[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-20818: Cryo-EM structure of HIV-1 neutralizing antibody DH270.6 in compl... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-20818 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
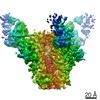
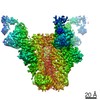
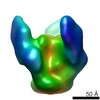
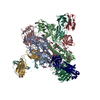
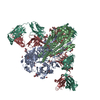
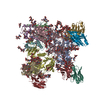
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of HIV-1 neutralizing antibody DH270.6 in complex with CH848 10.17DT Env | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | V3-glycan site / unmutated common ancestor / DH270 lineage / VIRAL PROTEIN / VIRAL PROTEIN-immune system complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationsymbiont-mediated perturbation of host defense response / positive regulation of plasma membrane raft polarization / positive regulation of receptor clustering / host cell endosome membrane / clathrin-dependent endocytosis of virus by host cell / viral protein processing / fusion of virus membrane with host plasma membrane / fusion of virus membrane with host endosome membrane / viral envelope / virion attachment to host cell ...symbiont-mediated perturbation of host defense response / positive regulation of plasma membrane raft polarization / positive regulation of receptor clustering / host cell endosome membrane / clathrin-dependent endocytosis of virus by host cell / viral protein processing / fusion of virus membrane with host plasma membrane / fusion of virus membrane with host endosome membrane / viral envelope / virion attachment to host cell / host cell plasma membrane / virion membrane / structural molecule activity / membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Human immunodeficiency virus 1 / Human immunodeficiency virus 1 /  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.3 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Acharya P / Henderson RC | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2 items United States, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2019 Journal: Science / Year: 2019Title: Targeted selection of HIV-specific antibody mutations by engineering B cell maturation. Authors: Kevin O Saunders / Kevin Wiehe / Ming Tian / Priyamvada Acharya / Todd Bradley / S Munir Alam / Eden P Go / Richard Scearce / Laura Sutherland / Rory Henderson / Allen L Hsu / Mario J ...Authors: Kevin O Saunders / Kevin Wiehe / Ming Tian / Priyamvada Acharya / Todd Bradley / S Munir Alam / Eden P Go / Richard Scearce / Laura Sutherland / Rory Henderson / Allen L Hsu / Mario J Borgnia / Haiyan Chen / Xiaozhi Lu / Nelson R Wu / Brian Watts / Chuancang Jiang / David Easterhoff / Hwei-Ling Cheng / Kelly McGovern / Peyton Waddicor / Aimee Chapdelaine-Williams / Amanda Eaton / Jinsong Zhang / Wes Rountree / Laurent Verkoczy / Mark Tomai / Mark G Lewis / Heather R Desaire / Robert J Edwards / Derek W Cain / Mattia Bonsignori / David Montefiori / Frederick W Alt / Barton F Haynes /  Abstract: INTRODUCTION: A major goal of HIV-1 vaccine development is the design of immunogens that induce broadly neutralizing antibodies (bnAbs). However, vaccination of humans has not resulted in the ...INTRODUCTION: A major goal of HIV-1 vaccine development is the design of immunogens that induce broadly neutralizing antibodies (bnAbs). However, vaccination of humans has not resulted in the induction of affinity-matured and potent HIV-1 bnAbs. To devise effective vaccine strategies, we previously determined the maturation pathway of select HIV-1 bnAbs from acute infection through neutralizing antibody development. During their evolution, bnAbs acquire an abundance of improbable amino acid substitutions as a result of nucleotide mutations at variable region sequences rarely targeted by activation-induced cytidine deaminase, the enzyme responsible for antibody mutation. A subset of improbable mutations is essential for broad neutralization activity, and their acquisition represents a key roadblock to bnAb development. RATIONALE: Current bnAb lineage-based vaccine strategies can initiate bnAb lineage development in animal models but have not specifically elicited the improbable mutations required for neutralization ...RATIONALE: Current bnAb lineage-based vaccine strategies can initiate bnAb lineage development in animal models but have not specifically elicited the improbable mutations required for neutralization breadth. Induction of bnAbs requires vaccine strategies that specifically engage bnAb precursors and subsequently select for improbable mutations required for broadly neutralizing activity. We hypothesized that vaccination with immunogens that bind with moderate to high affinity to bnAb B cell precursors, and with higher affinity to precursors that have acquired improbable mutations, could initiate bnAb B cell lineages and select for key improbable mutations required for bnAb development. RESULTS: We elicited serum neutralizing HIV-1 antibodies in human bnAb precursor knock-in mice and wild-type macaques vaccinated with immunogens designed to select for improbable mutations. We ...RESULTS: We elicited serum neutralizing HIV-1 antibodies in human bnAb precursor knock-in mice and wild-type macaques vaccinated with immunogens designed to select for improbable mutations. We designed two HIV-1 envelope immunogens that bound precursor B cells of either a CD4 binding site or V3-glycan bnAb lineage. In vitro, these immunogens bound more strongly to bnAb precursors once the precursor acquired the desired improbable mutations. Vaccination of macaques with the CD4 binding site–targeting immunogen induced CD4 binding site serum neutralizing antibodies. Antibody sequences elicited in human bnAb precursor knock-in mice encoded functional improbable mutations critical for bnAb development. In bnAb precursor knock-in mice, we isolated a vaccine-elicited monoclonal antibody bearing functional improbable mutations that was capable of neutralizing multiple HIV-1 global isolates. Structures of a bnAb precursor, a bnAb, and the vaccine-elicited antibody revealed the precise roles that acquired improbable mutations played in recognizing the HIV-1 envelope. Thus, our immunogens elicited antibody responses in macaques and knock-in mice that exhibited the mutational patterns, structural characteristics, or neutralization profiles of nascent broadly neutralizing antibodies. CONCLUSION: Our study represents a proof of concept for targeted selection of improbable mutations to guide antibody affinity maturation. Moreover, this study demonstrates a rational strategy for ...CONCLUSION: Our study represents a proof of concept for targeted selection of improbable mutations to guide antibody affinity maturation. Moreover, this study demonstrates a rational strategy for sequential immunogen design to circumvent the difficult roadblocks in HIV-1 bnAb induction by vaccination. We show that immunogens should exhibit differences in affinity across antibody maturation stages where improbable mutations are necessary for the desired antibody function. This strategy of selection of specific antibody nucleotides by immunogen design can be applied to B cell lineages targeting other pathogens where guided affinity maturation is needed for a protective antibody response. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_20818.map.gz emd_20818.map.gz | 117.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-20818-v30.xml emd-20818-v30.xml emd-20818.xml emd-20818.xml | 15.8 KB 15.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_20818.png emd_20818.png | 118.6 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-20818.cif.gz emd-20818.cif.gz | 6.7 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20818 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20818 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20818 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20818 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6um6MC  6um5C  6um7C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_20818.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_20818.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.08 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Complex of antibody DH270.6 with HIV-1 Env CH848 10.17DT
