[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-6dkf: Caseinolytic protease (ClpP) from Staphylococcus aureus mutant - V7A -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6dkf | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
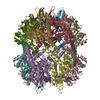
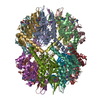
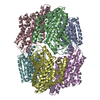
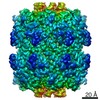
| Title | Caseinolytic protease (ClpP) from Staphylococcus aureus mutant - V7A | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components | ATP-dependent Clp protease proteolytic subunit | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | HYDROLASE / Protease | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationendopeptidase Clp / endopeptidase Clp complex / ATP-dependent peptidase activity / protein quality control for misfolded or incompletely synthesized proteins / ATPase binding / serine-type endopeptidase activity / identical protein binding / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Staphylococcus aureus subsp. aureus str. Newman (bacteria) Staphylococcus aureus subsp. aureus str. Newman (bacteria) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.7 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Ripstein, Z.A. / Vahidi, S. / Kay, L.E. / Rubinstein, J.L. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Canada, 6items Canada, 6items
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2018 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2018Title: Reversible inhibition of the ClpP protease via an N-terminal conformational switch. Authors: Siavash Vahidi / Zev A Ripstein / Massimiliano Bonomi / Tairan Yuwen / Mark F Mabanglo / Jordan B Juravsky / Kamran Rizzolo / Algirdas Velyvis / Walid A Houry / Michele Vendruscolo / John L ...Authors: Siavash Vahidi / Zev A Ripstein / Massimiliano Bonomi / Tairan Yuwen / Mark F Mabanglo / Jordan B Juravsky / Kamran Rizzolo / Algirdas Velyvis / Walid A Houry / Michele Vendruscolo / John L Rubinstein / Lewis E Kay /   Abstract: Protein homeostasis is critically important for cell viability. Key to this process is the refolding of misfolded or aggregated proteins by molecular chaperones or, alternatively, their degradation ...Protein homeostasis is critically important for cell viability. Key to this process is the refolding of misfolded or aggregated proteins by molecular chaperones or, alternatively, their degradation by proteases. In most prokaryotes and in chloroplasts and mitochondria, protein degradation is performed by the caseinolytic protease ClpP, a tetradecamer barrel-like proteolytic complex. Dysregulating ClpP function has shown promise in fighting antibiotic resistance and as a potential therapy for acute myeloid leukemia. Here we use methyl-transverse relaxation-optimized spectroscopy (TROSY)-based NMR, cryo-EM, biochemical assays, and molecular dynamics simulations to characterize the structural dynamics of ClpP from (SaClpP) in wild-type and mutant forms in an effort to discover conformational hotspots that regulate its function. Wild-type SaClpP was found exclusively in the active extended form, with the N-terminal domains of its component protomers in predominantly β-hairpin conformations that are less well-defined than other regions of the protein. A hydrophobic site was identified that, upon mutation, leads to unfolding of the N-terminal domains, loss of SaClpP activity, and formation of a previously unobserved split-ring conformation with a pair of 20-Å-wide pores in the side of the complex. The extended form of the structure and partial activity can be restored via binding of ADEP small-molecule activators. The observed structural plasticity of the N-terminal gates is shown to be a conserved feature through studies of and ClpP, suggesting a potential avenue for the development of molecules to allosterically modulate the function of ClpP. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6dkf.cif.gz 6dkf.cif.gz | 421.6 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6dkf.ent.gz pdb6dkf.ent.gz | 341.6 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6dkf.json.gz 6dkf.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dk/6dkf https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dk/6dkf ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dk/6dkf ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dk/6dkf | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7952MC  7950C  7951C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 21508.479 Da / Num. of mol.: 14 / Mutation: V7A Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Staphylococcus aureus subsp. aureus str. Newman (bacteria) Staphylococcus aureus subsp. aureus str. Newman (bacteria)Strain: Newman / Gene: clpP, NWMN_0736 / Plasmid: pET24 / Production host:  |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Caseinolytic protease from Staphylococcus aureus (V7A) Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.301 MDa / Experimental value: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Staphylococcus aureus (strain Newman) (bacteria) / Strain: Newman Staphylococcus aureus (strain Newman) (bacteria) / Strain: Newman | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 30 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Details: unspecified | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III / Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Details: Modified Vitrobot |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 75000 X / Calibrated defocus min: 1000 nm / Calibrated defocus max: 3200 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 100 µm / Alignment procedure: ZEMLIN TABLEAU |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 60 sec. / Electron dose: 43 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 2 / Num. of real images: 1837 / Details: movies were collected with 44 fractions |
| Image scans | Width: 4096 / Height: 4096 / Movie frames/image: 30 / Used frames/image: 1-30 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 878240 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C2 (2 fold cyclic) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.7 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 324522 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: OTHER / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | 3D fitting-ID: 1 / Pdb chain-ID: A / Pdb chain residue range: 20-193 / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


 PDBj
PDBj

