[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
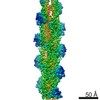
Yorodumi- PDB-5a20: Structure of bacteriophage SPP1 head-to-tail interface filled wit... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 5a20 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of bacteriophage SPP1 head-to-tail interface filled with DNA and tape measure protein | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | VIRAL PROTEIN / TAILED BACTERIOPHAGE / SIPHOVIRIDAE / SPP1 / VIRAL ASSEMBLY / HEAD-TO-TAIL INTERFACE / DNA GATEKEEPER / ALLOSTERIC MECHANISM / CONCERTED REORGANISATION / DIAPHRAGM GATING | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationviral head-tail joining / virus tail fiber assembly / viral DNA genome packaging, headful / virus tail, tube / viral procapsid / viral portal complex / symbiont genome ejection through host cell envelope, long flexible tail mechanism / virus tail / virion component / viral translational frameshifting Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  BACILLUS PHAGE SPP1 (virus) BACILLUS PHAGE SPP1 (virus) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 7.6 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Chaban, Y. / Lurz, R. / Brasiles, S. / Cornilleau, C. / Karreman, M. / Zinn-Justin, S. / Tavares, P. / Orlova, E.V. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2015 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2015Title: Structural rearrangements in the phage head-to-tail interface during assembly and infection. Authors: Yuriy Chaban / Rudi Lurz / Sandrine Brasilès / Charlène Cornilleau / Matthia Karreman / Sophie Zinn-Justin / Paulo Tavares / Elena V Orlova /    Abstract: Many icosahedral viruses use a specialized portal vertex to control genome encapsidation and release from the viral capsid. In tailed bacteriophages, the portal system is connected to a tail ...Many icosahedral viruses use a specialized portal vertex to control genome encapsidation and release from the viral capsid. In tailed bacteriophages, the portal system is connected to a tail structure that provides the pipeline for genome delivery to the host cell. We report the first, to our knowledge, subnanometer structures of the complete portal-phage tail interface that mimic the states before and after DNA release during phage infection. They uncover structural rearrangements associated with intimate protein-DNA interactions. The portal protein gp6 of bacteriophage SPP1 undergoes a concerted reorganization of the structural elements of its central channel during interaction with DNA. A network of protein-protein interactions primes consecutive binding of proteins gp15 and gp16 to extend and close the channel. This critical step that prevents genome leakage from the capsid is achieved by a previously unidentified allosteric mechanism: gp16 binding to two different regions of gp15 drives correct positioning and folding of an inner gp16 loop to interact with equivalent loops of the other gp16 subunits. Together, these loops build a plug that closes the channel. Gp16 then fastens the tail to yield the infectious virion. The gatekeeper system opens for viral genome exit at the beginning of infection but recloses afterward, suggesting a molecular diaphragm-like mechanism to control DNA efflux. The mechanisms described here, controlling the essential steps of phage genome movements during virus assembly and infection, are likely to be conserved among long-tailed phages, the largest group of viruses in the Biosphere. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  5a20.cif.gz 5a20.cif.gz | 297 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb5a20.ent.gz pdb5a20.ent.gz | 233.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  5a20.json.gz 5a20.