[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-9042: Yeast 26S proteasome bound to ubiquitinated substrate (1D* motor ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-9042 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
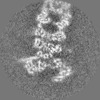
| Title | Yeast 26S proteasome bound to ubiquitinated substrate (1D* motor state) | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Yeast 26S proteasome bound to ubiquitinated substrate (1D* motor state) | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | 26S Proteasome / ATPase / AAA+ / Protease / Motor protein / Ubiquitin | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmitotic cell cycle phase transition / proteasome regulatory particle assembly / proteasome-activating activity / proteasome regulatory particle, base subcomplex / ER-Phagosome pathway / Antigen processing: Ub, ATP-independent proteasomal degradation / protein-containing complex localization / cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase regulator activity / proteasome core complex assembly / nuclear outer membrane-endoplasmic reticulum membrane network ...mitotic cell cycle phase transition / proteasome regulatory particle assembly / proteasome-activating activity / proteasome regulatory particle, base subcomplex / ER-Phagosome pathway / Antigen processing: Ub, ATP-independent proteasomal degradation / protein-containing complex localization / cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase regulator activity / proteasome core complex assembly / nuclear outer membrane-endoplasmic reticulum membrane network / Proteasome assembly / Cross-presentation of soluble exogenous antigens (endosomes) / TNFR2 non-canonical NF-kB pathway / nonfunctional rRNA decay / Ubiquitin-Mediated Degradation of Phosphorylated Cdc25A / Regulation of PTEN stability and activity / proteasomal ubiquitin-independent protein catabolic process / CDK-mediated phosphorylation and removal of Cdc6 / FBXL7 down-regulates AURKA during mitotic entry and in early mitosis / KEAP1-NFE2L2 pathway / Neddylation / peptide catabolic process / Orc1 removal from chromatin / MAPK6/MAPK4 signaling / proteasome storage granule / Antigen processing: Ubiquitination & Proteasome degradation / positive regulation of RNA polymerase II transcription preinitiation complex assembly / Ub-specific processing proteases / proteasome core complex, alpha-subunit complex / ERAD pathway / Neutrophil degranulation / proteasome complex / nucleotide-excision repair / positive regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / positive regulation of protein catabolic process / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / chromatin remodeling / protein domain specific binding / cell division / mRNA binding / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / mitochondrion / ATP binding / identical protein binding / nucleus / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.43 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | de la Pena AH / Goodall EA | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2 items United States, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2018 Journal: Science / Year: 2018Title: Substrate-engaged 26 proteasome structures reveal mechanisms for ATP-hydrolysis-driven translocation. Authors: Andres H de la Peña / Ellen A Goodall / Stephanie N Gates / Gabriel C Lander / Andreas Martin /  Abstract: The 26 proteasome is the primary eukaryotic degradation machine and thus is critically involved in numerous cellular processes. The heterohexameric adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase) motor of the ...The 26 proteasome is the primary eukaryotic degradation machine and thus is critically involved in numerous cellular processes. The heterohexameric adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase) motor of the proteasome unfolds and translocates targeted protein substrates into the open gate of a proteolytic core while a proteasomal deubiquitinase concomitantly removes substrate-attached ubiquitin chains. However, the mechanisms by which ATP hydrolysis drives the conformational changes responsible for these processes have remained elusive. Here we present the cryo-electron microscopy structures of four distinct conformational states of the actively ATP-hydrolyzing, substrate-engaged 26 proteasome. These structures reveal how mechanical substrate translocation accelerates deubiquitination and how ATP-binding, -hydrolysis, and phosphate-release events are coordinated within the AAA+ (ATPases associated with diverse cellular activities) motor to induce conformational changes and propel the substrate through the central pore. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_9042.map.gz emd_9042.map.gz | 12.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-9042-v30.xml emd-9042-v30.xml emd-9042.xml emd-9042.xml | 56.9 KB 56.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
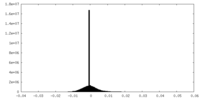
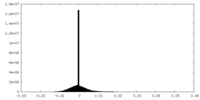
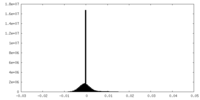
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_9042_fsc_1.xml emd_9042_fsc_1.xml emd_9042_fsc_2.xml emd_9042_fsc_2.xml emd_9042_fsc_3.xml emd_9042_fsc_3.xml | 12.1 KB 12.2 KB 12.1 KB | Display Display Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_9042.png emd_9042.png | 87.8 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_9042_msk_1.map emd_9042_msk_1.map emd_9042_msk_2.map emd_9042_msk_2.map emd_9042_msk_3.map emd_9042_msk_3.map | 149.9 MB 149.9 MB 149.9 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-9042.cif.gz emd-9042.cif.gz | 10.1 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_9042_additional_1.map.gz emd_9042_additional_1.map.gz emd_9042_additional_2.map.gz emd_9042_additional_2.map.gz emd_9042_additional_3.map.gz emd_9042_additional_3.map.gz emd_9042_additional_4.map.gz emd_9042_additional_4.map.gz emd_9042_additional_5.map.gz emd_9042_additional_5.map.gz emd_9042_additional_6.map.gz emd_9042_additional_6.map.gz emd_9042_additional_7.map.gz emd_9042_additional_7.map.gz emd_9042_additional_8.map.gz emd_9042_additional_8.map.gz emd_9042_additional_9.map.gz emd_9042_additional_9.map.gz | 118.3 MB 140.3 MB 118.4 MB 118.4 MB 118.5 MB 140.2 MB 140.5 MB 118.4 MB 118.3 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-9042 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-9042 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-9042 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-9042 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6ef0MC 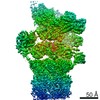 9043C 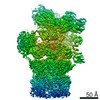 9044C  9045C  6ef1C  6ef2C  6ef3C C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_9042.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 149.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_9042.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 149.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Yeast 26S proteasome bound to ubiquitinated substrate (1D* motor state) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
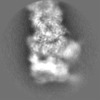
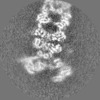
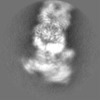
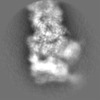
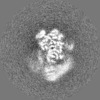
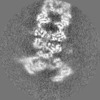
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.03 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
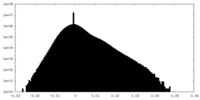
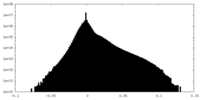
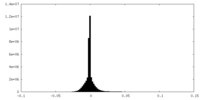
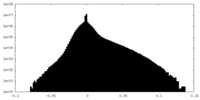
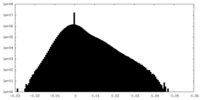
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
+Mask #1
+Mask #2
+Mask #3
+Additional map: Motor (half 1)
+Additional map: Motor (sharpened)
+Additional map: Global (half 2)
+Additional map: Global (half 1)
+Additional map: Alpha ring (half 1)
+Additional map: Alpha ring (sharpened)
+Additional map: Global (sharpened)
+Additional map: Alpha ring (half 2)
+Additional map: Motor (half 2)
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : Substrate-engaged 26S proteasome in the 1D* state
+Supramolecule #1: Substrate-engaged 26S proteasome in the 1D* state
+Supramolecule #2: proteasome
+Supramolecule #3: substrate
+Macromolecule #1: Proteasome subunit alpha type-1
+Macromolecule #2: Proteasome subunit alpha type-2
+Macromolecule #3: Proteasome subunit alpha type-3
+Macromolecule #4: Proteasome subunit alpha type-4
+Macromolecule #5: Proteasome subunit alpha type-5
+Macromolecule #6: Proteasome subunit alpha type-6
+Macromolecule #7: Probable proteasome subunit alpha type-7
+Macromolecule #8: 26S proteasome regulatory subunit 7 homolog
+Macromolecule #9: 26S proteasome regulatory subunit 4 homolog
+Macromolecule #10: 26S proteasome regulatory subunit 8 homolog
+Macromolecule #11: 26S proteasome regulatory subunit 6B homolog
+Macromolecule #12: 26S proteasome subunit RPT4
+Macromolecule #13: 26S proteasome regulatory subunit 6A
+Macromolecule #14: model substrate polypeptide
+Macromolecule #15: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
+Macromolecule #16: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 25 mg/mL | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.6 Component:
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R2/2 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 400 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 20 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR | ||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 90 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: HOMEMADE PLUNGER Details: specimens were manually blotted with Whatman #1 filter paper. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Details | 26S proteasomes were diluted to a concentration of 20 micromolar in a buffer with an ATP regeneration system, and 6 mM ortho-phenanthroline. This solution was mixed with an equal volume of 50 micromolar ubiquitinated model substrate |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Details | images were acquired in nanoprobe mode |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Digitization - Dimensions - Width: 3710 pixel / Digitization - Dimensions - Height: 3838 pixel / Digitization - Frames/image: 1-25 / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 11656 / Average exposure time: 6.25 sec. / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 70.0 µm / Calibrated defocus max: -3.0 µm / Calibrated defocus min: -1.5 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: -2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: -1.0 µm / Nominal magnification: 29000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






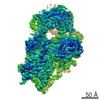



















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)