+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6vwk | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | E. coli ATP Synthase ADP Sub-state 3a Fo Focussed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / E coli ATP Synthase / ion channel / ATPase | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information: / proton motive force-driven plasma membrane ATP synthesis / proton motive force-driven ATP synthesis / proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex, proton-transporting domain / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / proton-transporting ATP synthase complex / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism / hydrolase activity / lipid binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.3 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Stewart, A.G. / Walshe, J.L. / Sobti, M. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Australia, 1items Australia, 1items
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
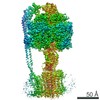
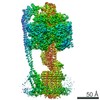
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2020 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2020Title: Cryo-EM structures provide insight into how E. coli FF ATP synthase accommodates symmetry mismatch. Authors: Meghna Sobti / James L Walshe / Di Wu / Robert Ishmukhametov / Yi C Zeng / Carol V Robinson / Richard M Berry / Alastair G Stewart /   Abstract: FF ATP synthase functions as a biological rotary generator that makes a major contribution to cellular energy production. It comprises two molecular motors coupled together by a central and a ...FF ATP synthase functions as a biological rotary generator that makes a major contribution to cellular energy production. It comprises two molecular motors coupled together by a central and a peripheral stalk. Proton flow through the F motor generates rotation of the central stalk, inducing conformational changes in the F motor that catalyzes ATP production. Here we present nine cryo-EM structures of E. coli ATP synthase to 3.1-3.4 Å resolution, in four discrete rotational sub-states, which provide a comprehensive structural model for this widely studied bacterial molecular machine. We observe torsional flexing of the entire complex and a rotational sub-step of F associated with long-range conformational changes that indicates how this flexibility accommodates the mismatch between the 3- and 10-fold symmetries of the F and F motors. We also identify density likely corresponding to lipid molecules that may contribute to the rotor/stator interaction within the F motor. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6vwk.cif.gz 6vwk.cif.gz | 192.1 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6vwk.ent.gz pdb6vwk.ent.gz | 154.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6vwk.json.gz 6vwk.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vw/6vwk https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vw/6vwk ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vw/6vwk ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vw/6vwk | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  21419MC  6oqrC  6oqsC  6oqtC  6oquC  6oqvC  6oqwC  6pqvC  6wnqC  6wnrC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 8259.064 Da / Num. of mol.: 10 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #2: Protein | Mass: 17289.953 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #3: Protein | | Mass: 30324.096 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Has protein modification | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: E. coli ATP Synthase / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.558 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 48 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: dev_3758: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 78283 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller















 PDBj
PDBj