| Entire | Name: Complex of antibody DH270.6 with HIV-1 Env CH848 10.17DT |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Complex of antibody DH270.6 with HIV-1 Env CH848 10.17DT
| Supramolecule | Name: Complex of antibody DH270.6 with HIV-1 Env CH848 10.17DT type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #2-#4, #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Human immunodeficiency virus 1 Human immunodeficiency virus 1 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 360 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: CH848 10.17DT gp120
| Macromolecule | Name: CH848 10.17DT gp120 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Human immunodeficiency virus 1 Human immunodeficiency virus 1 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 51.736535 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: AENLWVTVYY GVPVWKEAKT TLFCASDARA YEKEVHNVWA THACVPTDPS PQELVLGNVT ENFNMWKNDM VDQMHEDIIS LWDQSLKPC VKLTPLCVTL ICSDATVKTG TVEEMKNCSF NTTTEIRDKE KKEYALFYKP DIVPLSETNN TSEYRLINCN T SACTQACP ...String: AENLWVTVYY GVPVWKEAKT TLFCASDARA YEKEVHNVWA THACVPTDPS PQELVLGNVT ENFNMWKNDM VDQMHEDIIS LWDQSLKPC VKLTPLCVTL ICSDATVKTG TVEEMKNCSF NTTTEIRDKE KKEYALFYKP DIVPLSETNN TSEYRLINCN T SACTQACP KVTFEPIPIH YCAPAGYAIL KCNDETFNGT GPCSNVSTVQ CTHGIRPVVS TQLLLNGSLA EKEIVIRSEN LT NNAKIII VHLHTPVEIV CTRPNNNTRK SVRIGPGQTF YATGDIIGDI KQAHCNISEE KWNDTLQKVG IELQKHFPNK TIK YNQSAG GDMEITTHSF NCGGEFFYCN TSNLFNGTYN GTYISTNSSA NSTSTITLQC RIKQIINMWQ GVGRCMYAPP IAGN ITCRS NITGLLLTRD GGTNSNETET FRPAGGDMRD NWRSELYKYK VVKIEPLGVA PTRCKRRV UniProtKB: Envelope glycoprotein gp160 |
-Macromolecule #2: CH848 10.17DT gp41
| Macromolecule | Name: CH848 10.17DT gp41 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Human immunodeficiency virus 1 Human immunodeficiency virus 1 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 18.24583 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: VGRRRRRRAV GIGAVFLGFL GAAGSTMGAA SMTLTVQARN LLSGIVQQQS NLLRAPEAQQ HLLKLTVWGI KQLQARVLAV ERYLRDQQL LGIWGCSGKL ICCTNVPWNS SWSNRNLSEI WDNMTWLQWD KEISNYTQII YGLLEESQNQ QEKNEQDLLA L D UniProtKB: Envelope glycoprotein gp160 |
-Macromolecule #3: DH270.6 Heavy chain
| Macromolecule | Name: DH270.6 Heavy chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 25.895893 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: QVQLVQSGAQ MKNPGASVKV SCAPSGYTFT DFYIHWLRQA PGQGLQWMGW MNPQTGRTNT ARNFQGRVTM TRDTSIGTAY MELRSLTSD DTAIYYCTTG GWISLYYDSS YYPNFDHWGQ GTLLTVSGAS TKGPSVFPLA PSSKSTSGGT AALGCLVKDY F PEPVTVSW ...String: QVQLVQSGAQ MKNPGASVKV SCAPSGYTFT DFYIHWLRQA PGQGLQWMGW MNPQTGRTNT ARNFQGRVTM TRDTSIGTAY MELRSLTSD DTAIYYCTTG GWISLYYDSS YYPNFDHWGQ GTLLTVSGAS TKGPSVFPLA PSSKSTSGGT AALGCLVKDY F PEPVTVSW NSGALTSGVH TFPAVLQSSG LYSLSSVVTV PSSSLGTQTY ICNVNHKPSN TKVDKRVEPK SCDKHHHHHH |
-Macromolecule #4: DH270.6 Light chain
| Macromolecule | Name: DH270.6 Light chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 22.783273 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: QSALTQPASV SGSPGQSITI SCTGTKYDVG SHDLVSWYQQ YPGKVPKYMI YEVNKRPSGV SNRFSGSKSG NTASLTISGL RAEDEADYY CCSFGGSATV VCGGGTKVTV LGQPKGAPSV TLFPPSSEEL QANKATLVCL ISDFYPGAVT VAWKADSSPV K AGVETTTP ...String: QSALTQPASV SGSPGQSITI SCTGTKYDVG SHDLVSWYQQ YPGKVPKYMI YEVNKRPSGV SNRFSGSKSG NTASLTISGL RAEDEADYY CCSFGGSATV VCGGGTKVTV LGQPKGAPSV TLFPPSSEEL QANKATLVCL ISDFYPGAVT VAWKADSSPV K AGVETTTP SKQSNNKYAA SSYLSLTPEQ WKSHRSYSCQ VTHEGSTVEK TVAPTECS |
-Macromolecule #10: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 10 / Number of copies: 18 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.2 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 42.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: NONE |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C3 (3 fold cyclic) / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 4.3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 107646 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















