[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-6x0m: Bridging of double-strand DNA break activates PARP2/HPF1 to modif... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6x0m | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
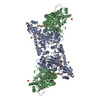
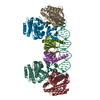
| Title | Bridging of double-strand DNA break activates PARP2/HPF1 to modify chromatin | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | GENE REGULATION / DNA repair / PARP1 / PARP2 / HPF1 / ADP-ribosylation / chromatin / histone modifications | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of protein ADP-ribosylation / protein ADP-ribosyltransferase-substrate adaptor activity / response to oxygen-glucose deprivation / hippocampal neuron apoptotic process / poly-ADP-D-ribose binding / positive regulation of cell growth involved in cardiac muscle cell development / NAD+-protein-serine ADP-ribosyltransferase activity / NAD DNA ADP-ribosyltransferase activity / DNA ADP-ribosylation / poly-ADP-D-ribose modification-dependent protein binding ...regulation of protein ADP-ribosylation / protein ADP-ribosyltransferase-substrate adaptor activity / response to oxygen-glucose deprivation / hippocampal neuron apoptotic process / poly-ADP-D-ribose binding / positive regulation of cell growth involved in cardiac muscle cell development / NAD+-protein-serine ADP-ribosyltransferase activity / NAD DNA ADP-ribosyltransferase activity / DNA ADP-ribosylation / poly-ADP-D-ribose modification-dependent protein binding / HDR through MMEJ (alt-NHEJ) / NAD+ ADP-ribosyltransferase / protein auto-ADP-ribosylation / NAD+-protein-aspartate ADP-ribosyltransferase activity / protein poly-ADP-ribosylation / NAD+-protein-glutamate ADP-ribosyltransferase activity / DNA repair-dependent chromatin remodeling / NAD+-protein mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase activity / decidualization / Transferases; Glycosyltransferases; Pentosyltransferases / POLB-Dependent Long Patch Base Excision Repair / site of DNA damage / NAD+ poly-ADP-ribosyltransferase activity / nucleosome binding / extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / nucleotidyltransferase activity / base-excision repair / DNA Damage Recognition in GG-NER / Dual Incision in GG-NER / Formation of Incision Complex in GG-NER / double-strand break repair / histone binding / damaged DNA binding / DNA repair / DNA damage response / chromatin binding / chromatin / nucleolus / nucleoplasm / nucleus / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)synthetic construct (others) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
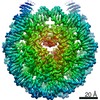
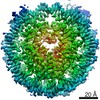
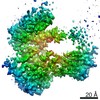
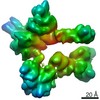
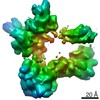
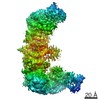
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 6.3 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Halic, M. / Bilokapic, S. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2020 Journal: Nature / Year: 2020Title: Bridging of DNA breaks activates PARP2-HPF1 to modify chromatin. Authors: Silvija Bilokapic / Marcin J Suskiewicz / Ivan Ahel / Mario Halic /   Abstract: Breaks in DNA strands recruit the protein PARP1 and its paralogue PARP2 to modify histones and other substrates through the addition of mono- and poly(ADP-ribose) (PAR). In the DNA damage responses, ...Breaks in DNA strands recruit the protein PARP1 and its paralogue PARP2 to modify histones and other substrates through the addition of mono- and poly(ADP-ribose) (PAR). In the DNA damage responses, this post-translational modification occurs predominantly on serine residues and requires HPF1, an accessory factor that switches the amino acid specificity of PARP1 and PARP2 from aspartate or glutamate to serine. Poly(ADP) ribosylation (PARylation) is important for subsequent chromatin decompaction and provides an anchor for the recruitment of downstream signalling and repair factors to the sites of DNA breaks. Here, to understand the molecular mechanism by which PARP enzymes recognize DNA breaks within chromatin, we determined the cryo-electron-microscopic structure of human PARP2-HPF1 bound to a nucleosome. This showed that PARP2-HPF1 bridges two nucleosomes, with the broken DNA aligned in a position suitable for ligation, revealing the initial step in the repair of double-strand DNA breaks. The bridging induces structural changes in PARP2 that signal the recognition of a DNA break to the catalytic domain, which licenses HPF1 binding and PARP2 activation. Our data suggest that active PARP2 cycles through different conformational states to exchange NAD and substrate, which may enable PARP enzymes to act processively while bound to chromatin. The processes of PARP activation and the PARP catalytic cycle we describe can explain mechanisms of resistance to PARP inhibitors and will aid the development of better inhibitors as cancer treatments. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6x0m.cif.gz 6x0m.cif.gz | 306.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6x0m.ent.gz pdb6x0m.ent.gz | 231.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6x0m.json.gz 6x0m.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/x0/6x0m https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/x0/6x0m ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/x0/6x0m ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/x0/6x0m | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 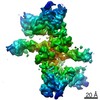 21979MC  6wz5C  6wz9C  6x0lC  6x0nC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 40598.293 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HPF1, C4orf27 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HPF1, C4orf27 / Production host:  #2: Protein | Mass: 67072.500 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PARP2, ADPRT2, ADPRTL2 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PARP2, ADPRT2, ADPRTL2 / Production host:  References: UniProt: Q9UGN5, NAD+ ADP-ribosyltransferase, Transferases; Glycosyltransferases; Pentosyltransferases #3: DNA chain | Mass: 51776.004 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.) synthetic construct (others) / Production host:  #4: DNA chain | Mass: 51330.684 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.) synthetic construct (others) / Production host:  Has protein modification | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.1 MDa / Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.1 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS | |||||||||||||||
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM | |||||||||||||||
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD | |||||||||||||||
| Image recording |
|
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.17.1_3660: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 934000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 6.3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 16000 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj






































