[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
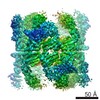
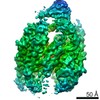
Yorodumi- PDB-6wxg: Cryo-EM reconstruction of VP5*/VP8* assembly from rhesus rotaviru... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6wxg | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM reconstruction of VP5*/VP8* assembly from rhesus rotavirus particles - Reversed conformation | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | VIRAL PROTEIN / Complex / non-enveloped virus / viral particle / entry / membrane-penetration / rotavirus / VP4 / VP5* / VP8* | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationviral intermediate capsid / host cell endoplasmic reticulum lumen / host cell rough endoplasmic reticulum / permeabilization of host organelle membrane involved in viral entry into host cell / T=13 icosahedral viral capsid / host cytoskeleton / viral outer capsid / host cell endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment / receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell / host cell surface receptor binding ...viral intermediate capsid / host cell endoplasmic reticulum lumen / host cell rough endoplasmic reticulum / permeabilization of host organelle membrane involved in viral entry into host cell / T=13 icosahedral viral capsid / host cytoskeleton / viral outer capsid / host cell endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment / receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell / host cell surface receptor binding / fusion of virus membrane with host plasma membrane / viral envelope / virion attachment to host cell / host cell plasma membrane / structural molecule activity / metal ion binding / membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Rotavirus A Rotavirus A | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.3 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Herrmann, T. / Harrison, S.C. / Jenni, S. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2021 Journal: Nature / Year: 2021Title: Functional refolding of the penetration protein on a non-enveloped virus. Authors: Tobias Herrmann / Raúl Torres / Eric N Salgado / Cristina Berciu / Daniel Stoddard / Daniela Nicastro / Simon Jenni / Stephen C Harrison /  Abstract: A non-enveloped virus requires a membrane lesion to deliver its genome into a target cell. For rotaviruses, membrane perforation is a principal function of the viral outer-layer protein, VP4. Here we ...A non-enveloped virus requires a membrane lesion to deliver its genome into a target cell. For rotaviruses, membrane perforation is a principal function of the viral outer-layer protein, VP4. Here we describe the use of electron cryomicroscopy to determine how VP4 performs this function and show that when activated by cleavage to VP8* and VP5*, VP4 can rearrange on the virion surface from an 'upright' to a 'reversed' conformation. The reversed structure projects a previously buried 'foot' domain outwards into the membrane of the host cell to which the virion has attached. Electron cryotomograms of virus particles entering cells are consistent with this picture. Using a disulfide mutant of VP4, we have also stabilized a probable intermediate in the transition between the two conformations. Our results define molecular mechanisms for the first steps of the penetration of rotaviruses into the membranes of target cells and suggest similarities with mechanisms postulated for other viruses. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6wxg.cif.gz 6wxg.cif.gz | 4 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6wxg.ent.gz pdb6wxg.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6wxg.json.gz 6wxg.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wx/6wxg https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wx/6wxg ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wx/6wxg ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wx/6wxg | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  21957MC  6wxeC  6wxfC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 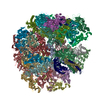
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 86655.586 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Rotavirus A (strain RVA/Monkey/United States/RRV/1975/G3P5B[3]) Rotavirus A (strain RVA/Monkey/United States/RRV/1975/G3P5B[3])Strain: RVA/Monkey/United States/RRV/1975/G3P5B[3] / Cell line (production host): Sf9 / Production host:  #2: Protein | Mass: 44934.766 Da / Num. of mol.: 18 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Rotavirus A (strain RVA/Monkey/United States/RRV/1975/G3P5B[3]) Rotavirus A (strain RVA/Monkey/United States/RRV/1975/G3P5B[3])Strain: RVA/Monkey/United States/RRV/1975/G3P5B[3] / Cell line (production host): Sf9 / Production host:  #3: Protein | Mass: 37136.531 Da / Num. of mol.: 18 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Rotavirus A (strain RVA/Monkey/United States/RRV/1975/G3P5B[3]) Rotavirus A (strain RVA/Monkey/United States/RRV/1975/G3P5B[3])Strain: RVA/Monkey/United States/RRV/1975/G3P5B[3] / Cell line (production host): Sf9 / Production host:  #4: Sugar | ChemComp-NAG / #5: Chemical | ChemComp-CA / Has ligand of interest | N | Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Rotavirus VP4, VP6, VP7 assembly in the foldback conformation Type: COMPLEX Details: Obtained from wild-type recoated rhesus rotavirus particles (wt rcTLP) Entity ID: #1-#3 / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 1.7 MDa / Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Rotavirus A (strain RVA/Monkey/United States/RRV/1975/G3P5B[3]) Rotavirus A (strain RVA/Monkey/United States/RRV/1975/G3P5B[3]) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 1.2 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 400 divisions/in. / Grid type: C-flat-1.2/1.3 4C | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: GATAN CRYOPLUNGE 3 / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 90 % / Chamber temperature: 298.15 K / Details: 4 ul sample volume, 4 sec blotting time |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai Polara / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI POLARA 300 |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 27500 X / Calibrated magnification: 40605 X / Nominal defocus max: 3000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm / Calibrated defocus min: 1000 nm / Calibrated defocus max: 3000 nm / Cs: 2 mm / Alignment procedure: BASIC |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 10 sec. / Electron dose: 33 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 4107 |
| Image scans | Width: 3838 / Height: 3701 / Movie frames/image: 50 / Used frames/image: 1-50 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 14579 / Details: whole viral particles | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 252548 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE Details: Reconstruction final map after classification of VP4 sub-particles . VP4 sub-particles extracted from viral particles (60 VP4 sub-particles per viral particle) Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: OTHER / Details: phenix.real_space_refine | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 17.97 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj











