+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6k4y | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
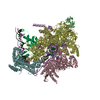
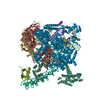
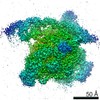
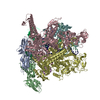
| Title | CryoEM structure of sigma appropriation complex | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSCRIPTION / RNA polymerase / sigma appropriation / transcription activation / promoter | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationsigma factor antagonist complex / RNA polymerase complex / submerged biofilm formation / cellular response to cell envelope stress / regulation of DNA-templated transcription initiation / sigma factor activity / bacterial-type flagellum assembly / bacterial-type RNA polymerase core enzyme binding / cytosolic DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / bacterial-type flagellum-dependent cell motility ...sigma factor antagonist complex / RNA polymerase complex / submerged biofilm formation / cellular response to cell envelope stress / regulation of DNA-templated transcription initiation / sigma factor activity / bacterial-type flagellum assembly / bacterial-type RNA polymerase core enzyme binding / cytosolic DNA-directed RNA polymerase complex / bacterial-type flagellum-dependent cell motility / nitrate assimilation / regulation of DNA-templated transcription elongation / transcription elongation factor complex / transcription antitermination / cell motility / DNA-templated transcription initiation / ribonucleoside binding / DNA-directed RNA polymerase / DNA-directed RNA polymerase activity / response to heat / protein-containing complex assembly / intracellular iron ion homeostasis / protein dimerization activity / response to antibiotic / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription / regulation of DNA-templated transcription / magnesium ion binding / DNA binding / zinc ion binding / membrane / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus) Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.79 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Shi, J. / Wen, A. / Feng, Y. | ||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1items China, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nucleic Acids Res / Year: 2019 Journal: Nucleic Acids Res / Year: 2019Title: Structural basis of σ appropriation. Authors: Jing Shi / Aijia Wen / Minxing Zhao / Linlin You / Yu Zhang / Yu Feng /  Abstract: Bacteriophage T4 middle promoters are activated through a process called σ appropriation, which requires the concerted effort of two T4-encoded transcription factors: AsiA and MotA. Despite ...Bacteriophage T4 middle promoters are activated through a process called σ appropriation, which requires the concerted effort of two T4-encoded transcription factors: AsiA and MotA. Despite extensive biochemical and genetic analyses, puzzle remains, in part, because of a lack of precise structural information for σ appropriation complex. Here, we report a single-particle cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure of an intact σ appropriation complex, comprising AsiA, MotA, Escherichia coli RNA polymerase (RNAP), σ70 and a T4 middle promoter. As expected, AsiA binds to and remodels σ region 4 to prevent its contact with host promoters. Unexpectedly, AsiA undergoes a large conformational change, takes over the job of σ region 4 and provides an anchor point for the upstream double-stranded DNA. Because σ region 4 is conserved among bacteria, other transcription factors may use the same strategy to alter the landscape of transcription immediately. Together, the structure provides a foundation for understanding σ appropriation and transcription activation. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6k4y.cif.gz 6k4y.cif.gz | 753.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6k4y.ent.gz pdb6k4y.ent.gz | 600.5 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6k4y.json.gz 6k4y.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  6k4y_validation.pdf.gz 6k4y_validation.pdf.gz | 1 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  6k4y_full_validation.pdf.gz 6k4y_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.1 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  6k4y_validation.xml.gz 6k4y_validation.xml.gz | 103.2 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  6k4y_validation.cif.gz 6k4y_validation.cif.gz | 159.8 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/k4/6k4y https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/k4/6k4y ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/k4/6k4y ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/k4/6k4y | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9916MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 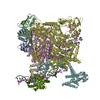
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-DNA-directed RNA polymerase subunit ... , 4 types, 5 molecules ABCDE
| #1: Protein | Mass: 36558.680 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #2: Protein | | Mass: 150820.875 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #3: Protein | | Mass: 155366.781 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #4: Protein | | Mass: 10249.547 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|
-Protein , 3 types, 3 molecules FIM
| #5: Protein | Mass: 70352.242 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|---|
| #6: Protein | Mass: 12775.375 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus) / Gene: asiA / Production host: Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus) / Gene: asiA / Production host:  |
| #7: Protein | Mass: 23608.334 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus) / Gene: motA / Production host: Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus) / Gene: motA / Production host:  |
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules NT
| #8: DNA chain | Mass: 18642.982 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus) Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus) |
|---|---|
| #9: DNA chain | Mass: 18504.877 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus) Enterobacteria phage T4 (virus) |
-Non-polymers , 2 types, 3 molecules 


| #10: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / |
|---|---|
| #11: Chemical |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: sigma appropriation complex / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#9 / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.9 | ||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 12 sec. / Electron dose: 56 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
|---|---|
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) |
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.79 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 105108 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj








































