[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-6qoz: CryoEM reconstruction of Cowpea Mosaic Virus (CPMV) bound to an A... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6qoz | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | CryoEM reconstruction of Cowpea Mosaic Virus (CPMV) bound to an Affimer reagent | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | VIRUS / CPMV / COMOVIRIDAE / PICORNAVIRALES / AFFIMEr REAGENT / antibody-like | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationtransport of virus in host, cell to cell / host cell plasmodesma / T=3 icosahedral viral capsid / symbiont-mediated suppression of host innate immune response / GTP binding / host cell nucleus / structural molecule activity / DNA binding / RNA binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  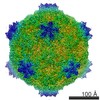 Cowpea mosaic virus Cowpea mosaic virussynthetic construct (others) | ||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.4 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Hesketh, E.L. / Tiede, C. / Adamson, H. / Adams, T.L. / Byrne, M.J. / Meshcheriakova, Y. / Lomonossoff, G.P. / Kruse, I. / McPherson, M.J. / Tomlinson, D.C. / Ranson, N.A. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 3items United Kingdom, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Rep / Year: 2019 Journal: Sci Rep / Year: 2019Title: Affimer reagents as tools in diagnosing plant virus diseases. Authors: Emma L Hesketh / Christian Tiede / Hope Adamson / Thomas L Adams / Matthew J Byrne / Yulia Meshcheriakova / Inga Kruse / Michael J McPherson / George P Lomonossoff / Darren C Tomlinson / Neil A Ranson /  Abstract: Plant viruses can cause devastating losses to agriculture and are therefore a major threat to food security. The rapid identification of virally-infected crops allowing containment is essential to ...Plant viruses can cause devastating losses to agriculture and are therefore a major threat to food security. The rapid identification of virally-infected crops allowing containment is essential to limit such threats, but plant viral diseases can be extremely challenging to diagnose. An ideal method for plant virus diagnosis would be a device which can be implemented easily in the field. Such devices require a binding reagent that is specific for the virus of interest. We chose to investigate the use of Affimer reagents, artificial binding proteins and a model plant virus Cowpea Mosaic virus (CPMV) empty virus like particles (eVLPs). CPMV-eVLP mimic the morphology of wild-type (WT) CPMV but lack any infectious genomic material and so do not have biocontainment issues. We have produced and purified an Affimer reagent selected for its ability to bind to CPMV-eVLP and have shown that the selected Affimer also specifically binds to WT CPMV. We have produced a 3.4 Å structure of WT CPMV bound to the Affimer using cryo-electron microscopy. Finally, we have shown that this Affimer is capable of reliably detecting the virus in crude extracts of CPMV-infected leaves and can therefore form the basis for the future development of diagnostic tests. #1:  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2015 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2015Title: Mechanisms of assembly and genome packaging in an RNA virus revealed by high-resolution cryo-EM. Authors: Emma L Hesketh / Yulia Meshcheriakova / Kyle C Dent / Pooja Saxena / Rebecca F Thompson / Joseph J Cockburn / George P Lomonossoff / Neil A Ranson /  Abstract: Cowpea mosaic virus is a plant-infecting member of the Picornavirales and is of major interest in the development of biotechnology applications. Despite the availability of >100 crystal structures of ...Cowpea mosaic virus is a plant-infecting member of the Picornavirales and is of major interest in the development of biotechnology applications. Despite the availability of >100 crystal structures of Picornavirales capsids, relatively little is known about the mechanisms of capsid assembly and genome encapsidation. Here we have determined cryo-electron microscopy reconstructions for the wild-type virus and an empty virus-like particle, to 3.4 Å and 3.0 Å resolution, respectively, and built de novo atomic models of their capsids. These new structures reveal the C-terminal region of the small coat protein subunit, which is essential for virus assembly and which was missing from previously determined crystal structures, as well as residues that bind to the viral genome. These observations allow us to develop a new model for genome encapsidation and capsid assembly. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6qoz.cif.gz 6qoz.cif.gz | 453.2 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6qoz.ent.gz pdb6qoz.ent.gz | 377.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6qoz.json.gz 6qoz.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qo/6qoz https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qo/6qoz ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qo/6qoz ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qo/6qoz | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  4610MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 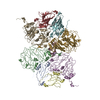
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 20961.564 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Cowpea mosaic virus / Strain: SB / Production host: Cowpea mosaic virus / Strain: SB / Production host:  #2: Protein | Mass: 40858.434 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Cowpea mosaic virus / Strain: SB / Production host: Cowpea mosaic virus / Strain: SB / Production host:  #3: Protein | | Mass: 9286.674 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.) synthetic construct (others) / Production host:  |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details of virus | Empty: NO / Enveloped: NO / Isolate: SPECIES / Type: VIRION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Natural host | Organism: Cowpea mosaic virus | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 400 divisions/in. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: LEICA EM GP / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 281 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 70 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 2 sec. / Electron dose: 45 e/Å2 / Detector mode: INTEGRATING / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 2980 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 144258 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: I (icosahedral) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.4 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 15441 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj


