+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
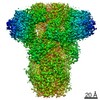
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6q04 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
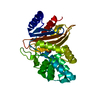
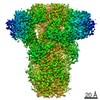
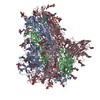
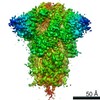
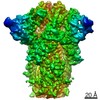
| Title | MERS-CoV S structure in complex with 5-N-acetyl neuraminic acid | |||||||||
 Components Components | Spike glycoprotein | |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | VIRAL PROTEIN / Coronavirus / spike glycoprotein / MERS-CoV / membrane fusion / Structural Genomics / Seattle Structural Genomics Center for Infectious Disease / SSGCID | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationreceptor-mediated endocytosis of virus by host cell / membrane fusion / host cell endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / positive regulation of viral entry into host cell / receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell / fusion of virus membrane with host plasma membrane / fusion of virus membrane with host endosome membrane / viral envelope / symbiont entry into host cell / host cell plasma membrane ...receptor-mediated endocytosis of virus by host cell / membrane fusion / host cell endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / positive regulation of viral entry into host cell / receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell / fusion of virus membrane with host plasma membrane / fusion of virus membrane with host endosome membrane / viral envelope / symbiont entry into host cell / host cell plasma membrane / virion membrane / membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Human betacoronavirus 2c EMC/2012 Human betacoronavirus 2c EMC/2012 | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.5 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Park, Y.J. / Walls, A.C. / Wang, Z. / Sauer, M. / Li, W. / Tortorici, M.A. / Bosch, B.J. / DiMaio, F.D. / Veesler, D. / Seattle Structural Genomics Center for Infectious Disease (SSGCID) | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2019 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2019Title: Structures of MERS-CoV spike glycoprotein in complex with sialoside attachment receptors. Authors: Young-Jun Park / Alexandra C Walls / Zhaoqian Wang / Maximillian M Sauer / Wentao Li / M Alejandra Tortorici / Berend-Jan Bosch / Frank DiMaio / David Veesler /    Abstract: The Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) causes severe and often lethal respiratory illness in humans, and no vaccines or specific treatments are available. Infections are ...The Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) causes severe and often lethal respiratory illness in humans, and no vaccines or specific treatments are available. Infections are initiated via binding of the MERS-CoV spike (S) glycoprotein to sialosides and dipeptidyl-peptidase 4 (the attachment and entry receptors, respectively). To understand MERS-CoV engagement of sialylated receptors, we determined the cryo-EM structures of S in complex with 5-N-acetyl neuraminic acid, 5-N-glycolyl neuraminic acid, sialyl-Lewis, α2,3-sialyl-N-acetyl-lactosamine and α2,6-sialyl-N-acetyl-lactosamine at 2.7-3.0 Å resolution. We show that recognition occurs via a conserved groove that is essential for MERS-CoV S-mediated attachment to sialosides and entry into human airway epithelial cells. Our data illuminate MERS-CoV S sialoside specificity and suggest that selectivity for α2,3-linked over α2,6-linked receptors results from enhanced interactions with the former class of oligosaccharides. This study provides a structural framework explaining MERS-CoV attachment to sialoside receptors and identifies a site of potential vulnerability to inhibitors of viral entry. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6q04.cif.gz 6q04.cif.gz | 715.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6q04.ent.gz pdb6q04.ent.gz | 577.7 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6q04.json.gz 6q04.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/q0/6q04 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/q0/6q04 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/q0/6q04 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/q0/6q04 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 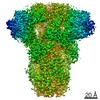 20542MC  6q05C  6q06C  6q07C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 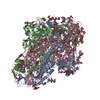
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 1 types, 3 molecules ABC
| #1: Protein | Mass: 149172.062 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Human betacoronavirus 2c EMC/2012 / Production host: Human betacoronavirus 2c EMC/2012 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: K0BRG7 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: K0BRG7 |
|---|
-Sugars , 7 types, 54 molecules 

| #2: Polysaccharide | alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-3)-beta-D-mannopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose-(1- ...alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-3)-beta-D-mannopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose #3: Polysaccharide | 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose #4: Polysaccharide | Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source #5: Polysaccharide | #6: Polysaccharide | alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-3)-[alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-6)]beta-D-mannopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2- ...alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-3)-[alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-6)]beta-D-mannopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source #7: Sugar | ChemComp-NAG / #9: Sugar | |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 2 types, 237 molecules 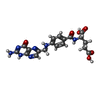


| #8: Chemical | | #10: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: MERS-CoV S ectodomain in complex with 5-N-acetyl neuraminic acid Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 70 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C3 (3 fold cyclic) | ||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 121443 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 6BN3 Accession code: 6BN3 / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model | ||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Highest resolution: 2.5 Å |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj