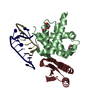
Entry Database : PDB / ID : 3qq8Title Crystal structure of p97-N in complex with FAF1-UBX FAS-associated factor 1 Transitional endoplasmic reticulum ATPase Keywords / / / / / / Function / homology Function Domain/homology Component
/ / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / Biological species Homo sapiens (human)Method / / / / Resolution : 2 Å Authors Haenzelmann, P. / Schindelin, H. Journal : Structure / Year : 2011Title : Hierarchical Binding of Cofactors to the AAA ATPase p97.Authors : Hanzelmann, P. / Buchberger, A. / Schindelin, H. History Deposition Feb 15, 2011 Deposition site / Processing site Revision 1.0 Jun 22, 2011 Provider / Type Revision 1.1 Jul 13, 2011 Group Revision 1.2 Sep 13, 2023 Group Data collection / Database references ... Data collection / Database references / Derived calculations / Refinement description Category chem_comp_atom / chem_comp_bond ... chem_comp_atom / chem_comp_bond / database_2 / pdbx_initial_refinement_model / struct_ref_seq_dif / struct_site Item _database_2.pdbx_DOI / _database_2.pdbx_database_accession ... _database_2.pdbx_DOI / _database_2.pdbx_database_accession / _struct_ref_seq_dif.details / _struct_site.pdbx_auth_asym_id / _struct_site.pdbx_auth_comp_id / _struct_site.pdbx_auth_seq_id
Show all Show less
 Open data
Open data Basic information
Basic information Components
Components Keywords
Keywords Function and homology information
Function and homology information Homo sapiens (human)
Homo sapiens (human) X-RAY DIFFRACTION /
X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON /
SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT /
MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT /  molecular replacement / Resolution: 2 Å
molecular replacement / Resolution: 2 Å  Authors
Authors Citation
Citation Journal: Structure / Year: 2011
Journal: Structure / Year: 2011 Structure visualization
Structure visualization Molmil
Molmil Jmol/JSmol
Jmol/JSmol Downloads & links
Downloads & links Download
Download 3qq8.cif.gz
3qq8.cif.gz PDBx/mmCIF format
PDBx/mmCIF format pdb3qq8.ent.gz
pdb3qq8.ent.gz PDB format
PDB format 3qq8.json.gz
3qq8.json.gz PDBx/mmJSON format
PDBx/mmJSON format Other downloads
Other downloads https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qq/3qq8
https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qq/3qq8 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qq/3qq8
ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qq/3qq8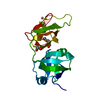



 Links
Links Assembly
Assembly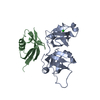
 Components
Components Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: VCP / Production host:
Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: VCP / Production host: 
 Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: FAF1, UBXD12, UBXN3A, CGI-03 / Production host:
Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: FAF1, UBXD12, UBXN3A, CGI-03 / Production host: 
 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1
X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1  Sample preparation
Sample preparation SYNCHROTRON / Site:
SYNCHROTRON / Site:  BESSY
BESSY  / Beamline: 14.1 / Wavelength: 0.9 Å
/ Beamline: 14.1 / Wavelength: 0.9 Å molecular replacement
molecular replacement Processing
Processing MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT
MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



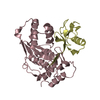






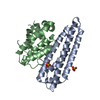

 PDBj
PDBj
















