+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6gfr | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | cyanobacterial GAPDH with NAD | ||||||
 Components Components | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | PHOTOSYNTHESIS / Calvin Cycle / Regulation | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationglyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (NADP+) (phosphorylating) activity / Oxidoreductases; Acting on the aldehyde or oxo group of donors; With NAD+ or NADP+ as acceptor / glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (NAD+) (phosphorylating) activity / glucose metabolic process / NAD binding / NADP binding / metal ion binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   Thermosynechococcus elongatus (bacteria) Thermosynechococcus elongatus (bacteria) | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 1.919 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 1.919 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | McFarlane, C.R. / Murray, J.W. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 1items United Kingdom, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2019 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2019Title: Structural basis of light-induced redox regulation in the Calvin-Benson cycle in cyanobacteria. Authors: Ciaran R McFarlane / Nita R Shah / Burak V Kabasakal / Blanca Echeverria / Charles A R Cotton / Doryen Bubeck / James W Murray /  Abstract: Plants, algae, and cyanobacteria fix carbon dioxide to organic carbon with the Calvin-Benson (CB) cycle. Phosphoribulokinase (PRK) and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) are essential ...Plants, algae, and cyanobacteria fix carbon dioxide to organic carbon with the Calvin-Benson (CB) cycle. Phosphoribulokinase (PRK) and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) are essential CB-cycle enzymes that control substrate availability for the carboxylation enzyme Rubisco. PRK consumes ATP to produce the Rubisco substrate ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). GAPDH catalyzes the reduction step of the CB cycle with NADPH to produce the sugar glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (GAP), which is used for regeneration of RuBP and is the main exit point of the cycle. GAPDH and PRK are coregulated by the redox state of a conditionally disordered protein CP12, which forms a ternary complex with both enzymes. However, the structural basis of CB-cycle regulation by CP12 is unknown. Here, we show how CP12 modulates the activity of both GAPDH and PRK. Using thermophilic cyanobacterial homologs, we solve crystal structures of GAPDH with different cofactors and CP12 bound, and the ternary GAPDH-CP12-PRK complex by electron cryo-microscopy, we reveal that formation of the N-terminal disulfide preorders CP12 prior to binding the PRK active site, which is resolved in complex with CP12. We find that CP12 binding to GAPDH influences substrate accessibility of all GAPDH active sites in the binary and ternary inhibited complexes. Our structural and biochemical data explain how CP12 integrates responses from both redox state and nicotinamide dinucleotide availability to regulate carbon fixation. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6gfr.cif.gz 6gfr.cif.gz | 280.8 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6gfr.ent.gz pdb6gfr.ent.gz | 227.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6gfr.json.gz 6gfr.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gf/6gfr https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gf/6gfr ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gf/6gfr ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gf/6gfr | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  0071C  6gfoC  6gfpC  6gfqC  6gg7C  6ghlC  6ghrC  6gveC  4boyS S: Starting model for refinement C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 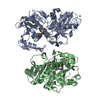
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 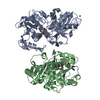
| |||||||||
| Unit cell |
| |||||||||
| Components on special symmetry positions |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 36792.734 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Thermosynechococcus elongatus (strain BP-1) (bacteria) Thermosynechococcus elongatus (strain BP-1) (bacteria)Strain: BP-1 / Gene: tll1466 / Plasmid: pRSETA / Details (production host): thrombin cleavable his-tag / Production host:  References: UniProt: Q8DIW5, Oxidoreductases; Acting on the aldehyde or oxo group of donors; With NAD+ or NADP+ as acceptor #2: Chemical | #3: Chemical | #4: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / | #5: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.69 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 54 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 290 K / Method: vapor diffusion / Details: 12% PEG3350 2% Tacsimate, 100 mM Hepes, pH 7 |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 200 K |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  Diamond Diamond  / Beamline: I24 / Wavelength: 0.96861 Å / Beamline: I24 / Wavelength: 0.96861 Å |
| Detector | Type: DECTRIS PILATUS3 6M / Detector: PIXEL / Date: Feb 27, 2017 |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 0.96861 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 1.919→69.93 Å / Num. obs: 61333 / % possible obs: 99.88 % / Redundancy: 12.9 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 24.85 Å2 / CC1/2: 0.995 / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.2205 / Rrim(I) all: 0.2297 / Net I/σ(I): 7.94 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 1.919→1.988 Å / Redundancy: 12.7 % / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.9235 / Mean I/σ(I) obs: 2.03 / CC1/2: 0.543 / Rrim(I) all: 0.9625 / % possible all: 99.08 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: 4BOY Resolution: 1.919→69.93 Å / SU ML: 0.2 / Cross valid method: FREE R-VALUE / σ(F): 1.37 / Phase error: 20.09
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.11 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 1.919→69.93 Å
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement TLS params. | Method: refined / Refine-ID: X-RAY DIFFRACTION
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement TLS group |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj