+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6wvv | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
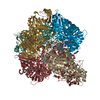
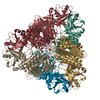
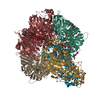
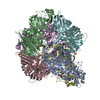
| Title | Plasmodium vivax M17 leucyl aminopeptidase | ||||||
 Components Components | M17 leucyl aminopeptidase | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | HYDROLASE / M17 Leucyl Aminopeptidase / Metalloprotease | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationHydrolases; Acting on peptide bonds (peptidases); Dipeptidases / leucyl aminopeptidase / metallodipeptidase activity / peptide catabolic process / metalloaminopeptidase activity / manganese ion binding / proteolysis / zinc ion binding / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.33 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.33 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Malcolm, T.R. / Drinkwater, N. / McGowan, S. | ||||||
| Funding support |  Australia, 1items Australia, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2021 Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2021Title: Active site metals mediate an oligomeric equilibrium in Plasmodium M17 aminopeptidases. Authors: Tess R Malcolm / Matthew J Belousoff / Hariprasad Venugopal / Natalie A Borg / Nyssa Drinkwater / Sarah C Atkinson / Sheena McGowan /  Abstract: M17 leucyl aminopeptidases are metal-dependent exopeptidases that rely on oligomerization to diversify their functional roles. The M17 aminopeptidases from Plasmodium falciparum (PfA-M17) and ...M17 leucyl aminopeptidases are metal-dependent exopeptidases that rely on oligomerization to diversify their functional roles. The M17 aminopeptidases from Plasmodium falciparum (PfA-M17) and Plasmodium vivax (Pv-M17) function as catalytically active hexamers to generate free amino acids from human hemoglobin and are drug targets for the design of novel antimalarial agents. However, the molecular basis for oligomeric assembly is not fully understood. In this study, we found that the active site metal ions essential for catalytic activity have a secondary structural role mediating the formation of active hexamers. We found that PfA-M17 and Pv-M17 exist in a metal-dependent dynamic equilibrium between active hexameric species and smaller inactive species that can be controlled by manipulating the identity and concentration of metals available. Mutation of residues involved in metal ion binding impaired catalytic activity and the formation of active hexamers. Structural resolution of Pv-M17 by cryoelectron microscopy and X-ray crystallography together with solution studies revealed that PfA-M17 and Pv-M17 bind metal ions and substrates in a conserved fashion, although Pv-M17 forms the active hexamer more readily and processes substrates faster than PfA-M17. On the basis of these studies, we propose a dynamic equilibrium between monomer ↔ dimer ↔ tetramer ↔ hexamer, which becomes directional toward the large oligomeric states with the addition of metal ions. This sophisticated metal-dependent dynamic equilibrium may apply to other M17 aminopeptidases and underpin the moonlighting capabilities of this enzyme family. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6wvv.cif.gz 6wvv.cif.gz | 2.4 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6wvv.ent.gz pdb6wvv.ent.gz | 1.6 MB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6wvv.json.gz 6wvv.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wv/6wvv https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wv/6wvv ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wv/6wvv ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wv/6wvv | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7k5kC  3kqzS S: Starting model for refinement C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 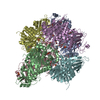
| ||||||||||||
| 2 | 
| ||||||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 1 types, 12 molecules ABCDEFGHIJKL
| #1: Protein | Mass: 58270.199 Da / Num. of mol.: 12 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: PVC01_120064700, PVP01_1260800 / Production host:  References: UniProt: A0A1G4HHP8, UniProt: A5K3U9*PLUS, leucyl aminopeptidase |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 5 types, 1525 molecules 
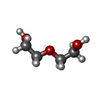







| #2: Chemical | ChemComp-GOL / #3: Chemical | ChemComp-PEG / #4: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / #5: Chemical | ChemComp-SO4 / #6: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.69 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 54.36 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 298 K / Method: vapor diffusion, hanging drop / pH: 6.5 / Details: 17% PEG 3350, 0.1 M HEPES pH 6.5, 0.15 M (NH4)2SO4 |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K / Serial crystal experiment: N |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  Australian Synchrotron Australian Synchrotron  / Beamline: MX2 / Wavelength: 0.9537 Å / Beamline: MX2 / Wavelength: 0.9537 Å |
| Detector | Type: DECTRIS EIGER X 16M / Detector: PIXEL / Date: Mar 28, 2019 |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 0.9537 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 2.29→48.95 Å / Num. obs: 327356 / % possible obs: 99.7 % / Redundancy: 4.5 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 35.02 Å2 / CC1/2: 0.992 / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.154 / Rpim(I) all: 0.081 / Rrim(I) all: 0.174 / Χ2: 0.54 / Net I/σ(I): 5.9 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 2.29→2.33 Å / Redundancy: 4 % / Num. unique obs: 15478 / CC1/2: 0.408 / % possible all: 95.3 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: 3KQZ Resolution: 2.33→44.32 Å / SU ML: 0.2867 / Cross valid method: FREE R-VALUE / σ(F): 1.34 / Phase error: 24.4933 Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.11 Å / Solvent model: FLAT BULK SOLVENT MODEL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 42.35 Å2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 2.33→44.32 Å
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj



