[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-6wtd: Monomer yeast ATP synthase Fo reconstituted in nanodisc with inhi... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6wtd | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
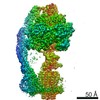
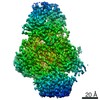
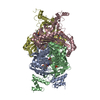
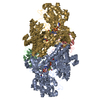
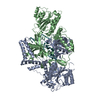
| Title | Monomer yeast ATP synthase Fo reconstituted in nanodisc with inhibitor of Bedaquiline bound | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | BIOSYNTHETIC PROTEIN / ATP synthase | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationMitochondrial protein degradation / mitochondrial proton-transporting ATP synthase complex assembly / proton transmembrane transporter activity / proton motive force-driven ATP synthesis / proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex, proton-transporting domain / proton-transporting ATP synthase complex / proton transmembrane transport / mitochondrial intermembrane space / protein-containing complex assembly / mitochondrial inner membrane ...Mitochondrial protein degradation / mitochondrial proton-transporting ATP synthase complex assembly / proton transmembrane transporter activity / proton motive force-driven ATP synthesis / proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex, proton-transporting domain / proton-transporting ATP synthase complex / proton transmembrane transport / mitochondrial intermembrane space / protein-containing complex assembly / mitochondrial inner membrane / lipid binding / mitochondrion / identical protein binding / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
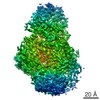
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.2 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Mueller, D.M. / Srivastava, A.P. / Symersky, J. / Luo, M. / Liao, M.F. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2items United States, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Commun Biol / Year: 2020 Journal: Commun Biol / Year: 2020Title: Bedaquiline inhibits the yeast and human mitochondrial ATP synthases. Authors: Min Luo / Wenchang Zhou / Hiral Patel / Anurag P Srivastava / Jindrich Symersky / Michał M Bonar / José D Faraldo-Gómez / Maofu Liao / David M Mueller /  Abstract: Bedaquiline (BDQ, Sirturo) has been approved to treat multidrug resistant forms of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Prior studies suggested that BDQ was a selective inhibitor of the ATP synthase from M. ...Bedaquiline (BDQ, Sirturo) has been approved to treat multidrug resistant forms of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Prior studies suggested that BDQ was a selective inhibitor of the ATP synthase from M. tuberculosis. However, Sirturo treatment leads to an increased risk of cardiac arrhythmias and death, raising the concern that this adverse effect results from inhibition at a secondary site. Here we show that BDQ is a potent inhibitor of the yeast and human mitochondrial ATP synthases. Single-particle cryo-EM reveals that the site of BDQ inhibition partially overlaps with that of the inhibitor oligomycin. Molecular dynamics simulations indicate that the binding mode of BDQ to this site is similar to that previously seen for a mycobacterial enzyme, explaining the observed lack of selectivity. We propose that derivatives of BDQ ought to be made to increase its specificity toward the mycobacterial enzyme and thereby reduce the side effects for patients that are treated with Sirturo. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6wtd.cif.gz 6wtd.cif.gz | 217.2 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6wtd.ent.gz pdb6wtd.ent.gz | 170.6 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6wtd.json.gz 6wtd.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  6wtd_validation.pdf.gz 6wtd_validation.pdf.gz | 1009.5 KB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  6wtd_full_validation.pdf.gz 6wtd_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1021.3 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  6wtd_validation.xml.gz 6wtd_validation.xml.gz | 37 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  6wtd_validation.cif.gz 6wtd_validation.cif.gz | 57.1 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wt/6wtd https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wt/6wtd ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wt/6wtd ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wt/6wtd | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  21894MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-ATP synthase subunit ... , 6 types, 15 molecules KLMNOPQRSTXZ7UJ
| #1: Protein | Mass: 7790.385 Da / Num. of mol.: 10 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #3: Protein | | Mass: 27900.430 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #4: Protein | | Mass: 23194.498 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P05626 #5: Protein | | Mass: 19709.424 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P30902 #6: Protein | | Mass: 10584.166 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: Q06405 #7: Protein/peptide | | Mass: 4145.884 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P81450 |
|---|
-Protein/peptide , 1 types, 1 molecules 8
| #2: Protein/peptide | Mass: 5825.215 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Monomer yeast ATP synthase Fo reconstituted in nanodisc generated in the presence of Bedaquiline Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 / Details: 20 mM Tris-HCl, 150 mM NaCl, pH 8.0 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 1.5 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 400 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 91 % |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TALOS ARCTICA |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 36000 X / Calibrated defocus min: 800 nm / Calibrated defocus max: 2800 nm / Cs: 2 mm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: GATAN LIQUID NITROGEN / Temperature (max): 105 K / Temperature (min): 80 K |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 8 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of real images: 9258 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.15.2_3472: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 541568 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 47169 / Algorithm: BACK PROJECTION / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 6CP7 Accession code: 6CP7 / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj


