+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6upl | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
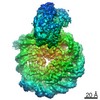
| Title | Structure of FACT_subnucleosome complex 2 | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSCRIPTION/DNA / nucleosome assembly / nucleosome disassembly / transient / integrity / TRANSCRIPTION / replication / histone chaperone / TRANSCRIPTION-DNA complex | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationFACT complex / regulation of chromatin organization / nucleosome disassembly / positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription, elongation / Pausing and recovery of Tat-mediated HIV elongation / Tat-mediated HIV elongation arrest and recovery / HIV elongation arrest and recovery / Pausing and recovery of HIV elongation / Tat-mediated elongation of the HIV-1 transcript / Formation of HIV-1 elongation complex containing HIV-1 Tat ...FACT complex / regulation of chromatin organization / nucleosome disassembly / positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription, elongation / Pausing and recovery of Tat-mediated HIV elongation / Tat-mediated HIV elongation arrest and recovery / HIV elongation arrest and recovery / Pausing and recovery of HIV elongation / Tat-mediated elongation of the HIV-1 transcript / Formation of HIV-1 elongation complex containing HIV-1 Tat / Formation of HIV elongation complex in the absence of HIV Tat / nucleosome binding / negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Elongation / Chromatin modifying enzymes / Formation of RNA Pol II elongation complex / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / CENP-A containing nucleosome / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / RNA Polymerase II Pre-transcription Events / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / telomere organization / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected pyrimidine / Cleavage of the damaged pyrimidine / Interleukin-7 signaling / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Opening / epigenetic regulation of gene expression / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / Meiotic synapsis / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by the Human Silencing Hub (HUSH) complex / DNA methylation / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / Chromatin modifications during the maternal to zygotic transition (MZT) / SIRT1 negatively regulates rRNA expression / HCMV Late Events / ERCC6 (CSB) and EHMT2 (G9a) positively regulate rRNA expression / PRC2 methylates histones and DNA / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by KRAB-ZFP proteins / innate immune response in mucosa / Defective pyroptosis / TP53 Regulates Transcription of DNA Repair Genes / HDACs deacetylate histones / transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / Formation of the beta-catenin:TCF transactivating complex / Activated PKN1 stimulates transcription of AR (androgen receptor) regulated genes KLK2 and KLK3 / RUNX1 regulates genes involved in megakaryocyte differentiation and platelet function / HDMs demethylate histones / G2/M DNA damage checkpoint / NoRC negatively regulates rRNA expression / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / PKMTs methylate histone lysines / DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence / Pre-NOTCH Transcription and Translation / Meiotic recombination / Activation of anterior HOX genes in hindbrain development during early embryogenesis / Metalloprotease DUBs / RMTs methylate histone arginines / Transcriptional regulation of granulopoiesis / HCMV Early Events / antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide / structural constituent of chromatin / UCH proteinases / antibacterial humoral response / heterochromatin formation / nucleosome / nucleosome assembly / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / HATs acetylate histones / RUNX1 regulates transcription of genes involved in differentiation of HSCs / Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production / MLL4 and MLL3 complexes regulate expression of PPARG target genes in adipogenesis and hepatic steatosis / chromatin organization / Processing of DNA double-strand break ends / Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP) / histone binding / Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence / gene expression / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / Regulation of TP53 Activity through Phosphorylation / transcription by RNA polymerase II / DNA replication / chromosome, telomeric region / defense response to Gram-positive bacterium / Ub-specific processing proteases / cadherin binding / protein heterodimerization activity / Amyloid fiber formation / negative regulation of cell population proliferation / DNA repair / nucleolus Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 7.4 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhou, K. / Tan, Y.Z. / Wei, H. / Liu, Y. / Carragher, B. / Potter, C. / Luger, K. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2020 Journal: Nature / Year: 2020Title: FACT caught in the act of manipulating the nucleosome. Authors: Yang Liu / Keda Zhou / Naifu Zhang / Hui Wei / Yong Zi Tan / Zhening Zhang / Bridget Carragher / Clinton S Potter / Sheena D'Arcy / Karolin Luger /  Abstract: The organization of genomic DNA into nucleosomes profoundly affects all DNA-related processes in eukaryotes. The histone chaperone known as 'facilitates chromatin transcription' (FACT) (consisting of ...The organization of genomic DNA into nucleosomes profoundly affects all DNA-related processes in eukaryotes. The histone chaperone known as 'facilitates chromatin transcription' (FACT) (consisting of subunits SPT16 and SSRP1) promotes both disassembly and reassembly of nucleosomes during gene transcription, DNA replication and DNA repair. However, the mechanism by which FACT causes these opposing outcomes is unknown. Here we report two cryo-electron-microscopic structures of human FACT in complex with partially assembled subnucleosomes, with supporting biochemical and hydrogen-deuterium exchange data. We find that FACT is engaged in extensive interactions with nucleosomal DNA and all histone variants. The large DNA-binding surface on FACT appears to be protected by the carboxy-terminal domains of both of its subunits, and this inhibition is released by interaction with H2A-H2B, allowing FACT-H2A-H2B to dock onto a complex containing DNA and histones H3 and H4 (ref. ). SPT16 binds nucleosomal DNA and tethers H2A-H2B through its carboxy-terminal domain by acting as a placeholder for DNA. SSRP1 also contributes to DNA binding, and can assume two conformations, depending on whether a second H2A-H2B dimer is present. Our data suggest a compelling mechanism for how FACT maintains chromatin integrity during polymerase passage, by facilitating removal of the H2A-H2B dimer, stabilizing intermediate subnucleosomal states and promoting nucleosome reassembly. Our findings reconcile discrepancies regarding the many roles of FACT and underscore the dynamic interactions between histone chaperones and nucleosomes. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6upl.cif.gz 6upl.cif.gz | 382.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6upl.ent.gz pdb6upl.ent.gz | 294.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6upl.json.gz 6upl.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  6upl_validation.pdf.gz 6upl_validation.pdf.gz | 1.6 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  6upl_full_validation.pdf.gz 6upl_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.6 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  6upl_validation.xml.gz 6upl_validation.xml.gz | 61.4 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  6upl_validation.cif.gz 6upl_validation.cif.gz | 93.5 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/up/6upl https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/up/6upl ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/up/6upl ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/up/6upl | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  20841MC 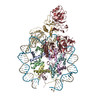 6upkC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-10333 (Title: Single Particle Cryo-EM Reconstructions of Human FACT in Complex with Partially Assembled Sub-nucleosomes EMPIAR-10333 (Title: Single Particle Cryo-EM Reconstructions of Human FACT in Complex with Partially Assembled Sub-nucleosomesData size: 2.2 TB Data #1: Unaligned multi-frame micrographs [micrographs - multiframe] Data #2: Aligned and dose-weighted micrographs [micrographs - single frame] Data #3: Final Particle Stacks for Class 1 and 2 with Euler Angles and Shifts [picked particles - single frame - processed]) |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 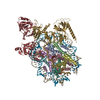
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 4 types, 8 molecules AEBFCKDL
