Å2 / Biso min: 17.01 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: final / Resolution: 2.09→38.576 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell | Refine-ID: X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Rfactor Rfree error: 0
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 PDBj
PDBj