[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-8706: Cryo-EM structure of yeast cytoplasmic dynein with Walker B mutat... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-8706 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
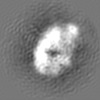
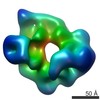
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of yeast cytoplasmic dynein with Walker B mutation at AAA3 in presence of ATP-VO4 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Yeast cytoplasmic dynein with Walker B mutation at AAA3 in presence of ATP-VO4 | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | cytoplasmic dynein / lis1 / MOTOR PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmicrotubule sliding / karyogamy / nuclear migration along microtubule / astral microtubule / establishment of mitotic spindle localization / spindle pole body / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / microtubule associated complex / dynein light intermediate chain binding / cytoplasmic dynein complex ...microtubule sliding / karyogamy / nuclear migration along microtubule / astral microtubule / establishment of mitotic spindle localization / spindle pole body / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / microtubule associated complex / dynein light intermediate chain binding / cytoplasmic dynein complex / nuclear migration / dynein intermediate chain binding / dynein complex binding / establishment of mitotic spindle orientation / mitotic sister chromatid segregation / cytoplasmic microtubule / cytoplasmic microtubule organization / Neutrophil degranulation / mitotic spindle organization / spindle pole / cell cortex / microtubule / cell division / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 10.5 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Cianfrocco MA / DeSantis ME | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2 items United States, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell / Year: 2017 Journal: Cell / Year: 2017Title: Lis1 Has Two Opposing Modes of Regulating Cytoplasmic Dynein. Authors: Morgan E DeSantis / Michael A Cianfrocco / Zaw Min Htet / Phuoc Tien Tran / Samara L Reck-Peterson / Andres E Leschziner /  Abstract: Regulation is central to the functional versatility of cytoplasmic dynein, a motor involved in intracellular transport, cell division, and neurodevelopment. Previous work established that Lis1, a ...Regulation is central to the functional versatility of cytoplasmic dynein, a motor involved in intracellular transport, cell division, and neurodevelopment. Previous work established that Lis1, a conserved regulator of dynein, binds to its motor domain and induces a tight microtubule-binding state in dynein. The work we present here-a combination of biochemistry, single-molecule assays, and cryoelectron microscopy-led to the surprising discovery that Lis1 has two opposing modes of regulating dynein, being capable of inducing both low and high affinity for the microtubule. We show that these opposing modes depend on the stoichiometry of Lis1 binding to dynein and that this stoichiometry is regulated by the nucleotide state of dynein's AAA3 domain. The low-affinity state requires Lis1 to also bind to dynein at a novel conserved site, mutation of which disrupts Lis1's function in vivo. We propose a new model for the regulation of dynein by Lis1. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_8706.map.gz emd_8706.map.gz | 7.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-8706-v30.xml emd-8706-v30.xml emd-8706.xml emd-8706.xml | 14.9 KB 14.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_8706.png emd_8706.png | 58 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-8706.cif.gz emd-8706.cif.gz | 7.2 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8706 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8706 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8706 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8706 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 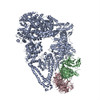 5vljMC 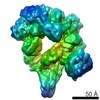 8673C  5vh9C C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_8706.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_8706.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Yeast cytoplasmic dynein with Walker B mutation at AAA3 in presence of ATP-VO4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
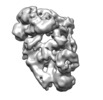
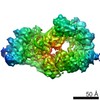
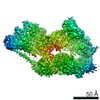
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 2.4 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Complex between yeast dynein (AAA3 Walker B) with Lis1 in the pre...
| Entire | Name: Complex between yeast dynein (AAA3 Walker B) with Lis1 in the presence of ATP.VO4 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Complex between yeast dynein (AAA3 Walker B) with Lis1 in the pre...
| Supramolecule | Name: Complex between yeast dynein (AAA3 Walker B) with Lis1 in the presence of ATP.VO4 type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 444 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Dynein heavy chain, cytoplasmic
| Macromolecule | Name: Dynein heavy chain, cytoplasmic / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 272.66625 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: VQFYWLDLYG ILGENLDIQN FLPLETSKFK SLTSEYKMIT TRAFQLDTTI EVIHIPNFDT TLKLTIDSLK MIKSSLSTFL ERQRRQFPR FYFLGNDDLL KIIGSGKHHD QVSKFMKKMF GSIESIIFFE DSITGVRSVE GEVLNLNEKI ELKDSIQAQE W LNILDTEI ...String: VQFYWLDLYG ILGENLDIQN FLPLETSKFK SLTSEYKMIT TRAFQLDTTI EVIHIPNFDT TLKLTIDSLK MIKSSLSTFL ERQRRQFPR FYFLGNDDLL KIIGSGKHHD QVSKFMKKMF GSIESIIFFE DSITGVRSVE GEVLNLNEKI ELKDSIQAQE W LNILDTEI KLSVFTQFRD CLGQLKDGTD IEVVVSKYIF QAILLSAQVM WTELVEKCLQ TNEFSKYWKE VDMKIKGLLD KL NKSSDNV KKKIEALLVE YLHFNNVIGQ LKNCSTKEEA RLLWAKVQKF YQKNDTLDDL NSVFISQSGY LLQYKFEYIG IPE RLIYTP LLLVGFATLT DSLHQKYGGC FFGPAGTGKT ETVKAFGQNL GRVVVVFNCD DSFDYQVLSR LLVGITQIGA WGCF DEFNR LDEKVLSAVS ANIQQIQNGL QVGKSHITLL EEETPLSPHT AVFITLNPGY NGRSELPENL KKSFREFSMK SPQSG TIAE MILQIMGFED SKSLASKIVH FLELLSSKCS SMNHYHFGLR TLKGVLRNCS PLVSEFGEGE KTVVESLKRV ILPSLG DTD ELVFKDELSK IFDSAGTPLN SKAIVQCLKD AGQRSGFSMS EEFLKKCMQF YYMQKTQQAL ILVGKAGCGK TATWKTV ID AMAIFDGHAN VVYVIDTKVL TKESLYGSML KATLEWRDGL FTSILRRVND DITGTFKNSR IWVVFDSDLD PEYVEAMN S VLDDNKILTL PNGERLPIPP NFRILFETDN LDHTTPATIT RCGLLWFSTD VCSISSKIDH LLNKSYEALD NKLSMFELD KLKDLISDSF DMASLTNIFT CSNDLVHILG VRTFNKLETA VQLAVHLISS YRQWFQNLDD KSLKDVITLL IKRSLLYALA GDSTGESQR AFIQTINTYF GHDSQELSDY STIVIANDKL SFSSFCSEIP SVSLEAHEVM RPDIVIPTID TIKHEKIFYD L LNSKRGII LCGPPGSGKT MIMNNALRNS SLYDVVGINF SKDTTTEHIL SALHRHTNYV TTSKGLTLLP KSDIKNLVLF CD EINLPKL DKYGSQNVVL FLRQLMEKQG FWKTPENKWV TIERIHIVGA CNPPTDPGRI PMSERFTRHA AILYLGYPSG KSL SQIYEI YYKAIFKLVP EFRSYTEPFA RASVHLYNEC KARYSTGLQS HYLFSPRELT RLVRGVYTAI NTGPRQTLRS LIRL WAYEA WRIFADRLVG VKEKNSFEQL LYETVDKYLP NQDLGNISST SLLFSGLLSL DFKEVNKTDL VNFIEERFKT FCDEE LEVP MVIHESMVDH ILRIDRALKQ VQGHMMLIGA SRTGKTILTR FVAWLNGLKI VQPKIHRHSN LSDFDMILKK AISDCS LKE SRTCLIIDES NILETAFLER MNTLLANADI PDLFQGEEYD KLLNNLRNKT RSLGLLLDTE QELYDWFVGE IAKNLHV VF TICDPTNNKS SAMISSPALF NRCIINWMGD WDTKTMSQVA NNMVDVVPME FTDFIVPEVN KELVFTEPIQ TIRDAVVN I LIHFDRNFYQ KMKVGVNPRS PGYFIDGLRA LVKLVTAKYQ DLQENQRFVN VGLEKLNESV SLTFEKERWL NTTKQFSKT SQELIGNCII SSIYETYFGH LNERERGDML VILKRLLGKF AVKYDVNYRF IDYLVTLDEK MKWLECGLDK NDYFLENMSI VMNSQDAVP FLLDPSSHMI TVISNYYGNK TVLLSFLEEG FVKRLENAVR FGSVVIIQDG EFFDPIISRL ISREFNHAGN R VTVEIGDH EVDVSGDFKL FIHSCDPSGD IPIFLRSRVR LVHFVTNKES IETRIFDITL TEENAEMQRK REDLIKLNTE YR LKLKNLE KRLLEELNNS QGNMLENDEL MVTLNNLKKE AMNIEKKLSE SEEFFPQFDN LVEEYSIIGK HSVKIFSMLE KFG QFHWFY GISIGQFLSC FKRVFIKKSR ETRAARTRVD EILWLLYQEV YCQFSTALDK KFKMIMAMTM FCLYKFDIES EQYK EAVLT MIGVLSESSD GVPKLTVDTN DDLRYLWDYV TTKSYISALN WFKNEFFVDE WNIADVVANS ENNYFTMASE RDVDG TFKL IELAKASKES LKIIPLGSIE NLNYAQEEIS KSKIEGGWIL LQNIQMSLSW VKTYLHKHVE ETKAAEEHEK FKMFMT CHL TGDKLPAPLL QRTDRVVYED IPGILDTVKD LWGSQFFTGK ISGVWSVYCT FLLSWFHALI TARTRLVPHG FSKKYYF ND CDFQFASVYL ENVLATNSTN NIPWAQVRDH IATIVYGGKI DEEKDLEVVA KLCAHVFCGS DNLQIVPGVR IPQPLLQQ S EEEERARLTA ILSNTIEPAD SLSSWLQLPR ESILDYERLQ AKEVASSTEQ LLQEM UniProtKB: Dynein heavy chain, cytoplasmic, Dynein heavy chain, cytoplasmic |
-Macromolecule #2: Nuclear distribution protein PAC1
| Macromolecule | Name: Nuclear distribution protein PAC1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.645449 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: LKWIPRNLPS CLINVESSVT SVKLHPNLPI VFVATDHGKL YAFDLFNYTI PLASLQSHTK AITSMDVLFT NYTNSSKKNY LVIVTASKD LQIHVFKWVS EECKFQQIRS LLGHEHIVSA VKIWQKNNDV HIASCSRDQT VKIWDFHNGW SLKTFQPHSQ W VRSIDVLG ...String: LKWIPRNLPS CLINVESSVT SVKLHPNLPI VFVATDHGKL YAFDLFNYTI PLASLQSHTK AITSMDVLFT NYTNSSKKNY LVIVTASKD LQIHVFKWVS EECKFQQIRS LLGHEHIVSA VKIWQKNNDV HIASCSRDQT VKIWDFHNGW SLKTFQPHSQ W VRSIDVLG DYIISGSHDT TLRLTHWPSG NGLSVGTGHE FPIEKVKFIH FIEDSPEIRF RTPSTDRYKN WGMQYCVSAS RD RTIKIWE IPLPTLMAHR APIPNPTDSN FRCVLTLKGH LSWVRDISIR GQYLFSCADD KSVRCWDLNT GQCLHVWEKL HTG FVNCLD LDVDFDSNVT PRQMMVTGGL DCKSNVFM UniProtKB: Nuclear distribution protein PAC1 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.23 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil UltrAuFoil 1.2/1.3 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 300 / Details: No grid pretreatment |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 276 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TECNAI ARCTICA |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 4826 / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 100.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal magnification: 36000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: EMDB MAP EMDB ID: |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 10.5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 27807 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: PROJECTION MATCHING |
| Final angle assignment | Type: PROJECTION MATCHING |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Overall B value: 800 |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-5vlj: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller

















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)