[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-6tm5: Cryo-EM structure of the Anaphase-promoting complex/Cyclosome, in... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6tm5 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
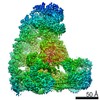
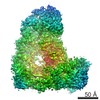
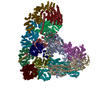
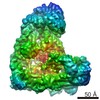
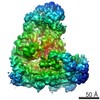
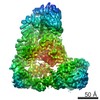
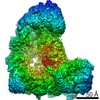
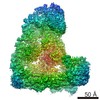
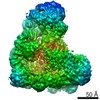
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the Anaphase-promoting complex/Cyclosome, in complex with the Nek2A substrate at 3.9 angstrom resolution | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | CELL CYCLE / E3 ubiquitin Ligase / Complex | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of centriole-centriole cohesion / centrosome separation / positive regulation of synapse maturation / Conversion from APC/C:Cdc20 to APC/C:Cdh1 in late anaphase / regulation of mitotic cell cycle spindle assembly checkpoint / Inactivation of APC/C via direct inhibition of the APC/C complex / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of mitotic proteins / regulation of attachment of spindle microtubules to kinetochore / positive regulation of synaptic plasticity / anaphase-promoting complex ...negative regulation of centriole-centriole cohesion / centrosome separation / positive regulation of synapse maturation / Conversion from APC/C:Cdc20 to APC/C:Cdh1 in late anaphase / regulation of mitotic cell cycle spindle assembly checkpoint / Inactivation of APC/C via direct inhibition of the APC/C complex / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of mitotic proteins / regulation of attachment of spindle microtubules to kinetochore / positive regulation of synaptic plasticity / anaphase-promoting complex / regulation of meiotic cell cycle / Aberrant regulation of mitotic exit in cancer due to RB1 defects / anaphase-promoting complex-dependent catabolic process / protein branched polyubiquitination / metaphase/anaphase transition of mitotic cell cycle / Phosphorylation of the APC/C / regulation of exit from mitosis / positive regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / regulation of mitotic centrosome separation / positive regulation of dendrite morphogenesis / protein K11-linked ubiquitination / regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition / ubiquitin-ubiquitin ligase activity / mitotic metaphase chromosome alignment / regulation of mitotic nuclear division / Regulation of APC/C activators between G1/S and early anaphase / positive regulation of telomere maintenance / Transcriptional Regulation by VENTX / cullin family protein binding / mitotic spindle assembly / blastocyst development / enzyme-substrate adaptor activity / positive regulation of axon extension / protein K48-linked ubiquitination / intercellular bridge / heterochromatin / spindle assembly / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / nuclear periphery / Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Cyclin B / regulation of mitotic cell cycle / APC-Cdc20 mediated degradation of Nek2A / AURKA Activation by TPX2 / condensed nuclear chromosome / meiotic cell cycle / Autodegradation of Cdh1 by Cdh1:APC/C / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Securin / chromosome segregation / Assembly of the pre-replicative complex / Cdc20:Phospho-APC/C mediated degradation of Cyclin A / APC/C:Cdh1 mediated degradation of Cdc20 and other APC/C:Cdh1 targeted proteins in late mitosis/early G1 / G protein-coupled receptor binding / brain development / kinetochore / CDK-mediated phosphorylation and removal of Cdc6 / spindle / neuron projection development / spindle pole / ubiquitin-protein transferase activity / mitotic spindle / Separation of Sister Chromatids / ubiquitin protein ligase activity / Regulation of PLK1 Activity at G2/M Transition / nervous system development / mitotic cell cycle / Antigen processing: Ubiquitination & Proteasome degradation / protein autophosphorylation / microtubule cytoskeleton / Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP) / midbody / protein phosphatase binding / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / microtubule / molecular adaptor activity / cell differentiation / protein phosphorylation / protein kinase activity / non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase / cilium / ciliary basal body / protein ubiquitination / negative regulation of gene expression / cell division / protein serine kinase activity / protein serine/threonine kinase activity / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / centrosome / nucleolus / protein-containing complex / zinc ion binding / nucleoplasm / ATP binding / metal ion binding / nucleus / plasma membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.9 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Alfieri, C. / Barford, D. | ||||||
| Funding support | 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: EMBO Rep / Year: 2020 Journal: EMBO Rep / Year: 2020Title: A unique binding mode of Nek2A to the APC/C allows its ubiquitination during prometaphase. Authors: Claudio Alfieri / Thomas Tischer / David Barford /  Abstract: The anaphase-promoting complex (APC/C) is the key E3 ubiquitin ligase which directs mitotic progression and exit by catalysing the sequential ubiquitination of specific substrates. The activity of ...The anaphase-promoting complex (APC/C) is the key E3 ubiquitin ligase which directs mitotic progression and exit by catalysing the sequential ubiquitination of specific substrates. The activity of the APC/C in mitosis is restrained by the spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC), which coordinates chromosome segregation with the assembly of the mitotic spindle. The SAC effector is the mitotic checkpoint complex (MCC), which binds and inhibits the APC/C. It is incompletely understood how the APC/C switches substrate specificity in a cell cycle-specific manner. For instance, it is unclear how in prometaphase, when APC/C activity towards cyclin B and securin is repressed by the MCC, the kinase Nek2A is ubiquitinated. Here, we combine biochemical and structural analysis with functional studies in cells to show that Nek2A is a conformational-specific binder of the APC/C-MCC complex (APC/C ) and that, in contrast to cyclin A, Nek2A can be ubiquitinated efficiently by the APC/C in conjunction with both the E2 enzymes UbcH10 and UbcH5. We propose that these special features of Nek2A allow its prometaphase-specific ubiquitination. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6tm5.cif.gz 6tm5.cif.gz | 1.4 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6tm5.ent.gz pdb6tm5.ent.gz | 1.1 MB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6tm5.json.gz 6tm5.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tm/6tm5 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tm/6tm5 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tm/6tm5 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tm/6tm5 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 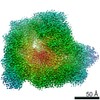 10518MC  6tljC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 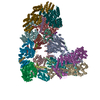