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/a2/5a20 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/a2/5a20 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/a2/5a20 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/a2/5a20 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  2993MC 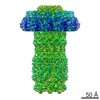 2994C  5a21C C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 57405.355 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  BACILLUS PHAGE SPP1 (virus) / References: UniProt: P54309 BACILLUS PHAGE SPP1 (virus) / References: UniProt: P54309#2: Protein | Mass: 11629.402 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  BACILLUS PHAGE SPP1 (virus) / References: UniProt: Q38584 BACILLUS PHAGE SPP1 (virus) / References: UniProt: Q38584#3: Protein | Mass: 12615.069 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  BACILLUS PHAGE SPP1 (virus) / References: UniProt: O48446 BACILLUS PHAGE SPP1 (virus) / References: UniProt: O48446#4: Protein | | Mass: 15025.014 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  BACILLUS PHAGE SPP1 (virus) / References: UniProt: O48448 BACILLUS PHAGE SPP1 (virus) / References: UniProt: O48448#5: Protein | | Mass: 19172.906 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  BACILLUS PHAGE SPP1 (virus) / References: UniProt: O48449 BACILLUS PHAGE SPP1 (virus) / References: UniProt: O48449 |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: BACTERIOPHAGE SPP1 HEAD- TO-TAIL INTERFACE / Type: VIRUS / Details: MICROGRAPHS SELECTED BY OPTICAL DIFFRACTION |
|---|---|
| Buffer solution | Name: SEE REFERENCE FOR DETAILS / pH: 7.5 / Details: SEE REFERENCE FOR DETAILS |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Details: CARBON |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK II / Cryogen name: ETHANE Details: VITRIFICATION 1 -- CRYOGEN- ETHANE, INSTRUMENT- FEI VITROBOT |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F30 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TECNAI F30 / Date: Oct 9, 2008 |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 39000 X / Nominal defocus max: 3600 nm / Nominal defocus min: 900 nm / Cs: 2 mm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 20 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: KODAK SO-163 FILM |
| Image scans | Num. digital images: 400 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Details: EACH PARTICLE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C6 (6 fold cyclic) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Method: ANGULAR RECONSTITUTION / Resolution: 7.6 Å / Num. of particles: 14000 / Nominal pixel size: 1.2 Å / Actual pixel size: 1.15 Å Magnification calibration: CROSS- -CORRELATION WITH FITTED ATOMIC COORDINATES Details: ATOMIC COORDINATES FOR GP6, GP15, GP16, GP17 WERE OBTAINED FROM PDB FILES 2JES (LEBEDEV ET AL., EMBO J., 2007, 26, 1984), 2KBZ, 2KCA (LHUILLIER ET AL., PROC.NATL.ACAD.SCI. USA, 2009, 106, ...Details: ATOMIC COORDINATES FOR GP6, GP15, GP16, GP17 WERE OBTAINED FROM PDB FILES 2JES (LEBEDEV ET AL., EMBO J., 2007, 26, 1984), 2KBZ, 2KCA (LHUILLIER ET AL., PROC.NATL.ACAD.SCI. USA, 2009, 106, 8507), 2LFP (CHAGOT ET AL., PROTEINS, 2012, 80, 319), CORRESPONDIGLY, AND DOCKED INTO EM ELECTRON DENSITY MAP USING FLEXIBLE FIT. ATOMIC COORDINATES FOR MISSING DOMAINS OF GP6 AND GP17.1. WERE MODELLED USING I-TASSER PROTEIN STRUCTURE PREDICTION SERVER (Y ZHANG, BMC BIOINFORMATICS, 2008, 9, 40) AND DOCKED INTO EM ELECTRON DENSITY MAP USING FLEXIBLE FIT. SUBMISSION BASED ON EXPERIMENTAL DATA FROM EMDB EMD-2993. (DEPOSITION ID: 13331). SEQUENCE N-TERMINAL RESIDUES 1-28 AND C-TERMINAL RESIDUES 468-509 WERE NOT INCLUDED IN THE ATOMIC COORDINATES USED FOR DOCKING DUE TO DIFFICULTIES TRACING CORRESPONDING DENSITIES IN THE EM MAP. ASN 365 IS SUBSTITUTED FOR LYS, SAME AS IN PDB COORDINATE FILE 2JES, WHICH WAS USED AS A STARTING POINT FOR THE FITTING. N-TERMINAL RESIDUES 1-3 ARE OMITTED FROM THE DOCKED GP15 SEQUENCE. PRO 6 IS SUBSTITUTED WITH ARG IN GP16 SEQUENCE, AS IT IS IN THE PDB COORDINATE FILE 2KCA USED FOR FITTING N-TERMINAL RESIDUE 1 IS MISSING FROM THE DOCKED GP17 SEQUENCE. N-TERMINAL RESIDUES 1-8 AND C-TERMINAL RESIDUES 170-177 ARE MISSING FROM THE DOCKED GP17.1 SEQUENCE DUE TO DIFFICULTIES TRACING CORRESPONDING DENSITIES IN THE EM MAP. Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL Details: METHOD--FLEXIBLE REFINEMENT PROTOCOL--X-RAY, NMR, PREDICTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Highest resolution: 7.6 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Highest resolution: 7.6 Å
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 PDBj
PDBj


