+ データを開く
データを開く
- 基本情報
基本情報
| 登録情報 | データベース: PDB / ID: 6um6 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
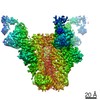
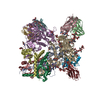
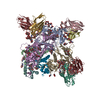
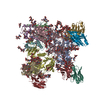
| タイトル | Cryo-EM structure of HIV-1 neutralizing antibody DH270.6 in complex with CH848 10.17DT Env | |||||||||
 要素 要素 |
| |||||||||
 キーワード キーワード | VIRAL PROTEIN/immune system / V3-glycan site / unmutated common ancestor / DH270 lineage / VIRAL PROTEIN / VIRAL PROTEIN-immune system complex | |||||||||
| 機能・相同性 |  機能・相同性情報 機能・相同性情報positive regulation of plasma membrane raft polarization / positive regulation of receptor clustering / host cell endosome membrane / clathrin-dependent endocytosis of virus by host cell / viral protein processing / fusion of virus membrane with host plasma membrane / fusion of virus membrane with host endosome membrane / viral envelope / virion attachment to host cell / host cell plasma membrane ...positive regulation of plasma membrane raft polarization / positive regulation of receptor clustering / host cell endosome membrane / clathrin-dependent endocytosis of virus by host cell / viral protein processing / fusion of virus membrane with host plasma membrane / fusion of virus membrane with host endosome membrane / viral envelope / virion attachment to host cell / host cell plasma membrane / virion membrane / structural molecule activity / membrane 類似検索 - 分子機能 | |||||||||
| 生物種 |   Human immunodeficiency virus 1 (ヒト免疫不全ウイルス) Human immunodeficiency virus 1 (ヒト免疫不全ウイルス) Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) | |||||||||
| 手法 | 電子顕微鏡法 / 単粒子再構成法 / クライオ電子顕微鏡法 / 解像度: 4.3 Å | |||||||||
 データ登録者 データ登録者 | Acharya, P. / Henderson, R.C. / Saunder, K.O. / Haynes, B.F. | |||||||||
| 資金援助 |  米国, 2件 米国, 2件
| |||||||||
 引用 引用 |  ジャーナル: Science / 年: 2019 ジャーナル: Science / 年: 2019タイトル: Targeted selection of HIV-specific antibody mutations by engineering B cell maturation. 著者: Kevin O Saunders / Kevin Wiehe / Ming Tian / Priyamvada Acharya / Todd Bradley / S Munir Alam / Eden P Go / Richard Scearce / Laura Sutherland / Rory Henderson / Allen L Hsu / Mario J Borgnia ...著者: Kevin O Saunders / Kevin Wiehe / Ming Tian / Priyamvada Acharya / Todd Bradley / S Munir Alam / Eden P Go / Richard Scearce / Laura Sutherland / Rory Henderson / Allen L Hsu / Mario J Borgnia / Haiyan Chen / Xiaozhi Lu / Nelson R Wu / Brian Watts / Chuancang Jiang / David Easterhoff / Hwei-Ling Cheng / Kelly McGovern / Peyton Waddicor / Aimee Chapdelaine-Williams / Amanda Eaton / Jinsong Zhang / Wes Rountree / Laurent Verkoczy / Mark Tomai / Mark G Lewis / Heather R Desaire / Robert J Edwards / Derek W Cain / Mattia Bonsignori / David Montefiori / Frederick W Alt / Barton F Haynes /  要旨: INTRODUCTION: A major goal of HIV-1 vaccine development is the design of immunogens that induce broadly neutralizing antibodies (bnAbs). However, vaccination of humans has not resulted in the ...INTRODUCTION: A major goal of HIV-1 vaccine development is the design of immunogens that induce broadly neutralizing antibodies (bnAbs). However, vaccination of humans has not resulted in the induction of affinity-matured and potent HIV-1 bnAbs. To devise effective vaccine strategies, we previously determined the maturation pathway of select HIV-1 bnAbs from acute infection through neutralizing antibody development. During their evolution, bnAbs acquire an abundance of improbable amino acid substitutions as a result of nucleotide mutations at variable region sequences rarely targeted by activation-induced cytidine deaminase, the enzyme responsible for antibody mutation. A subset of improbable mutations is essential for broad neutralization activity, and their acquisition represents a key roadblock to bnAb development. RATIONALE: Current bnAb lineage-based vaccine strategies can initiate bnAb lineage development in animal models but have not specifically elicited the improbable mutations required for neutralization ...RATIONALE: Current bnAb lineage-based vaccine strategies can initiate bnAb lineage development in animal models but have not specifically elicited the improbable mutations required for neutralization breadth. Induction of bnAbs requires vaccine strategies that specifically engage bnAb precursors and subsequently select for improbable mutations required for broadly neutralizing activity. We hypothesized that vaccination with immunogens that bind with moderate to high affinity to bnAb B cell precursors, and with higher affinity to precursors that have acquired improbable mutations, could initiate bnAb B cell lineages and select for key improbable mutations required for bnAb development. RESULTS: We elicited serum neutralizing HIV-1 antibodies in human bnAb precursor knock-in mice and wild-type macaques vaccinated with immunogens designed to select for improbable mutations. We ...RESULTS: We elicited serum neutralizing HIV-1 antibodies in human bnAb precursor knock-in mice and wild-type macaques vaccinated with immunogens designed to select for improbable mutations. We designed two HIV-1 envelope immunogens that bound precursor B cells of either a CD4 binding site or V3-glycan bnAb lineage. In vitro, these immunogens bound more strongly to bnAb precursors once the precursor acquired the desired improbable mutations. Vaccination of macaques with the CD4 binding site–targeting immunogen induced CD4 binding site serum neutralizing antibodies. Antibody sequences elicited in human bnAb precursor knock-in mice encoded functional improbable mutations critical for bnAb development. In bnAb precursor knock-in mice, we isolated a vaccine-elicited monoclonal antibody bearing functional improbable mutations that was capable of neutralizing multiple HIV-1 global isolates. Structures of a bnAb precursor, a bnAb, and the vaccine-elicited antibody revealed the precise roles that acquired improbable mutations played in recognizing the HIV-1 envelope. Thus, our immunogens elicited antibody responses in macaques and knock-in mice that exhibited the mutational patterns, structural characteristics, or neutralization profiles of nascent broadly neutralizing antibodies. CONCLUSION: Our study represents a proof of concept for targeted selection of improbable mutations to guide antibody affinity maturation. Moreover, this study demonstrates a rational strategy for ...CONCLUSION: Our study represents a proof of concept for targeted selection of improbable mutations to guide antibody affinity maturation. Moreover, this study demonstrates a rational strategy for sequential immunogen design to circumvent the difficult roadblocks in HIV-1 bnAb induction by vaccination. We show that immunogens should exhibit differences in affinity across antibody maturation stages where improbable mutations are necessary for the desired antibody function. This strategy of selection of specific antibody nucleotides by immunogen design can be applied to B cell lineages targeting other pathogens where guided affinity maturation is needed for a protective antibody response. | |||||||||
| 履歴 |
|
- 構造の表示
構造の表示
| ムービー |
 ムービービューア ムービービューア |
|---|---|
| 構造ビューア | 分子:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク
- ダウンロード
ダウンロード
| PDBx/mmCIF形式 |  6um6.cif.gz 6um6.cif.gz | 472.2 KB | 表示 |  PDBx/mmCIF形式 PDBx/mmCIF形式 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB形式 |  pdb6um6.ent.gz pdb6um6.ent.gz | 377.9 KB | 表示 |  PDB形式 PDB形式 |
| PDBx/mmJSON形式 |  6um6.json.gz 6um6.json.gz | ツリー表示 |  PDBx/mmJSON形式 PDBx/mmJSON形式 | |
| その他 |  その他のダウンロード その他のダウンロード |
