+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6pqv | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
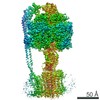
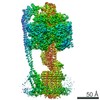
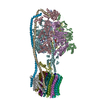
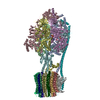
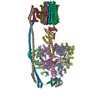
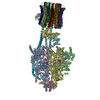
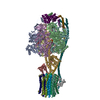
| Title | E. coli ATP Synthase State 1e | ||||||
 Components Components | (ATP synthase ...) x 8 | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / E coli ATP Synthase / ion channel / ATPase | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information: / : / proton motive force-driven plasma membrane ATP synthesis / proton motive force-driven ATP synthesis / proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex, proton-transporting domain / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / membrane => GO:0016020 / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / proton-transporting ATP synthase complex / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism ...: / : / proton motive force-driven plasma membrane ATP synthesis / proton motive force-driven ATP synthesis / proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex, proton-transporting domain / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / membrane => GO:0016020 / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / proton-transporting ATP synthase complex / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism / ADP binding / hydrolase activity / lipid binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.3 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Stewart, A.G. / Sobti, M. / Walshe, J.L. | ||||||
| Funding support |  Australia, 1items Australia, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2020 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2020Title: Cryo-EM structures provide insight into how E. coli FF ATP synthase accommodates symmetry mismatch. Authors: Meghna Sobti / James L Walshe / Di Wu / Robert Ishmukhametov / Yi C Zeng / Carol V Robinson / Richard M Berry / Alastair G Stewart /   Abstract: FF ATP synthase functions as a biological rotary generator that makes a major contribution to cellular energy production. It comprises two molecular motors coupled together by a central and a ...FF ATP synthase functions as a biological rotary generator that makes a major contribution to cellular energy production. It comprises two molecular motors coupled together by a central and a peripheral stalk. Proton flow through the F motor generates rotation of the central stalk, inducing conformational changes in the F motor that catalyzes ATP production. Here we present nine cryo-EM structures of E. coli ATP synthase to 3.1-3.4 Å resolution, in four discrete rotational sub-states, which provide a comprehensive structural model for this widely studied bacterial molecular machine. We observe torsional flexing of the entire complex and a rotational sub-step of F associated with long-range conformational changes that indicates how this flexibility accommodates the mismatch between the 3- and 10-fold symmetries of the F and F motors. We also identify density likely corresponding to lipid molecules that may contribute to the rotor/stator interaction within the F motor. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6pqv.cif.gz 6pqv.cif.gz | 807.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6pqv.ent.gz pdb6pqv.ent.gz | 665.8 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6pqv.json.gz 6pqv.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pq/6pqv https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pq/6pqv ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pq/6pqv ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pq/6pqv | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  20454MC  6oqrC  6oqsC  6oqtC  6oquC  6oqvC  6oqwC  6vwkC  6wnqC  6wnrC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-ATP synthase ... , 8 types, 22 molecules WCBAXYHGFEDJLMNOPQRISa
