[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
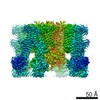
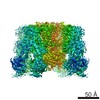
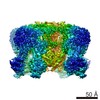
Yorodumi- PDB-5twv: Cryo-EM structure of the pancreatic ATP-sensitive K+ channel SUR1... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 5twv | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the pancreatic ATP-sensitive K+ channel SUR1/Kir6.2 in the presence of ATP and glibenclamide | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSPORT PROTEIN / katp / kir6.2 / sur1 / potassium channel | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationRegulation of insulin secretion / ATP sensitive Potassium channels / ABC-family proteins mediated transport / ATP-activated inward rectifier potassium channel activity / response to resveratrol / inward rectifying potassium channel / sulfonylurea receptor activity / ventricular cardiac muscle tissue development / cell body fiber / CAMKK-AMPK signaling cascade ...Regulation of insulin secretion / ATP sensitive Potassium channels / ABC-family proteins mediated transport / ATP-activated inward rectifier potassium channel activity / response to resveratrol / inward rectifying potassium channel / sulfonylurea receptor activity / ventricular cardiac muscle tissue development / cell body fiber / CAMKK-AMPK signaling cascade / voltage-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of presynaptic membrane potential / regulation of monoatomic ion transmembrane transport / ATPase-coupled monoatomic cation transmembrane transporter activity / inward rectifier potassium channel activity / nervous system process / : / ankyrin binding / Ion homeostasis / response to testosterone / response to ATP / potassium ion import across plasma membrane / response to stress / intercalated disc / action potential / axolemma / voltage-gated potassium channel activity / potassium channel activity / ABC-type transporter activity / heat shock protein binding / potassium ion transmembrane transport / cellular response to nutrient levels / T-tubule / regulation of insulin secretion / acrosomal vesicle / response to ischemia / determination of adult lifespan / positive regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / regulation of membrane potential / potassium ion transport / cellular response to glucose stimulus / negative regulation of insulin secretion / sarcolemma / cellular response to nicotine / glucose metabolic process / cellular response to tumor necrosis factor / response to estradiol / nuclear envelope / presynaptic membrane / transmembrane transporter binding / response to hypoxia / endosome / response to xenobiotic stimulus / neuronal cell body / apoptotic process / glutamatergic synapse / ATP hydrolysis activity / protein-containing complex / ATP binding / metal ion binding / plasma membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Cricetus cricetus (black-bellied hamster) Cricetus cricetus (black-bellied hamster) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 6.3 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Martin, G.M. / Yoshioka, C. / Chen, J.Z. / Shyng, S.L. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2items United States, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2017 Journal: Elife / Year: 2017Title: Cryo-EM structure of the ATP-sensitive potassium channel illuminates mechanisms of assembly and gating. Authors: Gregory M Martin / Craig Yoshioka / Emily A Rex / Jonathan F Fay / Qing Xie / Matthew R Whorton / James Z Chen / Show-Ling Shyng /  Abstract: K channels are metabolic sensors that couple cell energetics to membrane excitability. In pancreatic β-cells, channels formed by SUR1 and Kir6.2 regulate insulin secretion and are the targets of ...K channels are metabolic sensors that couple cell energetics to membrane excitability. In pancreatic β-cells, channels formed by SUR1 and Kir6.2 regulate insulin secretion and are the targets of antidiabetic sulfonylureas. Here, we used cryo-EM to elucidate structural basis of channel assembly and gating. The structure, determined in the presence of ATP and the sulfonylurea glibenclamide, at ~6 Å resolution reveals a closed Kir6.2 tetrameric core with four peripheral SUR1s each anchored to a Kir6.2 by its N-terminal transmembrane domain (TMD0). Intricate interactions between TMD0, the loop following TMD0, and Kir6.2 near the proposed PIP binding site, and where ATP density is observed, suggest SUR1 may contribute to ATP and PIP binding to enhance Kir6.2 sensitivity to both. The SUR1-ABC core is found in an unusual inward-facing conformation whereby the two nucleotide binding domains are misaligned along a two-fold symmetry axis, revealing a possible mechanism by which glibenclamide inhibits channel activity. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  5twv.cif.gz 5twv.cif.gz | 1 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb5twv.ent.gz pdb5twv.ent.gz | 794.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  5twv.json.gz 5twv.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tw/5twv https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tw/5twv ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tw/5twv ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tw/5twv | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 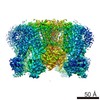 8470MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 43645.719 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #2: Protein | Mass: 178330.516 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Cricetus cricetus (black-bellied hamster) Cricetus cricetus (black-bellied hamster)Gene: ABCC8, SUR / Cell line (production host): INS-1 / Production host:  #3: Chemical | ChemComp-ATP / Has protein modification | Y | Sequence details | Kir6.2: GenBank reference BAA96239.1 | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 81000 X / Nominal defocus max: 3000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1500 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 40 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C4 (4 fold cyclic) | ||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 6.3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 20000 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj






