[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
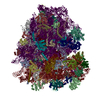
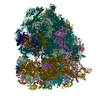
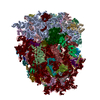
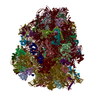
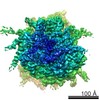
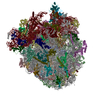
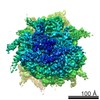
Yorodumi- PDB-6gz3: tRNA translocation by the eukaryotic 80S ribosome and the impact ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6gz3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | tRNA translocation by the eukaryotic 80S ribosome and the impact of GTP hydrolysis, Translocation-intermediate-POST-1 (TI-POST-1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | RIBOSOME / translocation rabbit ribosome / 80S / eEF2 / head swivel / rotation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationubiquitin ligase inhibitor activity / positive regulation of signal transduction by p53 class mediator / 90S preribosome / phagocytic cup / rough endoplasmic reticulum / translation regulator activity / gastrulation / MDM2/MDM4 family protein binding / cytosolic ribosome / maturation of SSU-rRNA ...ubiquitin ligase inhibitor activity / positive regulation of signal transduction by p53 class mediator / 90S preribosome / phagocytic cup / rough endoplasmic reticulum / translation regulator activity / gastrulation / MDM2/MDM4 family protein binding / cytosolic ribosome / maturation of SSU-rRNA / small-subunit processome / rRNA processing / positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway / rhythmic process / regulation of translation / large ribosomal subunit / ribosome binding / ribosomal small subunit biogenesis / ribosomal small subunit assembly / small ribosomal subunit / small ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / large ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / cytosolic small ribosomal subunit / perikaryon / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit / cytoplasmic translation / cell differentiation / rRNA binding / postsynaptic density / structural constituent of ribosome / ribosome / translation / ribonucleoprotein complex / mRNA binding / apoptotic process / dendrite / synapse / centrosome / nucleolus / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / endoplasmic reticulum / Golgi apparatus / RNA binding / zinc ion binding / nucleus / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Enterobacteria phage SP6 (virus) Enterobacteria phage SP6 (virus)  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.6 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Flis, J. / Holm, M. / Rundlet, E.J. / Loerke, J. / Hilal, T. / Dabrowski, M. / Buerger, J. / Mielke, T. / Blanchard, S.C. / Spahn, C.M.T. / Budkevich, T.V. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, Germany,  United States, 3items United States, 3items
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell Rep / Year: 2018 Journal: Cell Rep / Year: 2018Title: tRNA Translocation by the Eukaryotic 80S Ribosome and the Impact of GTP Hydrolysis. Authors: Julia Flis / Mikael Holm / Emily J Rundlet / Justus Loerke / Tarek Hilal / Marylena Dabrowski / Jörg Bürger / Thorsten Mielke / Scott C Blanchard / Christian M T Spahn / Tatyana V Budkevich /   Abstract: Translocation moves the tRNA⋅mRNA module directionally through the ribosome during the elongation phase of protein synthesis. Although translocation is known to entail large conformational changes ...Translocation moves the tRNA⋅mRNA module directionally through the ribosome during the elongation phase of protein synthesis. Although translocation is known to entail large conformational changes within both the ribosome and tRNA substrates, the orchestrated events that ensure the speed and fidelity of this critical aspect of the protein synthesis mechanism have not been fully elucidated. Here, we present three high-resolution structures of intermediates of translocation on the mammalian ribosome where, in contrast to bacteria, ribosomal complexes containing the translocase eEF2 and the complete tRNA⋅mRNA module are trapped by the non-hydrolyzable GTP analog GMPPNP. Consistent with the observed structures, single-molecule imaging revealed that GTP hydrolysis principally facilitates rate-limiting, final steps of translocation, which are required for factor dissociation and which are differentially regulated in bacterial and mammalian systems by the rates of deacyl-tRNA dissociation from the E site. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6gz3.cif.gz 6gz3.cif.gz | 4.8 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6gz3.ent.gz pdb6gz3.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6gz3.json.gz 6gz3.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gz/6gz3 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gz/6gz3 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gz/6gz3 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gz/6gz3 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  0098MC  0099C  0100C  6gz4C  6gz5C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-RNA chain , 7 types, 7 molecules A2BvBxBwB1A3A4
| #1: RNA chain | Mass: 1170164.875 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|---|
| #2: RNA chain | Mass: 24437.535 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #3: RNA chain | Mass: 3837.328 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Enterobacteria phage SP6 (virus) / Production host: Enterobacteria phage SP6 (virus) / Production host:  Enterobacteria phage SP6 (virus) Enterobacteria phage SP6 (virus) |
| #4: RNA chain | Mass: 24533.586 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #5: RNA chain | Mass: 551108.188 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #39: RNA chain | Mass: 50449.812 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #40: RNA chain | Mass: 38385.750 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
+Ribosomal protein ... , 72 types, 72 molecules BDBFBKBPBQBRBSBTBUBZBcBdBfBgBABCBEBIBJBLBNBOBVBWBXBYBaBbBeAA...
-40S ribosomal protein ... , 4 types, 4 molecules BMBBBGBH
| #9: Protein | Mass: 13393.658 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|---|
| #22: Protein | Mass: 24660.012 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #25: Protein | Mass: 26913.867 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #26: Protein | Mass: 20990.465 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
-Protein , 3 types, 3 molecules AZAuCt
| #65: Protein | Mass: 15647.584 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|---|
| #83: Protein | Mass: 24879.422 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
| #86: Protein | Mass: 95056.734 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
-Non-polymers , 3 types, 333 molecules 

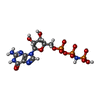


| #87: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / #88: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / #89: Chemical | ChemComp-GNP / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has protein modification | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 4.3 MDa / Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Enterobacteria phage SP6 (virus) Enterobacteria phage SP6 (virus) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai Polara / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI POLARA 300 |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 5 sec. / Electron dose: 30 e/Å2 / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
|---|---|
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 270000 |
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) |
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.6 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 32386 / Symmetry type: POINT |
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Space: REAL |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj

