| #1: Protein | Mass: 19289.061 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.) Escherichia coli / Gene: atpH, HMPREF1611_00658 / Production host:  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 55281.871 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.) Escherichia coli / Gene: atpA, AD31_4476 / Production host:  References: UniProt: A0A073FQ32, UniProt: P0ABB0*PLUS, H+-transporting two-sector ATPase #3: Protein | Mass: 17257.889 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.) Escherichia coli / Gene: atpF, AD31_4478 / Production host:  #4: Protein | | Mass: 15087.244 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.) Escherichia coli / Gene: atpC, CCU01_030215 / Production host:  #5: Protein | | Mass: 31539.285 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.) Escherichia coli / Gene: atpG, BN16_43751 / Production host:  #6: Protein | Mass: 51664.574 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.) Escherichia coli / Gene: atpD, CDCO157_4410 / Production host:  References: UniProt: A0A0F6CB56, UniProt: P0ABB4*PLUS, H+-transporting two-sector ATPase #7: Protein | Mass: 8259.064 Da / Num. of mol.: 10 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #8: Protein | | Mass: 30324.096 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: atpB, A6581_09625, A8C65_04635, A8G17_13205, A9819_21465, AC789_1c41260, ACN002_3840, ACN77_20010, ACN81_06510, ACU57_03300, ACU90_00315, AKG99_01200, AM464_11965, AMK83_17435, AML07_02005, ...Gene: atpB, A6581_09625, A8C65_04635, A8G17_13205, A9819_21465, AC789_1c41260, ACN002_3840, ACN77_20010, ACN81_06510, ACU57_03300, ACU90_00315, AKG99_01200, AM464_11965, AMK83_17435, AML07_02005, AML35_23925, APZ14_19970, AU473_02230, AUQ13_19445, AUS26_01135, AW059_18665, AW106_23235, B1K96_28785, B7C53_19560, BANRA_02401, BANRA_03128, BANRA_03214, BANRA_04536, BANRA_04611, BB545_21600, BHF46_03220, BHS81_22305, BIZ41_19310, BK292_20055, BK400_00980, BMT53_14990, BMT91_10650, BN17_36921, BTQ04_25560, BTQ06_19305, BUE81_18230, BVL39_06790, BW690_12705, BWP17_17405, BZL31_21415, C2U48_14255, C4J69_12205, C5N07_23075, C5P01_14375, C5P43_18495, C5P44_14015, C6669_08960, C7235_25075, C7B02_15545, C7B06_18115, C7B07_18555, CA593_07300, CG691_14695, CG692_21460, CG705_13230, CG706_05505, COD30_14545, COD46_05110, CR538_25535, CR539_00375, CRD98_06365, CRE06_22220, CRM83_19985, CV83915_02325, CVH05_22810, CWS33_22485, D0X26_21590, D2F89_18645, D3821_26125, D3I61_22220, D6Z21_17295, D7K63_14130, D8K42_12760, D9D20_15080, D9D23_18435, D9D65_17115, D9D69_04800, D9D77_23770, D9E35_19420, D9F57_04785, D9G42_23250, D9H12_19550, D9H53_20710, D9H66_14770, D9H68_12120, D9H70_07975, D9H84_13135, D9I18_08055, D9I52_22315, D9I93_11990, D9J11_15870, D9J44_15620, D9J48_14640, D9K10_12565, DIV22_14605, DL800_26315, DL925_10465, DLU27_05670, DM262_10125, DMI41_02740, DNQ45_04220, DOT75_06920, DP258_23940, DP277_10610, DQF57_16240, DS732_00235, DTL43_15450, DTL90_16085, DV750_19840, E2855_04743, EAI42_11905, EAI44_10320, EAI52_06435, EB510_22250, EB553_22600, EB569_11805, EB595_21530, EC1094V2_4559, EC3234A_68c00800, EC95NR1_03180, ECs4680, ED060_20795, ED098_20360, ED124_20405, ED133_14365, ED287_08070, ED600_20035, ED648_17305, ED653_18700, ED658_09750, ED944_14625, EEP03_14120, EEP23_14845, EF364_23525, EFV06_19295, EIA21_14165, EL75_4432, EL79_4683, EL80_4591, ERS085374_04660, ERS085379_02386, ERS085383_02615, ERS085386_04244, ERS085404_04407, ERS150876_04315, FORC28_6046, GJ11_23870, HW43_00205, JD73_04915, NCTC10090_03054, NCTC10418_07533, NCTC10429_00459, NCTC10444_05020, NCTC11022_03985, NCTC11126_01888, NCTC11181_02279, NCTC13125_03147, NCTC13127_06463, NCTC13462_03577, NCTC7152_05030, NCTC8179_05398, NCTC8622_01220, NCTC8960_02611, NCTC9036_04909, NCTC9037_05079, NCTC9045_05855, NCTC9054_05546, NCTC9055_01929, NCTC9058_01885, NCTC9062_03146, NCTC9073_06659, NCTC9111_05225, NCTC9117_06282, NCTC9119_05322, NCTC9701_05266, NCTC9703_04488, NCTC9706_02267, NCTC9969_05235, PU06_21025, RG28_23995, RK56_018685, RX35_03591, SAMEA3472044_00548, SAMEA3472047_02992, SAMEA3472055_04839, SAMEA3472056_03685, SAMEA3472067_04030, SAMEA3472070_05212, SAMEA3472080_03392, SAMEA3472108_02423, SAMEA3472114_05011, SAMEA3472147_03706, SAMEA3484427_03569, SAMEA3484429_03570, SAMEA3484433_04143, SAMEA3485101_04107, SAMEA3752557_01245, SAMEA3752559_04742, SAMEA3753064_05400, SAMEA3753097_00985, SAMEA3753290_05396, SAMEA3753300_04372, SAMEA3753397_02464, SK85_04068, UN86_05680, UN91_09915, WQ89_11300, WR15_16550 Production host:  |
-Non-polymers , 4 types, 12 molecules 






| #9: Chemical | | #10: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / #11: Chemical | #12: Chemical | ChemComp-PO4 / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: E. coli ATP synthase / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#8 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.558 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Details: unspecified |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 48 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: dev_3758: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 30404 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller














 PDBj
PDBj






