[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
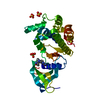
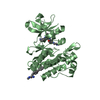
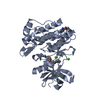
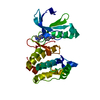
Yorodumi- PDB-1fpu: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF ABL KINASE DOMAIN IN COMPLEX WITH A SMALL MO... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 1fpu | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF ABL KINASE DOMAIN IN COMPLEX WITH A SMALL MOLECULE INHIBITOR | ||||||
 Components Components | PROTO-ONCOGENE TYROSINE-PROTEIN KINASE ABL | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSFERASE / kinase / kinase inhibitor / STI-571 / activation loop | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationRole of ABL in ROBO-SLIT signaling / HDR through Single Strand Annealing (SSA) / RHO GTPases Activate WASPs and WAVEs / Cyclin D associated events in G1 / MLL4 and MLL3 complexes regulate expression of PPARG target genes in adipogenesis and hepatic steatosis / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / Turbulent (oscillatory, disturbed) flow shear stress activates signaling by PIEZO1 and integrins in endothelial cells / protein localization to cytoplasmic microtubule plus-end / DNA conformation change / DN4 thymocyte differentiation ...Role of ABL in ROBO-SLIT signaling / HDR through Single Strand Annealing (SSA) / RHO GTPases Activate WASPs and WAVEs / Cyclin D associated events in G1 / MLL4 and MLL3 complexes regulate expression of PPARG target genes in adipogenesis and hepatic steatosis / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / Turbulent (oscillatory, disturbed) flow shear stress activates signaling by PIEZO1 and integrins in endothelial cells / protein localization to cytoplasmic microtubule plus-end / DNA conformation change / DN4 thymocyte differentiation / response to epinephrine / phospholipase C-inhibiting G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / podocyte apoptotic process / RUNX1 regulates transcription of genes involved in differentiation of HSCs / delta-catenin binding / transitional one stage B cell differentiation / regulation of postsynaptic specialization assembly / regulation of modification of synaptic structure / cerebellum morphogenesis / regulation of cellular senescence / neuroepithelial cell differentiation / B cell proliferation involved in immune response / Regulation of actin dynamics for phagocytic cup formation / positive regulation of extracellular matrix organization / positive regulation of Wnt signaling pathway, planar cell polarity pathway / microspike assembly / B-1 B cell homeostasis / neuropilin signaling pathway / neuropilin binding / regulation of extracellular matrix organization / Myogenesis / bubble DNA binding / positive regulation of establishment of T cell polarity / activated T cell proliferation / positive regulation of blood vessel branching / proline-rich region binding / negative regulation of mitotic cell cycle / regulation of Cdc42 protein signal transduction / circulatory system development / mitogen-activated protein kinase binding / positive regulation of cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis / positive regulation of dendrite development / syntaxin binding / alpha-beta T cell differentiation / positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation / regulation of axon extension / regulation of T cell differentiation / negative regulation of cell-cell adhesion / neuromuscular process controlling balance / positive regulation of osteoblast proliferation / platelet-derived growth factor receptor-beta signaling pathway / platelet-derived growth factor receptor signaling pathway / cell leading edge / Bergmann glial cell differentiation / regulation of microtubule polymerization / B cell proliferation / myoblast proliferation / negative regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation / negative regulation of cellular senescence / positive regulation of vasoconstriction / associative learning / positive regulation of focal adhesion assembly / negative regulation of BMP signaling pathway / canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / cardiac muscle cell proliferation / ephrin receptor signaling pathway / phagocytosis / BMP signaling pathway / cellular response to transforming growth factor beta stimulus / negative regulation of endothelial cell apoptotic process / positive regulation of T cell migration / endothelial cell migration / negative regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / spleen development / ephrin receptor binding / four-way junction DNA binding / positive regulation of stress fiber assembly / signal transduction in response to DNA damage / ruffle / ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / phosphotyrosine residue binding / actin filament polymerization / positive regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading / substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading / positive regulation of mitotic cell cycle / positive regulation of interleukin-2 production / SH2 domain binding / peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation / thymus development / protein kinase C binding / response to endoplasmic reticulum stress / positive regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / integrin-mediated signaling pathway / post-embryonic development / B cell receptor signaling pathway / regulation of actin cytoskeleton organization / non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine kinase activity / non-specific protein-tyrosine kinase / establishment of localization in cell / neural tube closure Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / Resolution: 2.4 Å SYNCHROTRON / Resolution: 2.4 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Schindler, T. / Bornmann, W. / Pellicena, P. / Miller, W.T. / Clarkson, B. / Kuriyan, J. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2000 Journal: Science / Year: 2000Title: Structural mechanism for STI-571 inhibition of abelson tyrosine kinase. Authors: Schindler, T. / Bornmann, W. / Pellicena, P. / Miller, W.T. / Clarkson, B. / Kuriyan, J. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  1fpu.cif.gz 1fpu.cif.gz | 122.8 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb1fpu.ent.gz pdb1fpu.ent.gz | 95.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  1fpu.json.gz 1fpu.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fp/1fpu https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fp/1fpu ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fp/1fpu ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/fp/1fpu | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Similar structure data |
|---|
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 
| ||||||||
| 2 | 
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
| ||||||||
| Details | There are two kinase molecules in the asymmetric unit. The biological assembly is a monomer. |
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 33743.523 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Fragment: KINASE DOMAIN Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #2: Chemical | #3: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.29 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 46.24 % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 277 K / Method: vapor diffusion, hanging drop / pH: 6.2 Details: PEG 4000, magnesium chloride, mes, pH 6.2, VAPOR DIFFUSION, HANGING DROP, temperature 277K | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal grow | *PLUS Temperature: 4 ℃ / pH: 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Components of the solutions | *PLUS
|
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 103 K |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  NSLS NSLS  / Beamline: X25 / Wavelength: 0.9393 / Beamline: X25 / Wavelength: 0.9393 |
| Detector | Type: BRANDEIS - B4 / Detector: CCD / Date: Sep 5, 1999 |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 0.9393 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 2.4→99 Å / Num. obs: 221636 / % possible obs: 98.7 % / Redundancy: 9.3 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 61 Å2 / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.068 / Net I/σ(I): 30.9 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 2.4→2.49 Å / Redundancy: 5.7 % / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.216 / Num. unique all: 2190 / % possible all: 90.6 |
| Reflection | *PLUS Num. obs: 24122 / Num. measured all: 221636 |
| Reflection shell | *PLUS % possible obs: 90.6 % |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Resolution: 2.4→99 Å / Stereochemistry target values: Engh & Huber Details: Tight, noncrystallographic restraints were utilized throughout the refinement so that the final r.m.s. deviation between the two molecules is 0.05 and 0.04 Angstrom for the N-terminal and ...Details: Tight, noncrystallographic restraints were utilized throughout the refinement so that the final r.m.s. deviation between the two molecules is 0.05 and 0.04 Angstrom for the N-terminal and the C-terminal lobes, respectively (excluding residues 229 to 337, 252, 262, 271, 294, 306, 404, 447, 450, 466, and 491, which were built in different conformations in the two molecules). The electron density map was significantly weaker for one of the two molecules in the asymmetric unit (chain ID B), and all the analysis (cf. primary citation) relied on the better-ordered one (chain ID A).
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 2.4→99 Å
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Software | *PLUS Name: CNS / Classification: refinement | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | *PLUS Highest resolution: 2.4 Å / Lowest resolution: 99 Å / Rfactor obs: 0.239 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | *PLUS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | *PLUS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints | *PLUS Type: c_angle_deg / Dev ideal: 1.4 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj









