+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6ykp | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
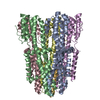
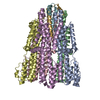
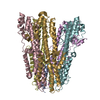
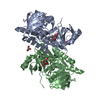
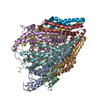
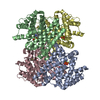
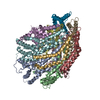
| Title | Structure of unplugged C. jejuni MotAB | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / Bacterial flagellar motor / stator unit / locomotion / proton transport / ion transport | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationbacterial-type flagellum-dependent swarming motility / chemotaxis / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Campylobacter jejuni subsp. jejuni serotype O:23/36 (Campylobacter) Campylobacter jejuni subsp. jejuni serotype O:23/36 (Campylobacter) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.98 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Santiveri, M. / Roa-Eguiara, A. / Taylor, N.M.I. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Denmark, 2items Denmark, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell / Year: 2020 Journal: Cell / Year: 2020Title: Structure and Function of Stator Units of the Bacterial Flagellar Motor. Authors: Mònica Santiveri / Aritz Roa-Eguiara / Caroline Kühne / Navish Wadhwa / Haidai Hu / Howard C Berg / Marc Erhardt / Nicholas M I Taylor /    Abstract: Many bacteria use the flagellum for locomotion and chemotaxis. Its bidirectional rotation is driven by a membrane-embedded motor, which uses energy from the transmembrane ion gradient to generate ...Many bacteria use the flagellum for locomotion and chemotaxis. Its bidirectional rotation is driven by a membrane-embedded motor, which uses energy from the transmembrane ion gradient to generate torque at the interface between stator units and rotor. The structural organization of the stator unit (MotAB), its conformational changes upon ion transport, and how these changes power rotation of the flagellum remain unknown. Here, we present ~3 Å-resolution cryoelectron microscopy reconstructions of the stator unit in different functional states. We show that the stator unit consists of a dimer of MotB surrounded by a pentamer of MotA. Combining structural data with mutagenesis and functional studies, we identify key residues involved in torque generation and present a detailed mechanistic model for motor function and switching of rotational direction. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6ykp.cif.gz 6ykp.cif.gz | 238.8 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6ykp.ent.gz pdb6ykp.ent.gz | 188 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6ykp.json.gz 6ykp.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/yk/6ykp https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/yk/6ykp ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/yk/6ykp ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/yk/6ykp | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 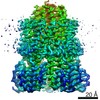 10829MC  6ykmC  6ykrC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 28195.816 Da / Num. of mol.: 5 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Campylobacter jejuni subsp. jejuni serotype O:23/36 (strain 81-176) (Campylobacter) Campylobacter jejuni subsp. jejuni serotype O:23/36 (strain 81-176) (Campylobacter)Strain: 81-176 / Gene: CJJ81176_0359 / Production host:  #2: Protein | Mass: 29863.627 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Mutation: Deletion of aminoacids 41 to 60 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Campylobacter jejuni subsp. jejuni serotype O:23/36 (strain 81-176) (Campylobacter) Campylobacter jejuni subsp. jejuni serotype O:23/36 (strain 81-176) (Campylobacter)Strain: 81-176 / Gene: CJJ81176_0358 / Production host:  #3: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Stator unit MotAB(Delta41-60) / Type: COMPLEX Details: The stator unit consists of a dimer of MotB surrounded by a pentamer of MotA. This stator unit is unplugged (deletion of aminoacids 41 to 60 of MotB). Entity ID: #1-#2 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Campylobacter jejuni subsp. jejuni 81-176 (Campylobacter) Campylobacter jejuni subsp. jejuni 81-176 (Campylobacter) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.75 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid type: Quantifoil R2/1 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 42.51 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: cryoSPARC / Category: 3D reconstruction | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.98 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 329503 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 74.45 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj
