+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6vgq | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
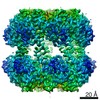
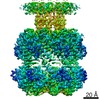
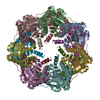
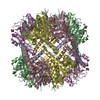
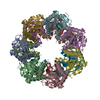
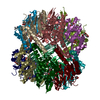
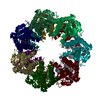
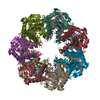
| Title | ClpP1P2 complex from M. tuberculosis with GLF-CMK bound to ClpP1 | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | HYDROLASE / Complex / protease / ClpP / tuberculosis | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationendopeptidase Clp / endopeptidase Clp complex / ATP-dependent peptidase activity / protein quality control for misfolded or incompletely synthesized proteins / peptidoglycan-based cell wall / ATPase binding / serine-type endopeptidase activity / plasma membrane / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  synthetic construct (others) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.5 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Ripstein, Z.A. / Vahidi, S. / Rubinstein, J.L. / Kay, L.E. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Canada, 2items Canada, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2020 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2020Title: An allosteric switch regulates ClpP1P2 protease function as established by cryo-EM and methyl-TROSY NMR. Authors: Siavash Vahidi / Zev A Ripstein / Jordan B Juravsky / Enrico Rennella / Alfred L Goldberg / Anthony K Mittermaier / John L Rubinstein / Lewis E Kay /   Abstract: The 300-kDa ClpP1P2 protease from collaborates with the AAA+ (ATPases associated with a variety of cellular activities) unfoldases, ClpC1 and ClpX, to degrade substrate proteins. Unlike in other ...The 300-kDa ClpP1P2 protease from collaborates with the AAA+ (ATPases associated with a variety of cellular activities) unfoldases, ClpC1 and ClpX, to degrade substrate proteins. Unlike in other bacteria, all of the components of the Clp system are essential for growth and virulence of mycobacteria, and their inhibitors show promise as antibiotics. MtClpP1P2 is unique in that it contains a pair of distinct ClpP1 and ClpP2 rings and also requires the presence of activator peptides, such as benzoyl-leucyl-leucine (Bz-LL), for function. Understanding the structural basis for this requirement has been elusive but is critical for the rational design and improvement of antituberculosis (anti-TB) therapeutics that target the Clp system. Here, we present a combined biophysical and biochemical study to explore the structure-dynamics-function relationship in MtClpP1P2. Electron cryomicroscopy (cryo-EM) structures of apo and acyldepsipeptide-bound MtClpP1P2 explain their lack of activity by showing loss of a key β-sheet in a sequence known as the handle region that is critical for the proper formation of the catalytic triad. Methyl transverse relaxation-optimized spectroscopy (TROSY)-based NMR, cryo-EM, and biochemical assays show that, on binding Bz-LL or covalent inhibitors, MtClpP1P2 undergoes a conformational change from an inactive compact state to an active extended structure that can be explained by a modified Monod-Wyman-Changeux model. Our study establishes a critical role for the handle region as an on/off switch for function and shows extensive allosteric interactions involving both intra- and interring communication that regulate MtClpP1P2 activity and that can potentially be exploited by small molecules to target . | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6vgq.cif.gz 6vgq.cif.gz | 452.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6vgq.ent.gz pdb6vgq.ent.gz | 369.4 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6vgq.json.gz 6vgq.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vg/6vgq https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vg/6vgq ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vg/6vgq ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vg/6vgq | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  21199MC  6vgkC  6vgnC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 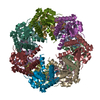
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 21065.934 Da / Num. of mol.: 7 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Details (production host): Cleavable N-terminal His 6 -SUMO tag Production host:  #2: Protein | Mass: 21914.957 Da / Num. of mol.: 7 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: clpP2, clpP, ERS007703_00186, ERS023446_00571, EZX46_04555, FDK60_08755, FDK62_16525, SAMEA2682864_03098, SAMEA2683035_00557 Plasmid: pet24a+ / Production host:  References: UniProt: A0A045HBE0, UniProt: P9WPC3*PLUS, endopeptidase Clp #3: Protein/peptide | Mass: 520.449 Da / Num. of mol.: 7 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) Has ligand of interest | Y | Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: ClpP1P2 complex bound to GLF-CMK / Type: COMPLEX Details: Complex formed between P1 and P2 heptameric rings with inhibitor GLF-CMK Entity ID: #1-#2 / Source: RECOMBINANT | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.3 MDa / Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7 Details: IGEPAL-CA630 was added shortly prior to vitrification | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 20 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES / Details: Mono-disperse complexes | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Details: unspecified | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III / Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Details: Blotted for 4.5 seconds at an offset of -5 mm |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: TFS KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 75000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 700 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm / Alignment procedure: ZEMLIN TABLEAU |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Temperature (max): 77 K / Temperature (min): 70 K |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 60 sec. / Electron dose: 43 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 1645 |
| Image scans | Width: 4096 / Height: 4096 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 257060 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C7 (7 fold cyclic) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 143748 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 5DZK Accession code: 5DZK / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj
