[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-4z2m: Crystal structure of human SPT16 Mid-AID/H3-H4 tetramer FACT Hist... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 4z2m | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Crystal structure of human SPT16 Mid-AID/H3-H4 tetramer FACT Histone complex | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Transcription/DNA binding protein / Transcription / Transcription-DNA binding protein complex | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationFACT complex / positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription, elongation / nucleosome disassembly / Pausing and recovery of Tat-mediated HIV elongation / Tat-mediated HIV elongation arrest and recovery / HIV elongation arrest and recovery / Pausing and recovery of HIV elongation / Tat-mediated elongation of the HIV-1 transcript / Formation of HIV-1 elongation complex containing HIV-1 Tat / Formation of HIV elongation complex in the absence of HIV Tat ...FACT complex / positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription, elongation / nucleosome disassembly / Pausing and recovery of Tat-mediated HIV elongation / Tat-mediated HIV elongation arrest and recovery / HIV elongation arrest and recovery / Pausing and recovery of HIV elongation / Tat-mediated elongation of the HIV-1 transcript / Formation of HIV-1 elongation complex containing HIV-1 Tat / Formation of HIV elongation complex in the absence of HIV Tat / nucleosome binding / negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Elongation / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / Formation of RNA Pol II elongation complex / Chromatin modifying enzymes / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / CENP-A containing nucleosome / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / RNA Polymerase II Pre-transcription Events / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / telomere organization / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected pyrimidine / Cleavage of the damaged pyrimidine / Interleukin-7 signaling / epigenetic regulation of gene expression / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Opening / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / Meiotic synapsis / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by the Human Silencing Hub (HUSH) complex / DNA methylation / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / Chromatin modifications during the maternal to zygotic transition (MZT) / SIRT1 negatively regulates rRNA expression / HCMV Late Events / ERCC6 (CSB) and EHMT2 (G9a) positively regulate rRNA expression / PRC2 methylates histones and DNA / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by KRAB-ZFP proteins / Defective pyroptosis / TP53 Regulates Transcription of DNA Repair Genes / Negative Regulation of CDH1 Gene Transcription / HDACs deacetylate histones / transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / Formation of the beta-catenin:TCF transactivating complex / Activated PKN1 stimulates transcription of AR (androgen receptor) regulated genes KLK2 and KLK3 / HDMs demethylate histones / RUNX1 regulates genes involved in megakaryocyte differentiation and platelet function / G2/M DNA damage checkpoint / NoRC negatively regulates rRNA expression / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / PKMTs methylate histone lysines / DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence / Pre-NOTCH Transcription and Translation / Meiotic recombination / Activation of anterior HOX genes in hindbrain development during early embryogenesis / Transcriptional regulation of granulopoiesis / RMTs methylate histone arginines / HCMV Early Events / structural constituent of chromatin / nucleosome / nucleosome assembly / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / HATs acetylate histones / RUNX1 regulates transcription of genes involved in differentiation of HSCs / Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production / MLL4 and MLL3 complexes regulate expression of PPARG target genes in adipogenesis and hepatic steatosis / chromatin organization / Processing of DNA double-strand break ends / Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP) / Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / Regulation of TP53 Activity through Phosphorylation / transcription by RNA polymerase II / DNA replication / chromosome, telomeric region / cadherin binding / Amyloid fiber formation / protein heterodimerization activity / DNA repair / protein-containing complex / DNA binding / RNA binding / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / nucleoplasm / membrane / nucleus Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.981 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.981 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Tsunaka, Y. / Fujiwara, Y. / Oyama, T. / Hirose, S. / Morikawa, K. | ||||||
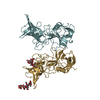
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Genes Dev / Year: 2016 Journal: Genes Dev / Year: 2016Title: Integrated molecular mechanism directing nucleosome reorganization by human FACT. Authors: Yasuo Tsunaka / Yoshie Fujiwara / Takuji Oyama / Susumu Hirose / Kosuke Morikawa /  Abstract: Facilitates chromatin transcription (FACT) plays essential roles in chromatin remodeling during DNA transcription, replication, and repair. Our structural and biochemical studies of human FACT- ...Facilitates chromatin transcription (FACT) plays essential roles in chromatin remodeling during DNA transcription, replication, and repair. Our structural and biochemical studies of human FACT-histone interactions present precise views of nucleosome reorganization, conducted by the FACT-SPT16 (suppressor of Ty 16) Mid domain and its adjacent acidic AID segment. AID accesses the H2B N-terminal basic region exposed by partial unwrapping of the nucleosomal DNA, thereby triggering the invasion of FACT into the nucleosome. The crystal structure of the Mid domain complexed with an H3-H4 tetramer exhibits two separate contact sites; the Mid domain forms a novel intermolecular β structure with H4. At the other site, the Mid-H2A steric collision on the H2A-docking surface of the H3-H4 tetramer within the nucleosome induces H2A-H2B displacement. This integrated mechanism results in disrupting the H3 αN helix, which is essential for retaining the nucleosomal DNA ends, and hence facilitates DNA stripping from histone. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  4z2m.cif.gz 4z2m.cif.gz | 242.6 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb4z2m.ent.gz pdb4z2m.ent.gz | 195.9 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  4z2m.json.gz 4z2m.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/z2/4z2m https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/z2/4z2m ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/z2/4z2m ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/z2/4z2m | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  4z2nC 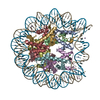 2cv5S C: citing same article ( S: Starting model for refinement |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 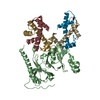
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 33372.195 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Fragment: UNP residues 644-930 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: SUPT16H, FACT140, FACTP140 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: SUPT16H, FACT140, FACTP140 / Production host:  Baculovirus expression vector pFastBac1-HM / References: UniProt: Q9Y5B9 Baculovirus expression vector pFastBac1-HM / References: UniProt: Q9Y5B9 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 11919.018 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Fragment: UNP residues 35-136 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HIST1H3A / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HIST1H3A / Production host:  Baculovirus expression vector pFastBac1-HM / References: UniProt: P68431 Baculovirus expression vector pFastBac1-HM / References: UniProt: P68431#3: Protein | Mass: 11394.426 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HIST1H4A / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HIST1H4A / Production host:  Baculovirus expression vector pFastBac1-HM / References: UniProt: P62805 Baculovirus expression vector pFastBac1-HM / References: UniProt: P62805 |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION X-RAY DIFFRACTION |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.68 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 54.12 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 277 K / Method: vapor diffusion, hanging drop / pH: 7 Details: 10% PEG400, 0.9-1.1 M Imidazole, 100-150 mM L-histidine |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  SPring-8 SPring-8  / Beamline: BL44XU / Wavelength: 0.9 Å / Beamline: BL44XU / Wavelength: 0.9 Å |
| Detector | Type: RAYONIX MX-300 / Detector: CCD / Date: Jul 18, 2014 |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 0.9 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 2.98→50 Å / Num. obs: 17819 / % possible obs: 97.7 % / Redundancy: 6.8 % / Rsym value: 0.078 / Net I/σ(I): 17.4 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: 2CV5 Resolution: 2.981→46.963 Å / SU ML: 0.36 / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / σ(F): 1.35 / Phase error: 25.86 / Stereochemistry target values: ML
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.11 Å / Solvent model: FLAT BULK SOLVENT MODEL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 2.981→46.963 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 PDBj
PDBj













