[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-2624: Recognition intermediate of Regulation of the mammalian elongatio... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-2624 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Recognition intermediate of Regulation of the mammalian elongation cycle by 40S subunit rolling: a eukaryotic-specific ribosome rearrangement | |||||||||
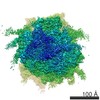
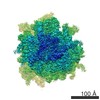
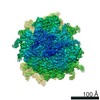
 Map data Map data | reconstruction of codon-recognition / GTPase activation state of 80S ribosome | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | translation / mammalian 80S ribosome / elongation cycle / tRNA selection / eukaryotic ternary complex / elongation factor eEF1A / cryo-electron microscopy | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationguanyl nucleotide binding / kinase activator activity / protein-synthesizing GTPase / Formation of the ternary complex, and subsequently, the 43S complex / Ribosomal scanning and start codon recognition / Translation initiation complex formation / Protein hydroxylation / SARS-CoV-1 modulates host translation machinery / Peptide chain elongation / Selenocysteine synthesis ...guanyl nucleotide binding / kinase activator activity / protein-synthesizing GTPase / Formation of the ternary complex, and subsequently, the 43S complex / Ribosomal scanning and start codon recognition / Translation initiation complex formation / Protein hydroxylation / SARS-CoV-1 modulates host translation machinery / Peptide chain elongation / Selenocysteine synthesis / Formation of a pool of free 40S subunits / Eukaryotic Translation Termination / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / Response of EIF2AK4 (GCN2) to amino acid deficiency / Viral mRNA Translation / Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) independent of the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) / GTP hydrolysis and joining of the 60S ribosomal subunit / translation elongation factor activity / L13a-mediated translational silencing of Ceruloplasmin expression / Major pathway of rRNA processing in the nucleolus and cytosol / Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) enhanced by the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) / rough endoplasmic reticulum / stress granule assembly / cytosolic ribosome / cellular response to epidermal growth factor stimulus / small-subunit processome / maintenance of translational fidelity / Regulation of expression of SLITs and ROBOs / ribosomal small subunit biogenesis / cytosolic small ribosomal subunit / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / SARS-CoV-2 modulates host translation machinery / cytoplasmic translation / structural constituent of ribosome / ribosome / translation / GTPase activity / synapse / GTP binding / nucleolus / endoplasmic reticulum / RNA binding / nucleoplasm / membrane / nucleus / plasma membrane / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 8.9 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Budkevich TV / Giesebrecht J / Behrmann E / Loerke J / Ramrath D / Mielke T / Ismer J / Hildebrand P / Tung C-S / Nierhaus KH ...Budkevich TV / Giesebrecht J / Behrmann E / Loerke J / Ramrath D / Mielke T / Ismer J / Hildebrand P / Tung C-S / Nierhaus KH / Sanbonmatsu KY / Spahn CMT | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell / Year: 2014 Journal: Cell / Year: 2014Title: Regulation of the mammalian elongation cycle by subunit rolling: a eukaryotic-specific ribosome rearrangement. Authors: Tatyana V Budkevich / Jan Giesebrecht / Elmar Behrmann / Justus Loerke / David J F Ramrath / Thorsten Mielke / Jochen Ismer / Peter W Hildebrand / Chang-Shung Tung / Knud H Nierhaus / ...Authors: Tatyana V Budkevich / Jan Giesebrecht / Elmar Behrmann / Justus Loerke / David J F Ramrath / Thorsten Mielke / Jochen Ismer / Peter W Hildebrand / Chang-Shung Tung / Knud H Nierhaus / Karissa Y Sanbonmatsu / Christian M T Spahn /    Abstract: The extent to which bacterial ribosomes and the significantly larger eukaryotic ribosomes share the same mechanisms of ribosomal elongation is unknown. Here, we present subnanometer resolution ...The extent to which bacterial ribosomes and the significantly larger eukaryotic ribosomes share the same mechanisms of ribosomal elongation is unknown. Here, we present subnanometer resolution cryoelectron microscopy maps of the mammalian 80S ribosome in the posttranslocational state and in complex with the eukaryotic eEF1A⋅Val-tRNA⋅GMPPNP ternary complex, revealing significant differences in the elongation mechanism between bacteria and mammals. Surprisingly, and in contrast to bacterial ribosomes, a rotation of the small subunit around its long axis and orthogonal to the well-known intersubunit rotation distinguishes the posttranslocational state from the classical pretranslocational state ribosome. We term this motion "subunit rolling." Correspondingly, a mammalian decoding complex visualized in substates before and after codon recognition reveals structural distinctions from the bacterial system. These findings suggest how codon recognition leads to GTPase activation in the mammalian system and demonstrate that in mammalia subunit rolling occurs during tRNA selection. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_2624.map.gz emd_2624.map.gz | 150.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-2624-v30.xml emd-2624-v30.xml emd-2624.xml emd-2624.xml | 15.8 KB 15.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  EMD-2624_500x500.tif EMD-2624_500x500.tif | 732.6 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2624 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2624 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2624 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2624 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  4cxhMC 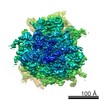 2620C 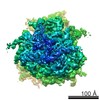 2621C  2622C  2623C  4cxgC  4ujeC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_2624.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 173.8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_2624.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 173.8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | reconstruction of codon-recognition / GTPase activation state of 80S ribosome | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.26 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
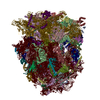
-Entire : Codon recognition /GTPase activated state of mammalian 80S ribosome
| Entire | Name: Codon recognition /GTPase activated state of mammalian 80S ribosome |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: Codon recognition /GTPase activated state of mammalian 80S ribosome
| Supramolecule | Name: Codon recognition /GTPase activated state of mammalian 80S ribosome type: sample / ID: 1000 Details: 80S were re-associated and the sample was assembled in vitro from individual components Oligomeric state: one 80S binds three tRNAs, one elongation factor eEF1A and one mRNA Number unique components: 6 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 4.5 MDa |
-Supramolecule #1: Re-associated 80S
| Supramolecule | Name: Re-associated 80S / type: complex / ID: 1 / Name.synonym: 80S ribosome / Recombinant expression: No / Ribosome-details: ribosome-eukaryote: ALL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 4.5 MDa |
-Macromolecule #1: transfer RNA
| Macromolecule | Name: transfer RNA / type: rna / ID: 1 / Name.synonym: tRNA / Details: tRNAPhe / Classification: TRANSFER / Structure: DOUBLE HELIX / Synthetic?: No |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 25 KDa |
-Macromolecule #2: transfer RNA
| Macromolecule | Name: transfer RNA / type: rna / ID: 2 / Name.synonym: tRNA / Classification: TRANSFER / Structure: DOUBLE HELIX / Synthetic?: No |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 25 KDa |
-Macromolecule #3: transfer RNA
| Macromolecule | Name: transfer RNA / type: rna / ID: 3 / Name.synonym: tRNA / Details: Val-tRNAVal / Classification: TRANSFER / Structure: DOUBLE HELIX / Synthetic?: No |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 25 KDa |
-Macromolecule #5: messenger RNA
| Macromolecule | Name: messenger RNA / type: rna / ID: 5 / Name.synonym: mRNA / Classification: OTHER / Structure: SINGLE STRANDED / Synthetic?: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 15 KDa |
| Sequence | String: GGGAAAAGAA AAGAAAAGAA AAUGUUCGUU AAAGAAAAGA AAAGAAAU |
-Macromolecule #4: elongation factor 1A
| Macromolecule | Name: elongation factor 1A / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Name.synonym: eEF1A / Number of copies: 1 / Oligomeric state: monomer / Recombinant expression: No |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 50 KDa |
| Sequence | UniProtKB: Elongation factor 1-alpha 1 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 1.3 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Details: 20 mM Hepes, 5 mM MgCl2, 100 mM NH4Cl, 6 mM beta-mercaptoethanol, 0.8 mM spermidine, 0.6 mM spermine |
| Grid | Details: Quantifoil grids with additional continuous carbon support. |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 80 % / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK II / Method: blot for 2/4 sec before plunging |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI POLARA 300 |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Min: 77 K |
| Alignment procedure | Legacy - Astigmatism: Objective lens astigmatism was corrected at 200,000 times magnification |
| Details | minimal dose system |
| Date | Sep 22, 2008 |
| Image recording | Category: FILM / Film or detector model: KODAK SO-163 FILM / Digitization - Scanner: OTHER / Number real images: 230 / Average electron dose: 20 e/Å2 / Bits/pixel: 16 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Calibrated magnification: 65520 / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2 mm / Nominal defocus max: 4.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 2.0 µm / Nominal magnification: 39000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder: Nitrogen cooled / Specimen holder model: GATAN LIQUID NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai Polara / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Details | The particles were selected using SIGNATURE and processed using SPIDER and SPARX. |
|---|---|
| CTF correction | Details: defocus group |
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C1 (asymmetric) / Algorithm: OTHER / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 8.9 Å / Resolution method: OTHER / Software - Name: Spider, Sparx / Number images used: 52686 |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model | PDB ID: Chain - Chain ID: A |
|---|---|
| Software | Name:  Chimera Chimera |
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Target criteria: correlation |
| Output model |  PDB-4cxh: |
-Atomic model buiding 2
| Initial model | PDB ID:  2xqd Chain - Chain ID: Y |
|---|---|
| Software | Name: Chimera, Coot |
| Details | Acceptor stem loop (2XQD) and tRNA body (1TTT) (cutting points 26-27, 43-44) were docked separately as rigid bodies. Cutting points were restored using Coot. |
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Target criteria: correlation |
| Output model |  PDB-4cxh: |
-Atomic model buiding 3
| Initial model | PDB ID: Chain - Chain ID: D |
|---|---|
| Software | Name: Chimera, Coot |
| Details | Acceptor stem loop (2XQD) and tRNA body (1TTT) (cutting points 26-27, 43-44) were docked separately as rigid bodies. Cutting points were restored using Coot. |
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Target criteria: correlation |
| Output model |  PDB-4cxh: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)