+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 5bup | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
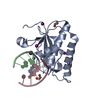
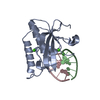
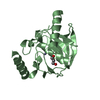
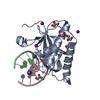
| Title | Crystal structure of the ZP-C domain of mouse ZP2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components | Zona pellucida sperm-binding protein 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | CELL ADHESION / Sperm receptor / immunoglobulin-like domain / zona pellucida / ZP domain / protein polymerization | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationInteraction With Cumulus Cells And The Zona Pellucida / structural constituent of egg coat / acrosin binding / egg coat / prevention of polyspermy / binding of sperm to zona pellucida / multivesicular body / extracellular matrix / endoplasmic reticulum / identical protein binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.251 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.251 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Nishimura, K. / Jovine, L. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Sweden, 7items Sweden, 7items
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2016 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2016Title: A structured interdomain linker directs self-polymerization of human uromodulin. Authors: Marcel Bokhove / Kaoru Nishimura / Martina Brunati / Ling Han / Daniele de Sanctis / Luca Rampoldi / Luca Jovine /    Abstract: Uromodulin (UMOD)/Tamm-Horsfall protein, the most abundant human urinary protein, plays a key role in chronic kidney diseases and is a promising therapeutic target for hypertension. Via its bipartite ...Uromodulin (UMOD)/Tamm-Horsfall protein, the most abundant human urinary protein, plays a key role in chronic kidney diseases and is a promising therapeutic target for hypertension. Via its bipartite zona pellucida module (ZP-N/ZP-C), UMOD forms extracellular filaments that regulate kidney electrolyte balance and innate immunity, as well as protect against renal stones. Moreover, salt-dependent aggregation of UMOD filaments in the urine generates a soluble molecular net that captures uropathogenic bacteria and facilitates their clearance. Despite the functional importance of its homopolymers, no structural information is available on UMOD and how it self-assembles into filaments. Here, we report the crystal structures of polymerization regions of human UMOD and mouse ZP2, an essential sperm receptor protein that is structurally related to UMOD but forms heteropolymers. The structure of UMOD reveals that an extensive hydrophobic interface mediates ZP-N domain homodimerization. This arrangement is required for filament formation and is directed by an ordered ZP-N/ZP-C linker that is not observed in ZP2 but is conserved in the sequence of deafness/Crohn's disease-associated homopolymeric glycoproteins α-tectorin (TECTA) and glycoprotein 2 (GP2). Our data provide an example of how interdomain linker plasticity can modulate the function of structurally similar multidomain proteins. Moreover, the architecture of UMOD rationalizes numerous pathogenic mutations in both UMOD and TECTA genes. #1: Journal: Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. / Year: 1980 Title: Synthesis of zona pellucida proteins by denuded and follicle-enclosed mouse oocytes during culture in vitro. Authors: Bleil, J.D. / Wassarman, P.M. #2: Journal: Dev. Biol. / Year: 1981 Title: Mammalian sperm-egg interaction: fertilization of mouse eggs triggers modification of the major zona pellucida glycoprotein, ZP2. Authors: Bleil, J.D. / Beall, C.F. / Wassarman, P.M. #3: Journal: J. Biol. Chem. / Year: 2003 Title: Structural characterization of native mouse zona pellucida proteins using mass spectrometry. Authors: Boja, E.S. / Hoodbhoy, T. / Fales, H.M. / Dean, J. #4: Journal: Mol. Reprod. Dev. / Year: 2008 Title: Disulfide linkage patterns of pig zona pellucida glycoproteins ZP3 and ZP4. Authors: Kanai, S. / Kitayama, T. / Yonezawa, N. / Sawano, Y. / Tanokura, M. / Nakano, M. #5:  Journal: Cell / Year: 2010 Journal: Cell / Year: 2010Title: Insights into egg coat assembly and egg-sperm interaction from the X-ray structure of full-length ZP3. Authors: Ling Han / Magnus Monné / Hiroki Okumura / Thomas Schwend / Amy L Cherry / David Flot / Tsukasa Matsuda / Luca Jovine /  Abstract: ZP3, a major component of the zona pellucida (ZP) matrix coating mammalian eggs, is essential for fertilization by acting as sperm receptor. By retaining a propeptide that contains a polymerization- ...ZP3, a major component of the zona pellucida (ZP) matrix coating mammalian eggs, is essential for fertilization by acting as sperm receptor. By retaining a propeptide that contains a polymerization-blocking external hydrophobic patch (EHP), we determined the crystal structure of an avian homolog of ZP3 at 2.0 Å resolution. The structure unveils the fold of a complete ZP domain module in a homodimeric arrangement required for secretion and reveals how EHP prevents premature incorporation of ZP3 into the ZP. This suggests mechanisms underlying polymerization and how local structural differences, reflected by alternative disulfide patterns, control the specificity of ZP subunit interaction. Close relative positioning of a conserved O-glycan important for sperm binding and the hypervariable, positively selected C-terminal region of ZP3 suggests a concerted role in the regulation of species-restricted gamete recognition. Alternative conformations of the area around the O-glycan indicate how sperm binding could trigger downstream events via intramolecular signaling. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  5bup.cif.gz 5bup.cif.gz | 109.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb5bup.ent.gz pdb5bup.ent.gz | 84.9 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  5bup.json.gz 5bup.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bu/5bup https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bu/5bup ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bu/5bup ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bu/5bup | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 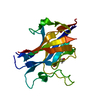
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 23826.770 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Fragment: UNP residues 463-664 / Mutation: K634N, R635A Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P20239 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P20239 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #2: Chemical | | #3: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | Has protein modification | Y | |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION X-RAY DIFFRACTION |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.7 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 54.5 % / Description: Needle |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 293 K / Method: vapor diffusion, hanging drop / pH: 5.5 Details: 25% PEG 3350, 0.1 M sodium acetate pH 5.5, 0.2 M ammonium sulfate, 20% glycerol |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  Diamond Diamond  / Beamline: I02 / Wavelength: 0.97939 Å / Beamline: I02 / Wavelength: 0.97939 Å |
| Detector | Type: DECTRIS PILATUS 6M / Detector: PIXEL / Date: Nov 29, 2014 |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 0.97939 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 2.25057→45.5573 Å / Num. obs: 12293 / % possible obs: 95 % / Redundancy: 3.4 % / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.1022 / Net I/σ(I): 9.74 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 2.251→2.332 Å / Redundancy: 3.3 % / Mean I/σ(I) obs: 1.19 / % possible all: 100 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.251→37.05 Å / SU ML: 0.33 / Cross valid method: FREE R-VALUE / σ(F): 0 / Phase error: 26.02 / Stereochemistry target values: ML MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.251→37.05 Å / SU ML: 0.33 / Cross valid method: FREE R-VALUE / σ(F): 0 / Phase error: 26.02 / Stereochemistry target values: ML
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.6 Å / VDW probe radii: 0.9 Å / Solvent model: FLAT BULK SOLVENT MODEL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 2.251→37.05 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement TLS params. | Details: Chain A / Method: refined / Refine-ID: X-RAY DIFFRACTION
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement TLS group |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj