[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-6vvs: Crystal structure of a Mycobacterium smegmatis RNA polymerase tra... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6vvs | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Crystal structure of a Mycobacterium smegmatis RNA polymerase transcription initiation complex with antibiotic Sorangicin | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSCRIPTION / TRANSFERASE/DNA/ANTIBIOTIC / DNA binding / antibiotic / TRANSFERASE-DNA-ANTIBIOTIC complex | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationsigma factor activity / bacterial-type RNA polymerase core enzyme binding / DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / DNA-templated transcription initiation / ribonucleoside binding / DNA-directed RNA polymerase / DNA-directed RNA polymerase activity / protein dimerization activity / response to antibiotic / DNA-templated transcription ...sigma factor activity / bacterial-type RNA polymerase core enzyme binding / DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / DNA-templated transcription initiation / ribonucleoside binding / DNA-directed RNA polymerase / DNA-directed RNA polymerase activity / protein dimerization activity / response to antibiotic / DNA-templated transcription / positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription / magnesium ion binding / DNA binding / zinc ion binding / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria)synthetic construct (others) | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 3.112 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 3.112 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Lilic, M. / Braffman, N. / Darst, S.A. / Campbell, E.A. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2020 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2020Title: The antibiotic sorangicin A inhibits promoter DNA unwinding in a rifampicin-resistant RNA polymerase. Authors: Mirjana Lilic / James Chen / Hande Boyaci / Nathaniel Braffman / Elizabeth A Hubin / Jennifer Herrmann / Rolf Müller / Rachel Mooney / Robert Landick / Seth A Darst / Elizabeth A Campbell /   Abstract: Rifampicin (Rif) is a first-line therapeutic used to treat the infectious disease tuberculosis (TB), which is caused by the pathogen (). The emergence of Rif-resistant (Rif) presents a need for new ...Rifampicin (Rif) is a first-line therapeutic used to treat the infectious disease tuberculosis (TB), which is caused by the pathogen (). The emergence of Rif-resistant (Rif) presents a need for new antibiotics. Rif targets the enzyme RNA polymerase (RNAP). Sorangicin A (Sor) is an unrelated inhibitor that binds in the Rif-binding pocket of RNAP. Sor inhibits a subset of Rif RNAPs, including the most prevalent clinical Rif RNAP substitution found in infected patients (S456>L of the β subunit). Here, we present structural and biochemical data demonstrating that Sor inhibits the wild-type RNAP by a similar mechanism as Rif: by preventing the translocation of very short RNAs. By contrast, Sor inhibits the Rif S456L enzyme at an earlier step, preventing the transition of a partially unwound promoter DNA intermediate to the fully opened DNA and blocking the template-strand DNA from reaching the active site in the RNAP catalytic center. By defining template-strand blocking as a mechanism for inhibition, we provide a mechanistic drug target in RNAP. Our finding that Sor inhibits the wild-type and mutant RNAPs through different mechanisms prompts future considerations for designing antibiotics against resistant targets. Also, we show that Sor has a better pharmacokinetic profile than Rif, making it a suitable starting molecule to design drugs to be used for the treatment of TB patients with comorbidities who require multiple medications. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
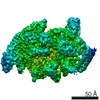
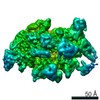
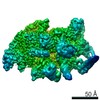
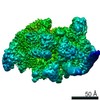
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6vvs.cif.gz 6vvs.cif.gz | 713 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6vvs.ent.gz pdb6vvs.ent.gz | 550.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6vvs.json.gz 6vvs.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vv/6vvs https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vv/6vvs ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vv/6vvs ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vv/6vvs | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6vvtC  6vvvC  6vvxC  6vvyC  6vvzC  6vw0C  5tw1S S: Starting model for refinement C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
-DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit ... , 4 types, 6 molecules ABTCDE
| #1: Protein | Mass: 37959.441 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (strain ATCC 700084 / mc(2)155) (bacteria) Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (strain ATCC 700084 / mc(2)155) (bacteria)Strain: ATCC 700084 / mc(2)155 / References: UniProt: A0QSL8, DNA-directed RNA polymerase #2: Protein | | Mass: 128680.141 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (strain ATCC 700084 / mc(2)155) (bacteria) Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (strain ATCC 700084 / mc(2)155) (bacteria)Strain: ATCC 700084 / mc(2)155 / References: UniProt: P60281, DNA-directed RNA polymerase #3: Protein | | Mass: 146712.891 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (strain ATCC 700084 / mc(2)155) (bacteria) Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (strain ATCC 700084 / mc(2)155) (bacteria)Strain: ATCC 700084 / mc(2)155 / References: UniProt: A0QS66, DNA-directed RNA polymerase #4: Protein | | Mass: 11544.763 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (strain ATCC 700084 / mc(2)155) (bacteria) Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (strain ATCC 700084 / mc(2)155) (bacteria)Strain: ATCC 700084 / mc(2)155 / References: UniProt: A0QWT1, DNA-directed RNA polymerase |
|---|
-Protein , 2 types, 2 molecules FJ
| #5: Protein | Mass: 51573.551 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (strain ATCC 700084 / mc(2)155) (bacteria) Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (strain ATCC 700084 / mc(2)155) (bacteria)Strain: ATCC 700084 / mc(2)155 / References: UniProt: A0QW02 |
|---|---|
| #7: Protein | Mass: 13078.731 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (strain ATCC 700084 / mc(2)155) (bacteria) Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (strain ATCC 700084 / mc(2)155) (bacteria)Strain: ATCC 700084 / mc(2)155 / Gene: rbpA, MSMEG_3858, MSMEI_3768 Production host:  References: UniProt: A0QZ11 |
-Protein/peptide , 1 types, 1 molecules G
| #6: Protein/peptide | Mass: 1464.797 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (strain ATCC 700084 / mc(2)155) (bacteria) Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (strain ATCC 700084 / mc(2)155) (bacteria)Strain: ATCC 700084 / mc(2)155 |
|---|
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules OP
| #8: DNA chain | Mass: 9565.193 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
|---|---|
| #9: DNA chain | Mass: 7930.155 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
-Non-polymers , 5 types, 67 molecules 







| #10: Chemical | ChemComp-SO4 / #11: Chemical | ChemComp-EDO / #12: Chemical | ChemComp-SRN / | #13: Chemical | #14: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.96 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 58.5 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 295 K / Method: vapor diffusion, hanging drop Details: 0.1 M Bis-Tris, pH 6.0, 0.2 M lithium sulfate, 20% w/v PEG3350, 2.5% v/v ethylene glycol, 1% v/v DMSO |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 80 K / Serial crystal experiment: N | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  APS APS  / Beamline: 24-ID-C / Wavelength: 0.9791 Å / Beamline: 24-ID-C / Wavelength: 0.9791 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Detector | Type: DECTRIS PILATUS 6M-F / Detector: PIXEL / Date: Apr 24, 2016 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Radiation | Monochromator: cryo-cooled double crystal Si(111) / Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 0.9791 Å / Relative weight: 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reflection | Resolution: 3.1→55 Å / Num. obs: 98175 / % possible obs: 97.7 % / Redundancy: 10.5 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 94.8 Å2 / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.162 / Rpim(I) all: 0.051 / Rrim(I) all: 0.17 / Χ2: 1.099 / Net I/σ(I): 5.6 / Num. measured all: 1026574 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reflection shell | Diffraction-ID: 1
|
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: PDB entry 5TW1 Resolution: 3.112→54.665 Å / SU ML: 0.49 / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / σ(F): 1.33 / Phase error: 31.33
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.11 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso max: 410.6 Å2 / Biso mean: 105.386 Å2 / Biso min: 29.81 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: final / Resolution: 3.112→54.665 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell | Refine-ID: X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Rfactor Rfree error: 0
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj










