-検証レポート
| 文書・要旨 |  6um6_validation.pdf.gz 6um6_validation.pdf.gz | 1.9 MB | 表示 |  wwPDB検証レポート wwPDB検証レポート |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文書・詳細版 |  6um6_full_validation.pdf.gz 6um6_full_validation.pdf.gz | 2 MB | 表示 | |
| XML形式データ |  6um6_validation.xml.gz 6um6_validation.xml.gz | 78.2 KB | 表示 | |
| CIF形式データ |  6um6_validation.cif.gz 6um6_validation.cif.gz | 115.1 KB | 表示 | |
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/um/6um6 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/um/6um6 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/um/6um6 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/um/6um6 | HTTPS FTP |
-関連構造データ
- リンク
リンク
- 集合体
集合体
| 登録構造単位 | 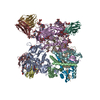
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- 要素
要素
-CH848 10.17DT ... , 2種, 6分子 AEIBFJ
| #1: タンパク質 | 分子量: 51736.535 Da / 分子数: 3 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 由来: (組換発現)   Human immunodeficiency virus 1 (ヒト免疫不全ウイルス) Human immunodeficiency virus 1 (ヒト免疫不全ウイルス)遺伝子: env / 発現宿主:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 参照: UniProt: A0A1W6IPB2 Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 参照: UniProt: A0A1W6IPB2#2: タンパク質 | 分子量: 18245.830 Da / 分子数: 3 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 由来: (組換発現)   Human immunodeficiency virus 1 (ヒト免疫不全ウイルス) Human immunodeficiency virus 1 (ヒト免疫不全ウイルス)遺伝子: env / 発現宿主:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 参照: UniProt: Q2N0S7 Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 参照: UniProt: Q2N0S7 |
|---|
-抗体 , 2種, 6分子 CGKDHL
| #3: 抗体 | 分子量: 25895.893 Da / 分子数: 3 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 / 由来: (組換発現)  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 発現宿主: Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 発現宿主:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト)#4: 抗体 | 分子量: 22783.273 Da / 分子数: 3 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 / 由来: (組換発現)  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 発現宿主: Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 発現宿主:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) |
|---|
-糖 , 6種, 33分子 
| #5: 多糖 | | #6: 多糖 | #7: 多糖 | #8: 多糖 | #9: 多糖 | #10: 糖 | ChemComp-NAG / |
|---|
-詳細
| 研究の焦点であるリガンドがあるか | N |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-実験情報
-実験
| 実験 | 手法: 電子顕微鏡法 |
|---|---|
| EM実験 | 試料の集合状態: PARTICLE / 3次元再構成法: 単粒子再構成法 |
- 試料調製
試料調製
| 構成要素 | 名称: Complex of antibody DH270.6 with HIV-1 Env CH848 10.17DT タイプ: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #2-#4, #1 / 由来: MULTIPLE SOURCES |
|---|---|
| 分子量 | 値: 0.36 MDa / 実験値: YES |
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:   Human immunodeficiency virus 1 (ヒト免疫不全ウイルス) Human immunodeficiency virus 1 (ヒト免疫不全ウイルス) |
| 由来(組換発現) | 生物種:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) |
| 緩衝液 | pH: 7.2 |
| 試料 | 包埋: NO / シャドウイング: NO / 染色: NO / 凍結: YES |
| 急速凍結 | 凍結剤: ETHANE |
- 電子顕微鏡撮影
電子顕微鏡撮影
| 実験機器 |  モデル: Titan Krios / 画像提供: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| 顕微鏡 | モデル: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| 電子銃 | 電子線源:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / 加速電圧: 300 kV / 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / 加速電圧: 300 kV / 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM |
| 電子レンズ | モード: BRIGHT FIELD |
| 撮影 | 電子線照射量: 42 e/Å2 フィルム・検出器のモデル: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) |
- 解析
解析
| CTF補正 | タイプ: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
|---|---|
| 対称性 | 点対称性: C3 (3回回転対称) |
| 3次元再構成 | 解像度: 4.3 Å / 解像度の算出法: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / 粒子像の数: 107646 / 対称性のタイプ: POINT |
| 精密化 | 最高解像度: 4.3 Å |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー







 PDBj
PDBj