[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-9699: Cryo-EM structure of the CMV-stalled human 80S ribosome (Structure i) -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-9699 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the CMV-stalled human 80S ribosome (Structure i) | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationtranslation at presynapse / exit from mitosis / eukaryotic 80S initiation complex / negative regulation of protein neddylation / response to insecticide / optic nerve development / negative regulation of endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response / regulation of G1 to G0 transition / axial mesoderm development / oxidized pyrimidine DNA binding ...translation at presynapse / exit from mitosis / eukaryotic 80S initiation complex / negative regulation of protein neddylation / response to insecticide / optic nerve development / negative regulation of endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response / regulation of G1 to G0 transition / axial mesoderm development / oxidized pyrimidine DNA binding / response to TNF agonist / negative regulation of formation of translation preinitiation complex / positive regulation of base-excision repair / regulation of translation involved in cellular response to UV / ribosomal protein import into nucleus / positive regulation of respiratory burst involved in inflammatory response / positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage / protein-DNA complex disassembly / positive regulation of gastrulation / regulation of adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / 90S preribosome assembly / protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor activity / IRE1-RACK1-PP2A complex / positive regulation of endodeoxyribonuclease activity / nucleolus organization / positive regulation of Golgi to plasma membrane protein transport / positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage by p53 class mediator / retinal ganglion cell axon guidance / TNFR1-mediated ceramide production / negative regulation of RNA splicing / negative regulation of DNA repair / GAIT complex / positive regulation of DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator / TORC2 complex binding / alpha-beta T cell differentiation / G1 to G0 transition / supercoiled DNA binding / neural crest cell differentiation / positive regulation of ubiquitin-protein transferase activity / NF-kappaB complex / cysteine-type endopeptidase activator activity involved in apoptotic process / oxidized purine DNA binding / negative regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to hydrogen peroxide / negative regulation of bicellular tight junction assembly / regulation of establishment of cell polarity / ubiquitin-like protein conjugating enzyme binding / middle ear morphogenesis / negative regulation of phagocytosis / rRNA modification in the nucleus and cytosol / Formation of the ternary complex, and subsequently, the 43S complex / erythrocyte homeostasis / cytoplasmic side of rough endoplasmic reticulum membrane / laminin receptor activity / negative regulation of ubiquitin protein ligase activity / ion channel inhibitor activity / protein kinase A binding / pigmentation / Ribosomal scanning and start codon recognition / homeostatic process / Translation initiation complex formation / positive regulation of mitochondrial depolarization / macrophage chemotaxis / positive regulation of T cell receptor signaling pathway / fibroblast growth factor binding / negative regulation of Wnt signaling pathway / lung morphogenesis / male meiosis I / monocyte chemotaxis / positive regulation of activated T cell proliferation / positive regulation of natural killer cell proliferation / negative regulation of translational frameshifting / Protein hydroxylation / TOR signaling / BH3 domain binding / regulation of cell division / SARS-CoV-1 modulates host translation machinery / mTORC1-mediated signalling / cellular response to ethanol / iron-sulfur cluster binding / Peptide chain elongation / Selenocysteine synthesis / Formation of a pool of free 40S subunits / positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway by p53 class mediator / endonucleolytic cleavage to generate mature 3'-end of SSU-rRNA from (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / Eukaryotic Translation Termination / ubiquitin ligase inhibitor activity / blastocyst development / cellular response to actinomycin D / Response of EIF2AK4 (GCN2) to amino acid deficiency / positive regulation of signal transduction by p53 class mediator / negative regulation of ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / protein serine/threonine kinase inhibitor activity / Viral mRNA Translation / negative regulation of respiratory burst involved in inflammatory response / Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) independent of the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) / protein localization to nucleus / GTP hydrolysis and joining of the 60S ribosomal subunit / L13a-mediated translational silencing of Ceruloplasmin expression / Major pathway of rRNA processing in the nucleolus and cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
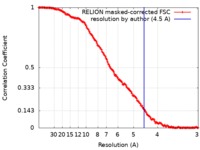
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.5 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Yokohama T / Shigematsu H / Shirouzu M / Imataka H / Ito T | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2019 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2019Title: HCV IRES Captures an Actively Translating 80S Ribosome. Authors: Takeshi Yokoyama / Kodai Machida / Wakana Iwasaki / Tomoaki Shigeta / Madoka Nishimoto / Mari Takahashi / Ayako Sakamoto / Mayumi Yonemochi / Yoshie Harada / Hideki Shigematsu / Mikako ...Authors: Takeshi Yokoyama / Kodai Machida / Wakana Iwasaki / Tomoaki Shigeta / Madoka Nishimoto / Mari Takahashi / Ayako Sakamoto / Mayumi Yonemochi / Yoshie Harada / Hideki Shigematsu / Mikako Shirouzu / Hisashi Tadakuma / Hiroaki Imataka / Takuhiro Ito /  Abstract: Translation initiation of hepatitis C virus (HCV) genomic RNA is induced by an internal ribosome entry site (IRES). Our cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) analysis revealed that the HCV IRES binds to ...Translation initiation of hepatitis C virus (HCV) genomic RNA is induced by an internal ribosome entry site (IRES). Our cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) analysis revealed that the HCV IRES binds to the solvent side of the 40S platform of the cap-dependently translating 80S ribosome. Furthermore, we obtained the cryo-EM structures of the HCV IRES capturing the 40S subunit of the IRES-dependently translating 80S ribosome. In the elucidated structures, the HCV IRES "body," consisting of domain III except for subdomain IIIb, binds to the 40S subunit, while the "long arm," consisting of domain II, remains flexible and does not impede the ongoing translation. Biochemical experiments revealed that the cap-dependently translating ribosome becomes a better substrate for the HCV IRES than the free ribosome. Therefore, the HCV IRES is likely to efficiently induce the translation initiation of its downstream mRNA with the captured translating ribosome as soon as the ongoing translation terminates. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_9699.map.gz emd_9699.map.gz | 264.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-9699-v30.xml emd-9699-v30.xml emd-9699.xml emd-9699.xml | 9.1 KB 9.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_9699_fsc.xml emd_9699_fsc.xml | 14.7 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_9699.png emd_9699.png | 153.6 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-9699 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-9699 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-9699 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-9699 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_9699_validation.pdf.gz emd_9699_validation.pdf.gz | 78.5 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_9699_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_9699_full_validation.pdf.gz | 77.7 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_9699_validation.xml.gz emd_9699_validation.xml.gz | 493 B | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-9699 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-9699 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-9699 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-9699 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 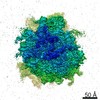 9701C  9702C  9703C  9704C  6ip5C  6ip6C  6ip8C C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_9699.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 282.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_9699.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 282.6 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.49 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Human 80S ribosome
| Entire | Name: Human 80S ribosome |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Human 80S ribosome
| Supramolecule | Name: Human 80S ribosome / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: CONTINUOUS |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TECNAI ARCTICA |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 50.0 µm / Calibrated magnification: 33557 / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal magnification: 23500 |
| Sample stage | Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



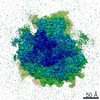

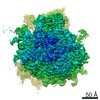

































 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)