+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6zfp | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
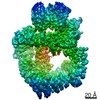
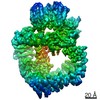
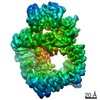
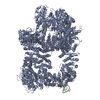
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of DNA-PKcs (State 2) | ||||||
 Components Components | DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit,DNA-PKcs,DNA-PKcs | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | DNA BINDING PROTEIN / Kinase / DNA-PKcs / NHEJ / DNA-repair / DNA-PK | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of platelet formation / T cell receptor V(D)J recombination / pro-B cell differentiation / DNA-dependent protein kinase activity / small-subunit processome assembly / positive regulation of lymphocyte differentiation / histone H2AXS139 kinase activity / DNA-dependent protein kinase complex / DNA-dependent protein kinase-DNA ligase 4 complex / immunoglobulin V(D)J recombination ...positive regulation of platelet formation / T cell receptor V(D)J recombination / pro-B cell differentiation / DNA-dependent protein kinase activity / small-subunit processome assembly / positive regulation of lymphocyte differentiation / histone H2AXS139 kinase activity / DNA-dependent protein kinase complex / DNA-dependent protein kinase-DNA ligase 4 complex / immunoglobulin V(D)J recombination / nonhomologous end joining complex / immature B cell differentiation / regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation / regulation of epithelial cell proliferation / double-strand break repair via alternative nonhomologous end joining / Cytosolic sensors of pathogen-associated DNA / telomere capping / IRF3-mediated induction of type I IFN / regulation of hematopoietic stem cell differentiation / U3 snoRNA binding / T cell lineage commitment / maturation of 5.8S rRNA / positive regulation of double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining / B cell lineage commitment / negative regulation of cGAS/STING signaling pathway / peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation / negative regulation of protein phosphorylation / somitogenesis / ectopic germ cell programmed cell death / mitotic G1 DNA damage checkpoint signaling / activation of innate immune response / positive regulation of erythrocyte differentiation / telomere maintenance / positive regulation of translation / response to gamma radiation / protein modification process / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / small-subunit processome / peptidyl-serine phosphorylation / protein-DNA complex / regulation of circadian rhythm / brain development / double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining / protein destabilization / cellular response to insulin stimulus / intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage / T cell differentiation in thymus / rhythmic process / double-strand break repair / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / heart development / double-stranded DNA binding / transcription regulator complex / RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding / protein phosphorylation / chromosome, telomeric region / protein kinase activity / non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase / positive regulation of apoptotic process / protein domain specific binding / innate immune response / protein serine kinase activity / protein serine/threonine kinase activity / DNA damage response / negative regulation of apoptotic process / chromatin / nucleolus / enzyme binding / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / protein-containing complex / RNA binding / nucleoplasm / ATP binding / membrane / nucleus / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.24 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Chaplin, A.K. / Hardwick, S.W. / Chirgadze, D.Y. / Blundell, T.L. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 1items United Kingdom, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2021 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2021Title: Dimers of DNA-PK create a stage for DNA double-strand break repair. Authors: Amanda K Chaplin / Steven W Hardwick / Shikang Liang / Antonia Kefala Stavridi / Ales Hnizda / Lee R Cooper / Taiana Maia De Oliveira / Dimitri Y Chirgadze / Tom L Blundell /  Abstract: DNA double-strand breaks are the most dangerous type of DNA damage and, if not repaired correctly, can lead to cancer. In humans, Ku70/80 recognizes DNA broken ends and recruits the DNA-dependent ...DNA double-strand breaks are the most dangerous type of DNA damage and, if not repaired correctly, can lead to cancer. In humans, Ku70/80 recognizes DNA broken ends and recruits the DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit (DNA-PKcs) to form DNA-dependent protein kinase holoenzyme (DNA-PK) in the process of non-homologous end joining (NHEJ). We present a 2.8-Å-resolution cryo-EM structure of DNA-PKcs, allowing precise amino acid sequence registration in regions uninterpreted in previous 4.3-Å X-ray maps. We also report a cryo-EM structure of DNA-PK at 3.5-Å resolution and reveal a dimer mediated by the Ku80 C terminus. Central to dimer formation is a domain swap of the conserved C-terminal helix of Ku80. Our results suggest a new mechanism for NHEJ utilizing a DNA-PK dimer to bring broken DNA ends together. Furthermore, drug inhibition of NHEJ in combination with chemo- and radiotherapy has proved successful, making these models central to structure-based drug targeting efforts. #1:  Journal: Nat.Struct.Mol.Biol. / Year: 2020 Journal: Nat.Struct.Mol.Biol. / Year: 2020Title: Dimers of DNA-PK create a stage for DNA-double strand break repair Authors: Chaplin, A.K. / Hardwick, S.W. / Liang, S. / Stavridi, A.K. / Hnizda, A. / Cooper, L.R. / De Oliveira, T.M. / Chirgadze, D.Y. / Blundell, T.L. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6zfp.cif.gz 6zfp.cif.gz | 654.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6zfp.ent.gz pdb6zfp.ent.gz | 527.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6zfp.json.gz 6zfp.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zf/6zfp https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zf/6zfp ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zf/6zfp ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zf/6zfp | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  11185MC  6zh2C  6zh4C  6zh6C  6zh8C  6zhaC  6zheC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 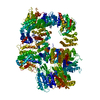
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 472056.281 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PRKDC, HYRC, HYRC1 Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PRKDC, HYRC, HYRC1Production host: Insect cell expression vector pTIE1 (others) References: UniProt: P78527, non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: DNA-PKcs / Type: ORGANELLE OR CELLULAR COMPONENT / Entity ID: all / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.47 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.6 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 53.95 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 378084 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.24 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 80688 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj