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Anaphase-promoting complex subunit ... , 11 types, 13 molecules ABDEGWILMNOXY
| #1: Protein | Mass: 216775.516 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ANAPC1, TSG24 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ANAPC1, TSG24 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9H1A4 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9H1A4 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 9854.647 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ANAPC11, HSPC214 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ANAPC11, HSPC214 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9NYG5 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9NYG5 | ||||||||||||
| #4: Protein | Mass: 14286.727 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ANAPC15, C11orf51, HSPC020 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ANAPC15, C11orf51, HSPC020 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P60006 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P60006 | ||||||||||||
| #5: Protein | Mass: 11677.995 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ANAPC16, C10orf104, CENP-27 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ANAPC16, C10orf104, CENP-27 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q96DE5 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q96DE5 | ||||||||||||
| #7: Protein | Mass: 9793.999 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CDC26, ANAPC12, C9orf17 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CDC26, ANAPC12, C9orf17 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q8NHZ8 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q8NHZ8#8: Protein | | Mass: 92219.227 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ANAPC4, APC4 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ANAPC4, APC4 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UJX5 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UJX5#10: Protein | | Mass: 21282.143 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ANAPC10, APC10 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ANAPC10, APC10 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UM13 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UM13#11: Protein | | Mass: 8528.309 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ANAPC13 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ANAPC13 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9BS18 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9BS18#12: Protein | | Mass: 93938.977 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ANAPC2, APC2, KIAA1406 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ANAPC2, APC2, KIAA1406 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UJX6 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UJX6#13: Protein | | Mass: 85179.766 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ANAPC5, APC5 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ANAPC5, APC5 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UJX4 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UJX4#15: Protein | Mass: 66929.367 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ANAPC7, APC7 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ANAPC7, APC7 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UJX3 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UJX3 |
-Cell division cycle protein ... , 3 types, 6 molecules CPFHJK
| #3: Protein | Mass: 68921.031 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CDC23, ANAPC8 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CDC23, ANAPC8 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UJX2 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9UJX2#6: Protein | Mass: 91973.125 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CDC27, ANAPC3, D0S1430E, D17S978E / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CDC27, ANAPC3, D0S1430E, D17S978E / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P30260 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P30260#9: Protein | Mass: 71747.516 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CDC16, ANAPC6 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CDC16, ANAPC6 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q13042 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q13042 |
|---|
-Serine/threonine-protein kinase ... , 2 types, 2 molecules SQ
| #16: Protein | Mass: 51788.434 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NEK2, NEK2A, NLK1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NEK2, NEK2A, NLK1 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper)References: UniProt: P51955, non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase |
|---|---|
| #17: Protein | Mass: 51848.551 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NEK2, NEK2A, NLK1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NEK2, NEK2A, NLK1 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper)References: UniProt: P51955, non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase |
-Protein/peptide / Non-polymers , 2 types, 4 molecules T

| #14: Protein/peptide | Mass: 1183.313 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) |
|---|---|
| #18: Chemical |
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Cryo-EM structure of the Anaphase-promoting complex/Cyclosome, in complex with the Nek2A substrate at 3.9 angstrom resolution Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#17 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 29 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.9 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 233840 / Symmetry type: POINT |
| Refinement | Highest resolution: 3.9 Å |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj















