+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-22682 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
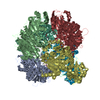
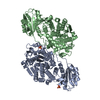
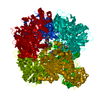
| Title | Plasmodium vivax M17 leucyl aminopeptidase Pv-M17 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Plasmodium vivax M17 leucyl aminopeptidase Pv-M17 | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | M17 aminopeptidase / leucyl aminopeptidase / HYDROLASE | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationHydrolases; Acting on peptide bonds (peptidases); Dipeptidases / leucyl aminopeptidase / metallodipeptidase activity / peptide catabolic process / metalloaminopeptidase activity / manganese ion binding / proteolysis / zinc ion binding / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
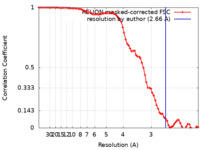
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.66 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Malcolm TR / McGowan S | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Australia, 1 items Australia, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2021 Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2021Title: Active site metals mediate an oligomeric equilibrium in Plasmodium M17 aminopeptidases. Authors: Tess R Malcolm / Matthew J Belousoff / Hariprasad Venugopal / Natalie A Borg / Nyssa Drinkwater / Sarah C Atkinson / Sheena McGowan /  Abstract: M17 leucyl aminopeptidases are metal-dependent exopeptidases that rely on oligomerization to diversify their functional roles. The M17 aminopeptidases from Plasmodium falciparum (PfA-M17) and ...M17 leucyl aminopeptidases are metal-dependent exopeptidases that rely on oligomerization to diversify their functional roles. The M17 aminopeptidases from Plasmodium falciparum (PfA-M17) and Plasmodium vivax (Pv-M17) function as catalytically active hexamers to generate free amino acids from human hemoglobin and are drug targets for the design of novel antimalarial agents. However, the molecular basis for oligomeric assembly is not fully understood. In this study, we found that the active site metal ions essential for catalytic activity have a secondary structural role mediating the formation of active hexamers. We found that PfA-M17 and Pv-M17 exist in a metal-dependent dynamic equilibrium between active hexameric species and smaller inactive species that can be controlled by manipulating the identity and concentration of metals available. Mutation of residues involved in metal ion binding impaired catalytic activity and the formation of active hexamers. Structural resolution of Pv-M17 by cryoelectron microscopy and X-ray crystallography together with solution studies revealed that PfA-M17 and Pv-M17 bind metal ions and substrates in a conserved fashion, although Pv-M17 forms the active hexamer more readily and processes substrates faster than PfA-M17. On the basis of these studies, we propose a dynamic equilibrium between monomer ↔ dimer ↔ tetramer ↔ hexamer, which becomes directional toward the large oligomeric states with the addition of metal ions. This sophisticated metal-dependent dynamic equilibrium may apply to other M17 aminopeptidases and underpin the moonlighting capabilities of this enzyme family. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_22682.map.gz emd_22682.map.gz | 5.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-22682-v30.xml emd-22682-v30.xml emd-22682.xml emd-22682.xml | 24.9 KB 24.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
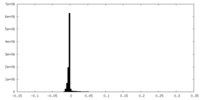
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_22682_fsc.xml emd_22682_fsc.xml | 7.7 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_22682.png emd_22682.png | 66 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_22682_msk_1.map emd_22682_msk_1.map | 38.4 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-22682.cif.gz emd-22682.cif.gz | 6.9 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_22682_additional_1.map.gz emd_22682_additional_1.map.gz emd_22682_additional_2.map.gz emd_22682_additional_2.map.gz emd_22682_half_map_1.map.gz emd_22682_half_map_1.map.gz emd_22682_half_map_2.map.gz emd_22682_half_map_2.map.gz | 25.1 MB 29.4 MB 29.4 MB 29.4 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22682 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22682 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22682 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22682 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 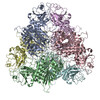 7k5kMC  6wvvC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_22682.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 38.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_22682.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 38.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Plasmodium vivax M17 leucyl aminopeptidase Pv-M17 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.06 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
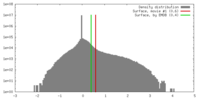
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_22682_msk_1.map emd_22682_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
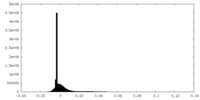
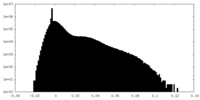
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: Local resolution map
| File | emd_22682_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Local resolution map | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: Unfiltered map
| File | emd_22682_additional_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Unfiltered map | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: half-volume 1
| File | emd_22682_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | half-volume 1 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: half-volume 2
| File | emd_22682_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | half-volume 2 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : PvM17-hexamer
| Entire | Name: PvM17-hexamer |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: PvM17-hexamer
| Supramolecule | Name: PvM17-hexamer / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: M17 leucyl aminopeptidase, putative
| Macromolecule | Name: M17 leucyl aminopeptidase, putative / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 6 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: leucyl aminopeptidase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 60.442328 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MATTVPQVVS LDPTTIPIDY HTPIDDLSIE VKDISAEACP ADEGLIVFLL NSAPKHSSSG GSGGNGGSAG SSGNGEGGAQ IKINSSVKD NTINEFLKEG NMENFTGKLG TSKSFYIAND QKKYVSLAYV GCGPANEETE LEIRKVAYAL VTLLHDSKHK K VSIIFEIK ...String: MATTVPQVVS LDPTTIPIDY HTPIDDLSIE VKDISAEACP ADEGLIVFLL NSAPKHSSSG GSGGNGGSAG SSGNGEGGAQ IKINSSVKD NTINEFLKEG NMENFTGKLG TSKSFYIAND QKKYVSLAYV GCGPANEETE LEIRKVAYAL VTLLHDSKHK K VSIIFEIK IEEALFRFFL EHLFYEYVTD ERFKSADKST ETDFIKNLSL HIANADAYKG QIDKARVYFY GTYYAAQLIA AP SNYCNPV SLSNAAVELA QKVNLECKIL DVKELEELKM GAYLSVGKGS MYPNKFIHLT YKGAQTGASQ NEKKKIALIG KGI TFDSGG YNLKAAPGSM IDLMKFDMSG CAAVLGCAYC IGTIKPDNVE VHFLSAVCEN MVSKNSYRPG DIITASNGKT IEVG NTDAE GRLTLADALV YAEKLGVDYI VDIATLTGAM LYSLGTSYAG VFGNNDQLIN KILSSSKTSN EPVWWLPIIN EYRSS LNSK YADLNNISSS VKASSVVASL FLKEFIENTP WAHIDIAGVS WNFKARKPKG FGVRLLTEFV LNDAVHHHHH H UniProtKB: Leucine aminopeptidase |
-Macromolecule #2: CARBONATE ION
| Macromolecule | Name: CARBONATE ION / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 6 / Formula: CO3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 60.009 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-CO3: |
-Macromolecule #3: MANGANESE (II) ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MANGANESE (II) ION / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 12 / Formula: MN |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 54.938 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 2.9 mg/mL | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 Component:
| ||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil / Material: COPPER / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE | ||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV Details: Blot for 3 seconds with blot force of -1. Drain time of 1 second.. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Average electron dose: 63.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




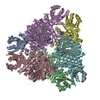
 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)