| #1: Protein | Mass: 15437.167 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: H3C1, H3FA, HIST1H3A, H3C2, H3FL, HIST1H3B, H3C3, H3FC HIST1H3C, H3C4, H3FB, HIST1H3D, H3C6, H3FD, HIST1H3E, H3C7, H3FI, HIST1H3F, H3C8, H3FH, HIST1H3G, H3C10, H3FK, HIST1H3H, H3C11, H3FF, ...Gene: H3C1, H3FA, HIST1H3A, H3C2, H3FL, HIST1H3B, H3C3, H3FC HIST1H3C, H3C4, H3FB, HIST1H3D, H3C6, H3FD, HIST1H3E, H3C7, H3FI, HIST1H3F, H3C8, H3FH, HIST1H3G, H3C10, H3FK, HIST1H3H, H3C11, H3FF, HIST1H3I, H3C12, H3FJ, HIST1H3J Production host:  References: UniProt: P68431 #2: Protein | Mass: 11394.426 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: HIST1H4A, H4/A, H4FA, HIST1H4B, H4/I, H4FI, HIST1H4C, H4/G, H4FG, HIST1H4D, H4/B, H4FB, HIST1H4E, H4/J, H4FJ, HIST1H4F, H4/C, H4FC, HIST1H4H, H4/H, H4FH, HIST1H4I, H4/M, H4FM, HIST1H4J, H4/E, ...Gene: HIST1H4A, H4/A, H4FA, HIST1H4B, H4/I, H4FI, HIST1H4C, H4/G, H4FG, HIST1H4D, H4/B, H4FB, HIST1H4E, H4/J, H4FJ, HIST1H4F, H4/C, H4FC, HIST1H4H, H4/H, H4FH, HIST1H4I, H4/M, H4FM, HIST1H4J, H4/E, H4FE, HIST1H4K, H4/D, H4FD, HIST1H4L, H4/K, H4FK, HIST2H4A, H4/N, H4F2, H4FN, HIST2H4, HIST2H4B, H4/O, H4FO, HIST4H4 Production host:  References: UniProt: P62805 #3: Protein | Mass: 14135.523 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HIST1H2AC, H2AFL Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HIST1H2AC, H2AFLProduction host:  References: UniProt: Q93077 #4: Protein | Mass: 13937.213 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: HIST1H2BC, H2BFL, HIST1H2BE, H2BFH, HIST1H2BF, H2BFG, HIST1H2BG, H2BFA, HIST1H2BI, H2BFK Production host:  References: UniProt: P62807 |
|---|
-FACT complex subunit ... , 2 types, 2 molecules GH
| #5: Protein | Mass: 109574.867 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: Amino acids 640-651 cannot be identified due to the resolution limitations. To show the connectivity of the electron density, poly-(UNK) was placed. This was also done for the end of this ...Details: Amino acids 640-651 cannot be identified due to the resolution limitations. To show the connectivity of the electron density, poly-(UNK) was placed. This was also done for the end of this chain (926-967). The full sequence for the experiment is: MHHHHHHAVTLDKDAYYRRVKRLYSNWRKGEDEYANVDAIVVSVGVDEEIVYAKSTALQTWLFGYELTDTIMVFCDDKII FMASKKKVEFLKQIANTKGNENANGAPAITLLIREKNESNKSSFDKMIEAIKESKNGKKIGVFSKDKFPGEFMKSWNDCL NKEGFDKIDISAVVAYTIAVKEDGELNLMKKAASITSEVFNKFFKERVMEIVDADEKVRHSKLAESVEKAIEEKKYLAGA DPSTVEMCYPPIIQSGGNYNLKFSVVSDKNHMHFGAITCAMGIRFKSYCSNLVRTLMVDPSQEVQENYNFLLQLQEELLK ELRHGVKICDVYNAVMDVVKKQKPELLNKITKNLGFGMGIEFREGSLVINSKNQYKLKKGMVFSINLGFSDLTNKEGKKP EEKTYALFIGDTVLVDEDGPATVLTSVKKKVKNVGIFLKNEDEEEEEEEKDEAEDLLGRGSRAALLTERTRNEMTAEEKR RAHQKELAAQLNEEAKRRLTEQKGEQQIQKARKSNVSYKNPSLMPKEPHIREMKIYIDKKYETVIMPVFGIATPFHIATI KNISMSVEGDYTYLRINFYCPGSALGRNEGNIFPNPEATFVKEITYRASNIKAPGEQTVPALNLQNAFRIIKEVQKRYKT REAEEKEKEGIVKQDSLVINLNRSNPKLKDLYIRPNIAQKRMQGSLEAHVNGFRFTSVRGDKVDILYNNIKHALFQPCDG EMIIVLHFHLKNAIMFGKKRHTDVQFYTEVGEITTDLGKHQHMHDRDDLYAEQMEREMRHKLKTAFKNFIEKVEALTKEE LEFEVPFRDLGFNGAPYRSTCLLQPTSSALVNATEWPPFVVTLDEVELIHFERVQFHLKNFDMVIVYKDYSKKVTMINAI PVASLDPIKEWLNSCDLKYTEGVQSLNWTKIMKTIVDDPEGFFEQGGWSFLEPEGEGSDAEEGDSESEIEDETFNPSEDD YEEEEEDSDEDYSSEAEESDYSKESLGSEEESGKDWDELEEEARKADRESRYEEEEEQSRSMSRKRKASVHSSGRGSNRG SRHSSAPPKKKRK Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #6: Protein | Mass: 73361.172 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: The poly-(UNK) was placed to show the electron density between 171-198. The full sequence for the experiment is: ...Details: The poly-(UNK) was placed to show the electron density between 171-198. The full sequence for the experiment is: MAETLEFNDVYQEVKGSMNDGRLRLSRQGIIFKNSKTGKVDNIQAGELTEGIWRRVALGHGLKLLTKNGHVYKYDGFRES EFEKLSDFFKTHYRLELMEKDLCVKGWNWGTVKFGGQLLSFDIGDQPVFEIPLSNVSQCTTGKNEVTLEFHQNDDAEVSL MEVRFYVPPTQEDGVDPVEAFAQNVLSKADVIQATGDAICIFRELQCLTPRGRYDIRIYPTFLHLHGKTFDYKIPYTTVL RLFLLPHKDQRQMFFVISLDPPIKQGQTRYHFLILLFSKDEDISLTLNMNEEEVEKRFEGRLTKNMSGSLYEMVSRVMKA LVNRKITVPGNFQGHSGAQCITCSYKASSGLLYPLERGFIYVHKPPVHIRFDEISFVNFARGTTTTRSFDFEIETKQGTQ YTFSSIEREEYGKLFDFVNAKKLNIKNRGLKEGMNPSYDEYADSDEDQHDAYLERMKEEGKIREENANDSSDDSGEETDE SFNPGEEEEDVAEEFDSNASASSSSNEGDSDRDEKKRKQLKKAKMAKDRKSRKKPVEVKKGKDPNAPKRPMSAYMLWLNA SREKIKSDHPGISITDLSKKAGEIWKGMSKEKKEEWDRKAEDARRDYEKAMKEYEGGRGESSKRDKSKKKKKVKVKMEKK STPSRGSSSKSSSRQLSESFKSKEFVSSDESSSGENKSKKKRRRSEDSEEEELASTPPSSEDSASGSDE Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Production host:  |
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules IJ
| #7: DNA chain | Mass: 24144.422 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  |
|---|---|
| #8: DNA chain | Mass: 24584.680 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: FACT_subNucleosome_complex_class2 / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.35 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 7.8 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.12_2829: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 7.4 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 6990 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj












































