[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
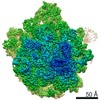
Yorodumi- PDB-6qul: Structure of a bacterial 50S ribosomal subunit in complex with th... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6qul | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
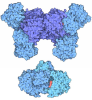
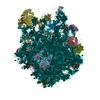
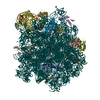
| Title | Structure of a bacterial 50S ribosomal subunit in complex with the novel quinoxolidinone antibiotic cadazolid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ANTIBIOTIC / ribosome / cadazolid / quinoxolidinone / 50S | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationtranscriptional attenuation / endoribonuclease inhibitor activity / positive regulation of ribosome biogenesis / RNA-binding transcription regulator activity / negative regulation of cytoplasmic translation / DnaA-L2 complex / translation repressor activity / negative regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication initiation / mRNA regulatory element binding translation repressor activity / assembly of large subunit precursor of preribosome ...transcriptional attenuation / endoribonuclease inhibitor activity / positive regulation of ribosome biogenesis / RNA-binding transcription regulator activity / negative regulation of cytoplasmic translation / DnaA-L2 complex / translation repressor activity / negative regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication initiation / mRNA regulatory element binding translation repressor activity / assembly of large subunit precursor of preribosome / cytosolic ribosome assembly / response to reactive oxygen species / ribosome assembly / regulation of cell growth / DNA-templated transcription termination / response to radiation / mRNA 5'-UTR binding / large ribosomal subunit / transferase activity / ribosome binding / ribosomal large subunit assembly / 5S rRNA binding / large ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit / cytoplasmic translation / tRNA binding / negative regulation of translation / rRNA binding / structural constituent of ribosome / ribosome / translation / response to antibiotic / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription / mRNA binding / DNA binding / RNA binding / zinc ion binding / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Scaiola, A. / Leibundgut, M. / Boehringer, D. / Ritz, D. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Rep / Year: 2019 Journal: Sci Rep / Year: 2019Title: Structural basis of translation inhibition by cadazolid, a novel quinoxolidinone antibiotic. Authors: Alain Scaiola / Marc Leibundgut / Daniel Boehringer / Patrick Caspers / Daniel Bur / Hans H Locher / Georg Rueedi / Daniel Ritz /  Abstract: Oxazolidinones are synthetic antibiotics used for treatment of infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria. They target the bacterial protein synthesis machinery by binding to the peptidyl ...Oxazolidinones are synthetic antibiotics used for treatment of infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria. They target the bacterial protein synthesis machinery by binding to the peptidyl transferase centre (PTC) of the ribosome and interfering with the peptidyl transferase reaction. Cadazolid is the first member of quinoxolidinone antibiotics, which are characterized by combining the pharmacophores of oxazolidinones and fluoroquinolones, and it is evaluated for treatment of Clostridium difficile gastrointestinal infections that frequently occur in hospitalized patients. In vitro protein synthesis inhibition by cadazolid was shown in Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus, including an isolate resistant against linezolid, the prototypical oxazolidinone antibiotic. To better understand the mechanism of inhibition, we determined a 3.0 Å cryo-electron microscopy structure of cadazolid bound to the E. coli ribosome in complex with mRNA and initiator tRNA. Here we show that cadazolid binds with its oxazolidinone moiety in a binding pocket in close vicinity of the PTC as observed previously for linezolid, and that it extends its unique fluoroquinolone moiety towards the A-site of the PTC. In this position, the drug inhibits protein synthesis by interfering with the binding of tRNA to the A-site, suggesting that its chemical features also can enable the inhibition of linezolid-resistant strains. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6qul.cif.gz 6qul.cif.gz | 1.9 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6qul.ent.gz pdb6qul.ent.gz | 1.5 MB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6qul.json.gz 6qul.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qu/6qul https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qu/6qul ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qu/6qul ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qu/6qul | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  4638MC  4639C  4641C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-RNA chain , 3 types, 3 molecules 1AB
| #1: RNA chain | Mass: 1223.818 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|---|
| #2: RNA chain | Mass: 906514.125 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #3: RNA chain | Mass: 38790.090 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
+50S ribosomal protein ... , 28 types, 28 molecules CDEFGHKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdef
-Non-polymers , 5 types, 386 molecules 







| #32: Chemical | ChemComp-FME / | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #33: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / #34: Chemical | ChemComp-AMP / | #35: Chemical | ChemComp-JJH / | #36: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / | |
-Details
| Has protein modification | N |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Structure of a bacterial 50S ribosomal subunit in complex with the novel quinoxolidinone antibiotic cadazolid Type: RIBOSOME / Entity ID: #1-#31 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Units: MEGADALTONS / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/2 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 1.14 e/Å2 / Detector mode: INTEGRATING / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 59148 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj