+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6hr1 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Crystal structure of the YFPnano fusion protein | |||||||||
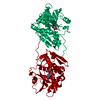
 Components Components | Myosin light chain kinase 2, skeletal/cardiac muscle,Unconventional myosin-X,Green fluorescent protein,Calmodulin-1 | |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Fusion protein / fluorescent engineered / STRUCTURAL PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationplus-end directed microfilament motor activity / regulation of muscle filament sliding / myosin-light-chain kinase / myosin light chain kinase activity / cytoskeleton-dependent intracellular transport / filopodium tip / regulation of filopodium assembly / calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase activity / filopodium membrane / myosin complex ...plus-end directed microfilament motor activity / regulation of muscle filament sliding / myosin-light-chain kinase / myosin light chain kinase activity / cytoskeleton-dependent intracellular transport / filopodium tip / regulation of filopodium assembly / calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase activity / filopodium membrane / myosin complex / CaM pathway / Cam-PDE 1 activation / Sodium/Calcium exchangers / Calmodulin induced events / Reduction of cytosolic Ca++ levels / Activation of Ca-permeable Kainate Receptor / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of CaMKII/CaMKK/CaMKIV cascasde / Loss of phosphorylation of MECP2 at T308 / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of Adenylate Cyclase / CaMK IV-mediated phosphorylation of CREB / PKA activation / negative regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / Glycogen breakdown (glycogenolysis) / CLEC7A (Dectin-1) induces NFAT activation / Activation of RAC1 downstream of NMDARs / negative regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / organelle localization by membrane tethering / microfilament motor activity / mitochondrion-endoplasmic reticulum membrane tethering / autophagosome membrane docking / negative regulation of calcium ion export across plasma membrane / regulation of cardiac muscle cell action potential / presynaptic endocytosis / Synthesis of IP3 and IP4 in the cytosol / regulation of cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction / Phase 0 - rapid depolarisation / Negative regulation of NMDA receptor-mediated neuronal transmission / calcineurin-mediated signaling / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / RHO GTPases activate PAKs / phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate binding / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / Uptake and function of anthrax toxins / regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / Long-term potentiation / protein phosphatase activator activity / Calcineurin activates NFAT / Regulation of MECP2 expression and activity / DARPP-32 events / catalytic complex / Smooth Muscle Contraction / detection of calcium ion / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion / cellular response to interferon-beta / Protein methylation / calcium channel inhibitor activity / Activation of AMPK downstream of NMDARs / presynaptic cytosol / Ion homeostasis / regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / eNOS activation / titin binding / Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) synthesis, recycling, salvage and regulation / ruffle / sperm midpiece / regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / voltage-gated potassium channel complex / calcium channel complex / FCERI mediated Ca+2 mobilization / substantia nigra development / Ras activation upon Ca2+ influx through NMDA receptor / regulation of heart rate / FCGR3A-mediated IL10 synthesis / Antigen activates B Cell Receptor (BCR) leading to generation of second messengers / calyx of Held / bioluminescence / adenylate cyclase activator activity / sarcomere / VEGFR2 mediated cell proliferation / protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity / regulation of cytokinesis / VEGFR2 mediated vascular permeability / generation of precursor metabolites and energy / spindle microtubule / calcium channel regulator activity / Translocation of SLC2A4 (GLUT4) to the plasma membrane / positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT / filopodium / RAF activation / Transcriptional activation of mitochondrial biogenesis / response to calcium ion / cellular response to type II interferon / Stimuli-sensing channels / G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / long-term synaptic potentiation / spindle pole / RAS processing / Signaling by RAF1 mutants Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |     Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT /  molecular replacement / Resolution: 1.901 Å molecular replacement / Resolution: 1.901 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Benoit, R.M. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Switzerland, 2items Switzerland, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Structure / Year: 2022 Journal: Structure / Year: 2022Title: Chimeric single α-helical domains as rigid fusion protein connections for protein nanotechnology and structural biology. Authors: Gabriella Collu / Tobias Bierig / Anna-Sophia Krebs / Sylvain Engilberge / Niveditha Varma / Ramon Guixà-González / Timothy Sharpe / Xavier Deupi / Vincent Olieric / Emiliya Poghosyan / Roger M Benoit /  Abstract: Chimeric fusion proteins are essential tools for protein nanotechnology. Non-optimized protein-protein connections are usually flexible and therefore unsuitable as structural building blocks. Here we ...Chimeric fusion proteins are essential tools for protein nanotechnology. Non-optimized protein-protein connections are usually flexible and therefore unsuitable as structural building blocks. Here we show that the ER/K motif, a single α-helical domain (SAH), can be seamlessly fused to terminal helices of proteins, forming an extended, partially free-standing rigid helix. This enables the connection of two domains at a defined distance and orientation. We designed three constructs termed YFPnano, T4Lnano, and MoStoNano. Analysis of experimentally determined structures and molecular dynamics simulations reveals a certain degree of plasticity in the connections that allows the adaptation to crystal contact opportunities. Our data show that SAHs can be stably integrated into designed structural elements, enabling new possibilities for protein nanotechnology, for example, to improve the exposure of epitopes on nanoparticles (structural vaccinology), to engineer crystal contacts with minimal impact on construct flexibility (for the study of protein dynamics), and to design novel biomaterials. #1:  Journal: Biorxiv / Year: 2020 Journal: Biorxiv / Year: 2020Title: Chimeric single alpha-helical domains as rigid fusion protein connections for protein nanotechnology and structural biology Authors: Krebs, A.S. / Collu, G. / Bierig, T. / Varma, N. / Benoit, R.M.B. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6hr1.cif.gz 6hr1.cif.gz | 198 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6hr1.ent.gz pdb6hr1.ent.gz | 151.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6hr1.json.gz 6hr1.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  6hr1_validation.pdf.gz 6hr1_validation.pdf.gz | 490.1 KB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  6hr1_full_validation.pdf.gz 6hr1_full_validation.pdf.gz | 507.8 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  6hr1_validation.xml.gz 6hr1_validation.xml.gz | 35.7 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  6hr1_validation.cif.gz 6hr1_validation.cif.gz | 50.4 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/hr/6hr1 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/hr/6hr1 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/hr/6hr1 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/hr/6hr1 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6xyrC  6yt3C  3v3dS S: Starting model for refinement C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 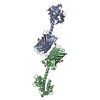
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 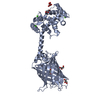
| ||||||||
| 2 | 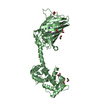
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 1 types, 2 molecules AB
| #1: Protein | Mass: 49199.820 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: residues -35 to -32 = leftovers from cleaved-off tag res -31 t -11 = Calmodulin-binding peptide (very similar to the peptide in PDB entry 2BBM) res -10 to 0 = ER/K helix (small fragment from ...Details: residues -35 to -32 = leftovers from cleaved-off tag res -31 t -11 = Calmodulin-binding peptide (very similar to the peptide in PDB entry 2BBM) res -10 to 0 = ER/K helix (small fragment from the protein in PDB entry 5HMO, res 818-828) res 1 to 238 = Yellow Fluorescent Protein (nearly identical to pdb entry 3V3D) res 239 - 252 = flexible linker res 253 - 400 = Calmodulin (as in PDB entry 2BBM),residues -35 to -32 = leftovers from cleaved-off tag Source: (gene. exp.)     Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: MYLK2, MYO10, GFP, CALM1, CALM, CAM, CAM1 / Plasmid: pET28a / Production host:  References: UniProt: P07313, UniProt: P79114, UniProt: P42212, UniProt: P0DP23, myosin-light-chain kinase |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 6 types, 391 molecules 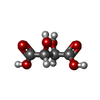










| #2: Chemical | ChemComp-TLA / | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #3: Chemical | ChemComp-CA / #4: Chemical | ChemComp-EDO / #5: Chemical | ChemComp-GOL / #6: Chemical | #7: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | |
-Details
| Has protein modification | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.67 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 54.01 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 293 K / Method: vapor diffusion / pH: 7.8 Details: 24% w/v PEG 3350 0.2 M di-Ammonium tartrate 10% v/v Glycerol |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  SLS SLS  / Beamline: X06DA / Wavelength: 1 Å / Beamline: X06DA / Wavelength: 1 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Detector | Type: DECTRIS PILATUS 2M / Detector: PIXEL / Date: Oct 18, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 1 Å / Relative weight: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reflection | Resolution: 1.9→48.589 Å / Num. obs: 81149 / % possible obs: 99.9 % / Redundancy: 6.491 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 28.71 Å2 / CC1/2: 0.998 / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.09 / Rrim(I) all: 0.097 / Χ2: 1.032 / Net I/σ(I): 14 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reflection shell | Diffraction-ID: 1
|
-Phasing
| Phasing | Method:  molecular replacement molecular replacement | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phasing MR |
|
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: PDB entry 3V3D Resolution: 1.901→48.589 Å / SU ML: 0.23 / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / σ(F): 1.38 / Phase error: 22.18
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.11 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso max: 97.13 Å2 / Biso mean: 36.7914 Å2 / Biso min: 14.33 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: final / Resolution: 1.901→48.589 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell | Refine-ID: X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Rfactor Rfree error: 0 / Total num. of bins used: 29
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 PDBj
PDBj