+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | The antibiotic sorangicin A inhibits promoter DNA unwinding in a rifampicin-resistant RNA polymerase. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, Vol. 117, Issue 48, Page 30423-30432, Year 2020 |
| Publish date | Dec 1, 2020 |
 Authors Authors | Mirjana Lilic / James Chen / Hande Boyaci / Nathaniel Braffman / Elizabeth A Hubin / Jennifer Herrmann / Rolf Müller / Rachel Mooney / Robert Landick / Seth A Darst / Elizabeth A Campbell /   |
| PubMed Abstract | Rifampicin (Rif) is a first-line therapeutic used to treat the infectious disease tuberculosis (TB), which is caused by the pathogen (). The emergence of Rif-resistant (Rif) presents a need for new ...Rifampicin (Rif) is a first-line therapeutic used to treat the infectious disease tuberculosis (TB), which is caused by the pathogen (). The emergence of Rif-resistant (Rif) presents a need for new antibiotics. Rif targets the enzyme RNA polymerase (RNAP). Sorangicin A (Sor) is an unrelated inhibitor that binds in the Rif-binding pocket of RNAP. Sor inhibits a subset of Rif RNAPs, including the most prevalent clinical Rif RNAP substitution found in infected patients (S456>L of the β subunit). Here, we present structural and biochemical data demonstrating that Sor inhibits the wild-type RNAP by a similar mechanism as Rif: by preventing the translocation of very short RNAs. By contrast, Sor inhibits the Rif S456L enzyme at an earlier step, preventing the transition of a partially unwound promoter DNA intermediate to the fully opened DNA and blocking the template-strand DNA from reaching the active site in the RNAP catalytic center. By defining template-strand blocking as a mechanism for inhibition, we provide a mechanistic drug target in RNAP. Our finding that Sor inhibits the wild-type and mutant RNAPs through different mechanisms prompts future considerations for designing antibiotics against resistant targets. Also, we show that Sor has a better pharmacokinetic profile than Rif, making it a suitable starting molecule to design drugs to be used for the treatment of TB patients with comorbidities who require multiple medications. |
 External links External links |  Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A /  PubMed:33199626 / PubMed:33199626 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) / X-ray diffraction |
| Resolution | 2.901 - 4.38 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-21406, PDB-6vvx: EMDB-21407, PDB-6vvy: EMDB-21408, PDB-6vvz: EMDB-21409, PDB-6vw0:  EMDB-22573:  EMDB-22575:  EMDB-22577:  EMDB-22578:  EMDB-22579:  EMDB-22580:  PDB-6vvs:  PDB-6vvt:  PDB-6vvv: |
| Chemicals |  ChemComp-SO4:  ChemComp-EDO: 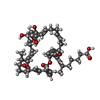 ChemComp-SRN:  ChemComp-ZN:  ChemComp-HOH:  ChemComp-MG: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSCRIPTION / TRANSFERASE/DNA/ANTIBIOTIC / DNA binding / antibiotic / TRANSFERASE-DNA-ANTIBIOTIC complex / TRANSFERASE/DNA / TRANSFERASE-DNA complex / initiation / transcription bubble / sorangicin / open promoter complex |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers