[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-6tmh: Cryo-EM structure of Toxoplasma gondii mitochondrial ATP synthase... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6tmh | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
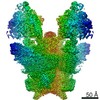
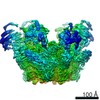
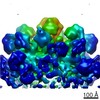
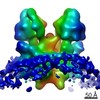
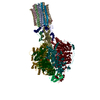
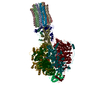
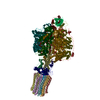
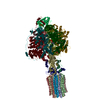
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of Toxoplasma gondii mitochondrial ATP synthase dimer, OSCP/F1/c-ring model | |||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / mitochondrial / ATP synthase / F1 / c-ring | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationthylakoid / proton transmembrane transporter activity / proton motive force-driven ATP synthesis / proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex, proton-transporting domain / proton motive force-driven mitochondrial ATP synthesis / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / proton-transporting ATP synthase complex / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism / ADP binding / mitochondrial inner membrane ...thylakoid / proton transmembrane transporter activity / proton motive force-driven ATP synthesis / proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex, proton-transporting domain / proton motive force-driven mitochondrial ATP synthesis / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / proton-transporting ATP synthase complex / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism / ADP binding / mitochondrial inner membrane / hydrolase activity / lipid binding / mitochondrion / ATP binding / membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   | |||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.1 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Muhleip, A. / Kock Flygaard, R. / Amunts, A. | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Sweden, 4items Sweden, 4items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2021 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2021Title: ATP synthase hexamer assemblies shape cristae of Toxoplasma mitochondria. Authors: Alexander Mühleip / Rasmus Kock Flygaard / Jana Ovciarikova / Alice Lacombe / Paula Fernandes / Lilach Sheiner / Alexey Amunts /   Abstract: Mitochondrial ATP synthase plays a key role in inducing membrane curvature to establish cristae. In Apicomplexa causing diseases such as malaria and toxoplasmosis, an unusual cristae morphology has ...Mitochondrial ATP synthase plays a key role in inducing membrane curvature to establish cristae. In Apicomplexa causing diseases such as malaria and toxoplasmosis, an unusual cristae morphology has been observed, but its structural basis is unknown. Here, we report that the apicomplexan ATP synthase assembles into cyclic hexamers, essential to shape their distinct cristae. Cryo-EM was used to determine the structure of the hexamer, which is held together by interactions between parasite-specific subunits in the lumenal region. Overall, we identified 17 apicomplexan-specific subunits, and a minimal and nuclear-encoded subunit-a. The hexamer consists of three dimers with an extensive dimer interface that includes bound cardiolipins and the inhibitor IF. Cryo-ET and subtomogram averaging revealed that hexamers arrange into ~20-megadalton pentagonal pyramids in the curved apical membrane regions. Knockout of the linker protein ATPTG11 resulted in the loss of pentagonal pyramids with concomitant aberrantly shaped cristae. Together, this demonstrates that the unique macromolecular arrangement is critical for the maintenance of cristae morphology in Apicomplexa. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6tmh.cif.gz 6tmh.cif.gz | 1.3 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6tmh.ent.gz pdb6tmh.ent.gz | 1.1 MB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6tmh.json.gz 6tmh.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tm/6tmh https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tm/6tmh ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tm/6tmh ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tm/6tmh | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  10521MC  6tmgC  6tmiC  6tmjC  6tmkC  6tmlC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 3 types, 12 molecules iGHIJKLMNOPQ
| #1: Protein | Mass: 16167.462 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 50853 / GT1 / References: UniProt: A0A125YJP2 |
|---|---|
| #7: Protein | Mass: 27669.994 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 50853 / GT1 / References: UniProt: A0A125YKF8 |
| #8: Protein | Mass: 17753.504 Da / Num. of mol.: 10 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 50853 / GT1 / References: UniProt: A0A125YJV2 |
-ATP synthase subunit ... , 5 types, 9 molecules AECBFDgde
| #2: Protein | Mass: 61189.168 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)   Strain: ATCC 50853 / GT1 / References: UniProt: S7UU80 #3: Protein | Mass: 59983.316 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 50853 / GT1 References: UniProt: A0A125YYY4, H+-transporting two-sector ATPase #4: Protein | | Mass: 34573.031 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 50853 / GT1 / References: UniProt: A0A125YUH0 #5: Protein | | Mass: 19476.082 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 50853 / GT1 / References: UniProt: A0A125YRE2 #6: Protein | | Mass: 8492.709 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 50853 / GT1 / References: UniProt: S7VV10 |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 3 types, 10 molecules 




| #9: Chemical | | #10: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / #11: Chemical | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Mitochondrial ATP synthase dimer, OSCP/F1/c-ring model Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#8 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.46 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 5 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Details: 3 seconds blot. |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 165000 X / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 30 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 QUANTUM (4k x 4k) / Num. of real images: 4860 |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: GIF Quantum LS / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV |
| Image scans | Movie frames/image: 20 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.1 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 203010 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Space: REAL |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller











 PDBj
PDBj





